Minjee Kim
FedCAR: Cross-client Adaptive Re-weighting for Generative Models in Federated Learning
Dec 16, 2024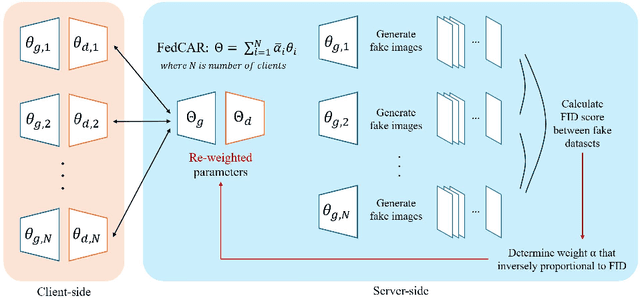
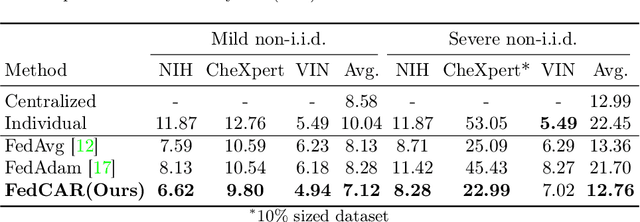
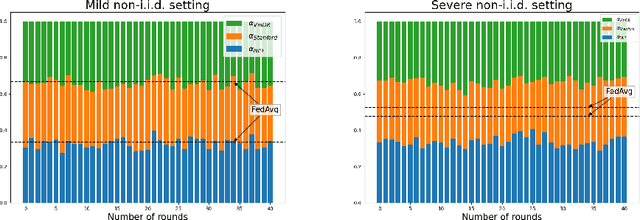
Abstract:Generative models trained on multi-institutional datasets can provide an enriched understanding through diverse data distributions. However, training the models on medical images is often challenging due to hospitals' reluctance to share data for privacy reasons. Federated learning(FL) has emerged as a privacy-preserving solution for training distributed datasets across data centers by aggregating model weights from multiple clients instead of sharing raw data. Previous research has explored the adaptation of FL to generative models, yet effective aggregation algorithms specifically tailored for generative models remain unexplored. We hereby propose a novel algorithm aimed at improving the performance of generative models within FL. Our approach adaptively re-weights the contribution of each client, resulting in well-trained shared parameters. In each round, the server side measures the distribution distance between fake images generated by clients instead of directly comparing the Fr\'echet Inception Distance per client, thereby enhancing efficiency of the learning. Experimental results on three public chest X-ray datasets show superior performance in medical image generation, outperforming both centralized learning and conventional FL algorithms. Our code is available at https://github.com/danny0628/FedCAR.
Barcode Method for Generative Model Evaluation driven by Topological Data Analysis
Jun 04, 2021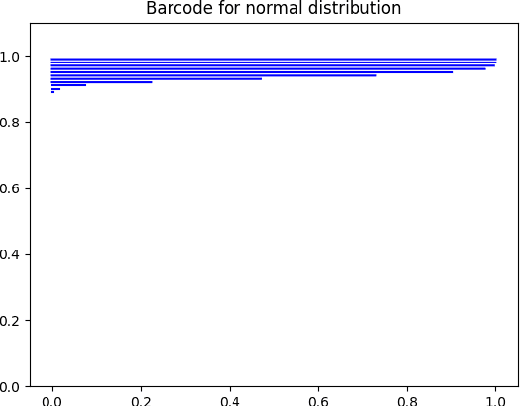
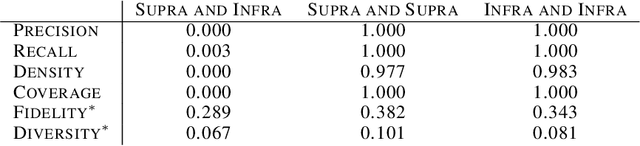
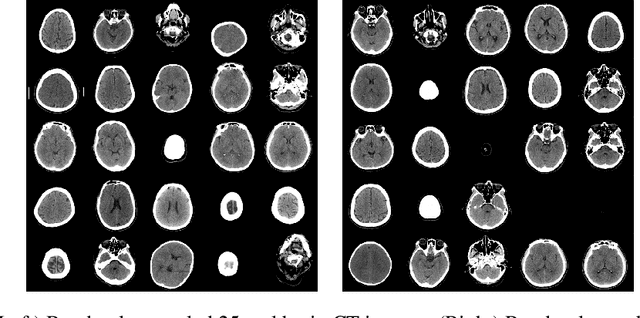
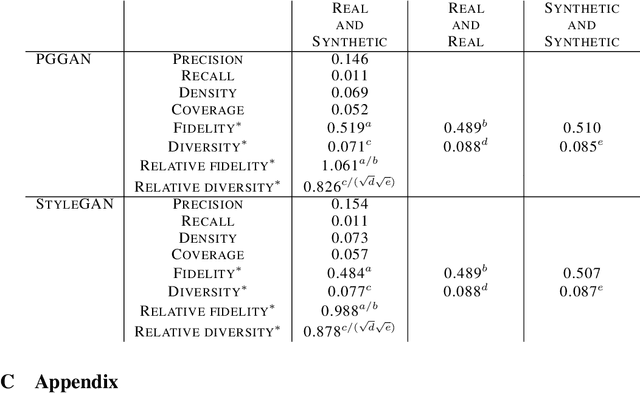
Abstract:Evaluating the performance of generative models in image synthesis is a challenging task. Although the Fr\'echet Inception Distance is a widely accepted evaluation metric, it integrates different aspects (e.g., fidelity and diversity) of synthesized images into a single score and assumes the normality of embedded vectors. Recent methods such as precision-and-recall and its variants such as density-and-coverage have been developed to separate fidelity and diversity based on k-nearest neighborhood methods. In this study, we propose an algorithm named barcode, which is inspired by the topological data analysis and is almost free of assumption and hyperparameter selections. In extensive experiments on real-world datasets as well as theoretical approach on high-dimensional normal samples, it was found that the 'usual' normality assumption of embedded vectors has several drawbacks. The experimental results demonstrate that barcode outperforms other methods in evaluating fidelity and diversity of GAN outputs. Official codes can be found in https://github.com/minjeekim00/Barcode.
Fully Automated Hand Hygiene Monitoring\\in Operating Room using 3D Convolutional Neural Network
Mar 20, 2020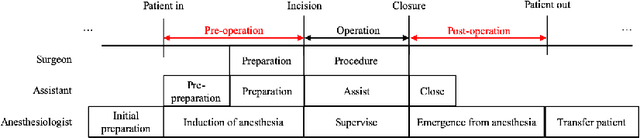
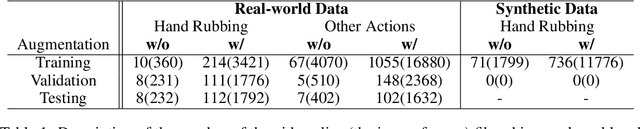
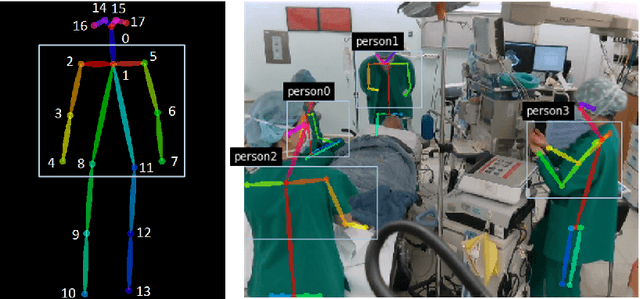
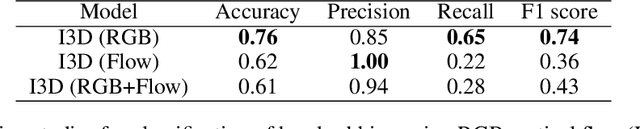
Abstract:Hand hygiene is one of the most significant factors in preventing hospital acquired infections (HAI) which often be transmitted by medical staffs in contact with patients in the operating room (OR). Hand hygiene monitoring could be important to investigate and reduce the outbreak of infections within the OR. However, an effective monitoring tool for hand hygiene compliance is difficult to develop due to the visual complexity of the OR scene. Recent progress in video understanding with convolutional neural net (CNN) has increased the application of recognition and detection of human actions. Leveraging this progress, we proposed a fully automated hand hygiene monitoring tool of the alcohol-based hand rubbing action of anesthesiologists on OR video using spatio-temporal features with 3D CNN. First, the region of interest (ROI) of anesthesiologists' upper body were detected and cropped. A temporal smoothing filter was applied to the ROIs. Then, the ROIs were given to a 3D CNN and classified into two classes: rubbing hands or other actions. We observed that a transfer learning from Kinetics-400 is beneficial and the optical flow stream was not helpful in our dataset. The final accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score in testing is 0.76, 0.85, 0.65 and 0.74, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge