Mingxing Rao
Training Noise Token Pruning
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:In the present work we present Training Noise Token (TNT) Pruning for vision transformers. Our method relaxes the discrete token dropping condition to continuous additive noise, providing smooth optimization in training, while retaining discrete dropping computational gains in deployment settings. We provide theoretical connections to Rate-Distortion literature, and empirical evaluations on the ImageNet dataset using ViT and DeiT architectures demonstrating TNT's advantages over previous pruning methods.
Zero-shot Prompt-based Video Encoder for Surgical Gesture Recognition
Mar 28, 2024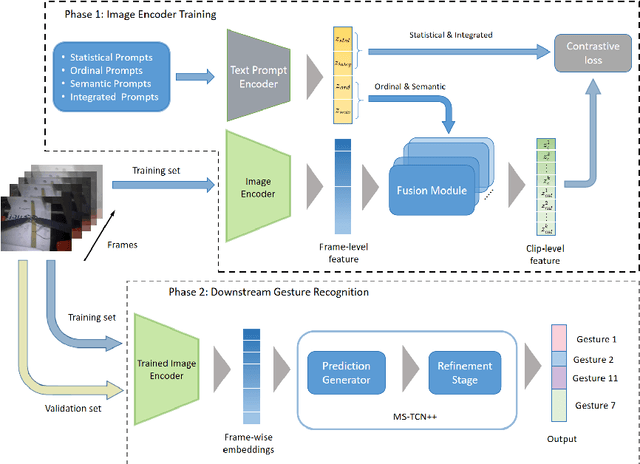



Abstract:Purpose: Surgical video is an important data stream for gesture recognition. Thus, robust visual encoders for those data-streams is similarly important. Methods: Leveraging the Bridge-Prompt framework, we fine-tune a pre-trained vision-text model (CLIP) for gesture recognition in surgical videos. This can utilize extensive outside video data such as text, but also make use of label meta-data and weakly supervised contrastive losses. Results: Our experiments show that prompt-based video encoder outperforms standard encoders in surgical gesture recognition tasks. Notably, it displays strong performance in zero-shot scenarios, where gestures/tasks that were not provided during the encoder training phase are included in the prediction phase. Additionally, we measure the benefit of inclusion text descriptions in the feature extractor training schema. Conclusion: Bridge-Prompt and similar pre-trained+fine-tuned video encoder models present significant visual representation for surgical robotics, especially in gesture recognition tasks. Given the diverse range of surgical tasks (gestures), the ability of these models to zero-shot transfer without the need for any task (gesture) specific retraining makes them invaluable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge