Jinhoon Jeong
FedCAR: Cross-client Adaptive Re-weighting for Generative Models in Federated Learning
Dec 16, 2024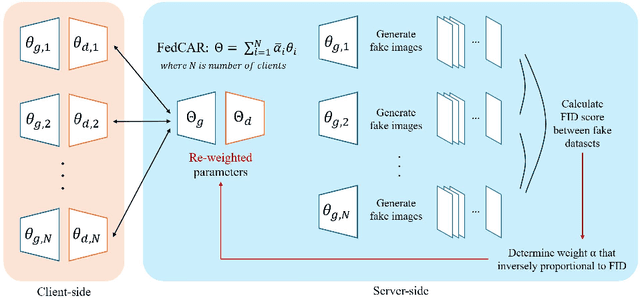
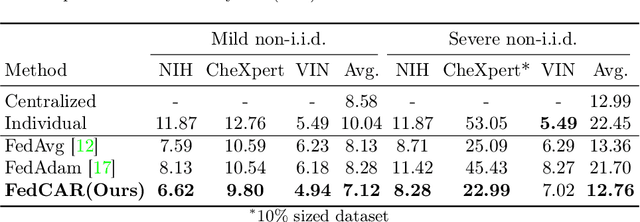
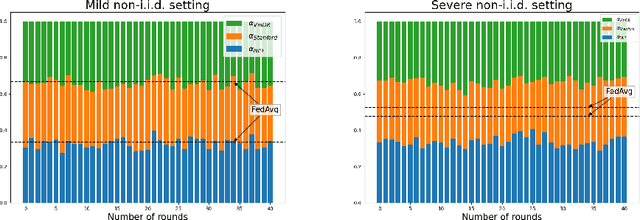
Abstract:Generative models trained on multi-institutional datasets can provide an enriched understanding through diverse data distributions. However, training the models on medical images is often challenging due to hospitals' reluctance to share data for privacy reasons. Federated learning(FL) has emerged as a privacy-preserving solution for training distributed datasets across data centers by aggregating model weights from multiple clients instead of sharing raw data. Previous research has explored the adaptation of FL to generative models, yet effective aggregation algorithms specifically tailored for generative models remain unexplored. We hereby propose a novel algorithm aimed at improving the performance of generative models within FL. Our approach adaptively re-weights the contribution of each client, resulting in well-trained shared parameters. In each round, the server side measures the distribution distance between fake images generated by clients instead of directly comparing the Fr\'echet Inception Distance per client, thereby enhancing efficiency of the learning. Experimental results on three public chest X-ray datasets show superior performance in medical image generation, outperforming both centralized learning and conventional FL algorithms. Our code is available at https://github.com/danny0628/FedCAR.
Automatic Tip Detection of Surgical Instruments in Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Nov 07, 2019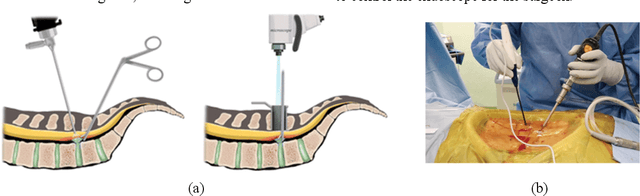
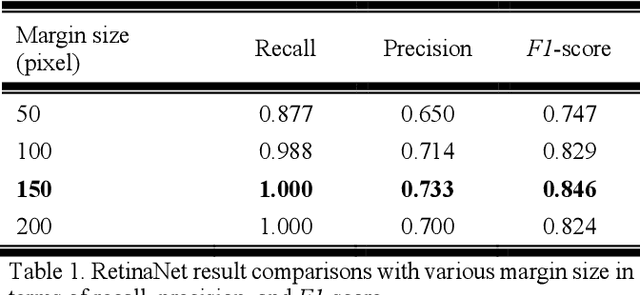
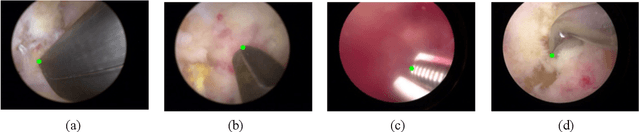
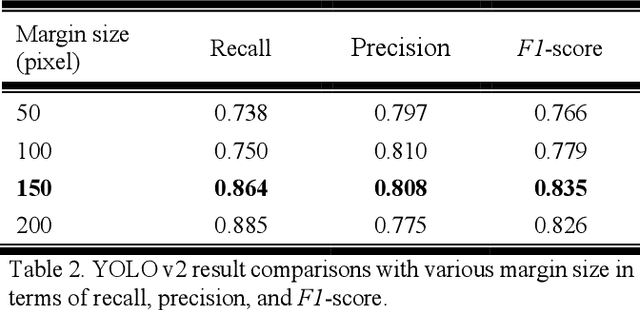
Abstract:Some endoscopic surgeries require a surgeon to hold the endoscope with one hand and the surgical instruments with the other hand to perform the actual surgery with correct vision. Recent technical advances in deep learning as well as in robotics can introduce robotics to these endoscopic surgeries. This can have numerous advantages by freeing one hand of the surgeon, which will allow the surgeon to use both hands and to use more intricate and sophisticated techniques. Recently, deep learning with convolutional neural network achieves state-of-the-art results in computer vision. Therefore, the aim of this study is to automatically detect the tip of the instrument, localize a point, and evaluate detection accuracy in biportal endoscopic spine surgery. The localized point could be used for the controller's inputs of robotic endoscopy in these types of endoscopic surgeries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge