Kyungjin Cho
Self-accumulative Vision Transformer for Bone Age Assessment Using the Sauvegrain Method
Mar 30, 2023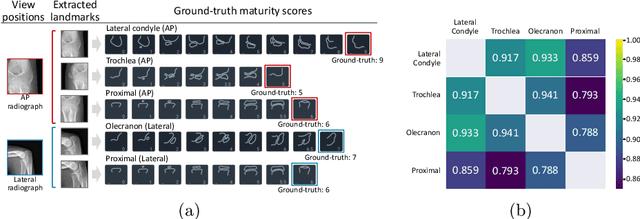
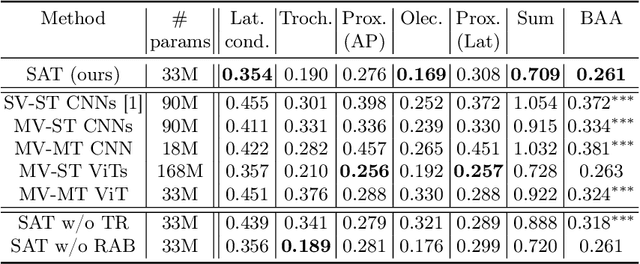
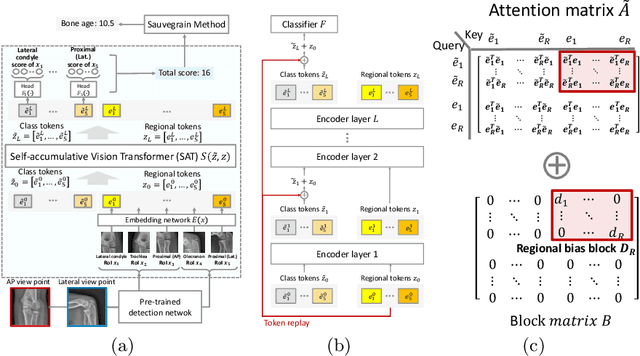
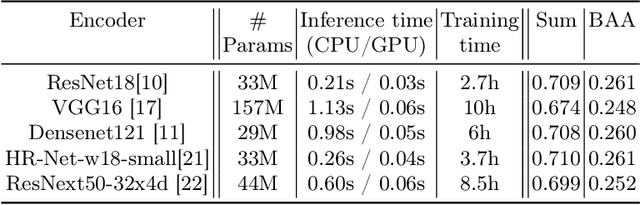
Abstract:This study presents a novel approach to bone age assessment (BAA) using a multi-view, multi-task classification model based on the Sauvegrain method. A straightforward solution to automating the Sauvegrain method, which assesses a maturity score for each landmark in the elbow and predicts the bone age, is to train classifiers independently to score each region of interest (RoI), but this approach limits the accessible information to local morphologies and increases computational costs. As a result, this work proposes a self-accumulative vision transformer (SAT) that mitigates anisotropic behavior, which usually occurs in multi-view, multi-task problems and limits the effectiveness of a vision transformer, by applying token replay and regional attention bias. A number of experiments show that SAT successfully exploits the relationships between landmarks and learns global morphological features, resulting in a mean absolute error of BAA that is 0.11 lower than that of the previous work. Additionally, the proposed SAT has four times reduced parameters than an ensemble of individual classifiers of the previous work. Lastly, this work also provides informative implications for clinical practice, improving the accuracy and efficiency of BAA in diagnosing abnormal growth in adolescents.
Barcode Method for Generative Model Evaluation driven by Topological Data Analysis
Jun 04, 2021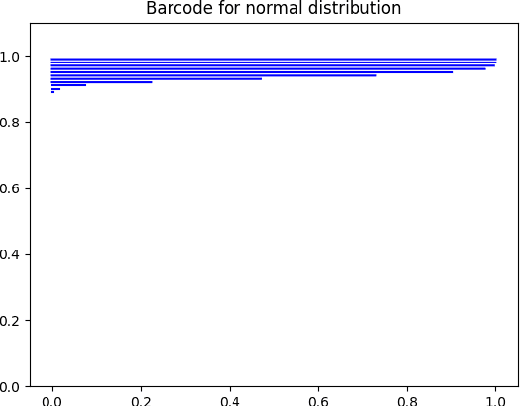
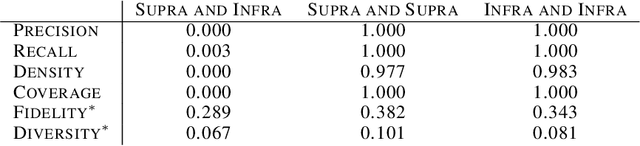
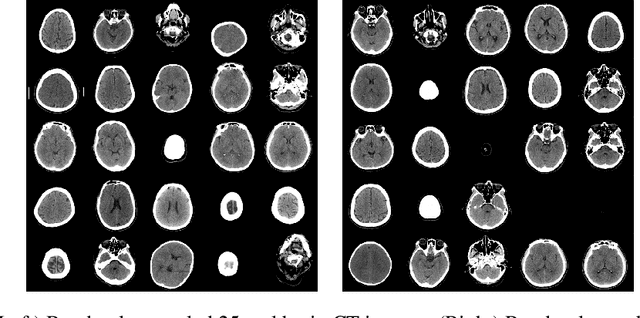
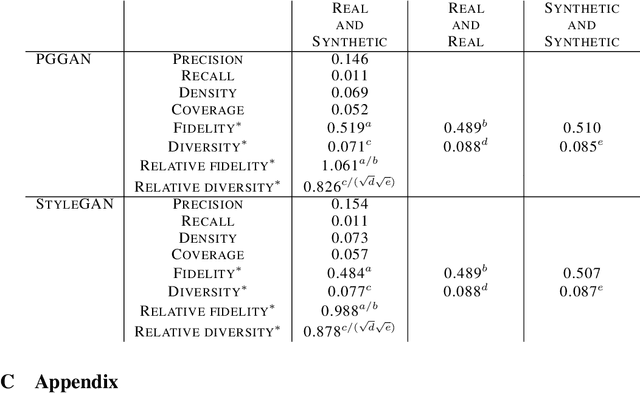
Abstract:Evaluating the performance of generative models in image synthesis is a challenging task. Although the Fr\'echet Inception Distance is a widely accepted evaluation metric, it integrates different aspects (e.g., fidelity and diversity) of synthesized images into a single score and assumes the normality of embedded vectors. Recent methods such as precision-and-recall and its variants such as density-and-coverage have been developed to separate fidelity and diversity based on k-nearest neighborhood methods. In this study, we propose an algorithm named barcode, which is inspired by the topological data analysis and is almost free of assumption and hyperparameter selections. In extensive experiments on real-world datasets as well as theoretical approach on high-dimensional normal samples, it was found that the 'usual' normality assumption of embedded vectors has several drawbacks. The experimental results demonstrate that barcode outperforms other methods in evaluating fidelity and diversity of GAN outputs. Official codes can be found in https://github.com/minjeekim00/Barcode.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge