Minghao Tian
The 2nd Place Solution for 2023 Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge
Jun 28, 2023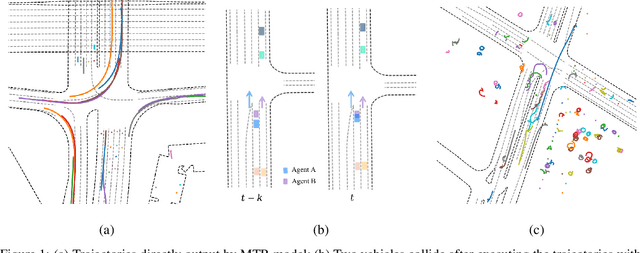
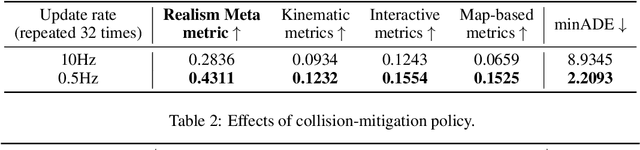
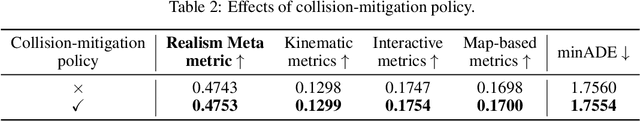
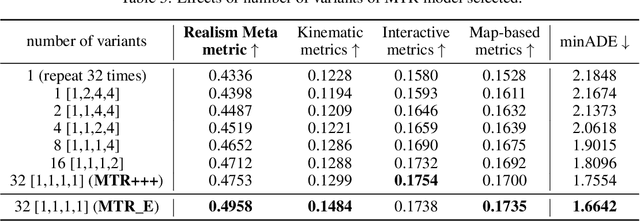
Abstract:In this technical report, we present the 2nd place solution of 2023 Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge (WOSAC)[4]. We propose a simple yet effective autoregressive method for simulating multi-agent behaviors, which is built upon a well-known multimodal motion forecasting framework called Motion Transformer (MTR)[5] with postprocessing algorithms applied. Our submission named MTR+++ achieves 0.4697 on the Realism Meta metric in 2023 WOSAC. Besides, a modified model based on MTR named MTR_E is proposed after the challenge, which has a better score 0.4911 and is ranked the 3rd on the leaderboard of WOSAC as of June 25, 2023.
Harmonic Extension
Sep 22, 2015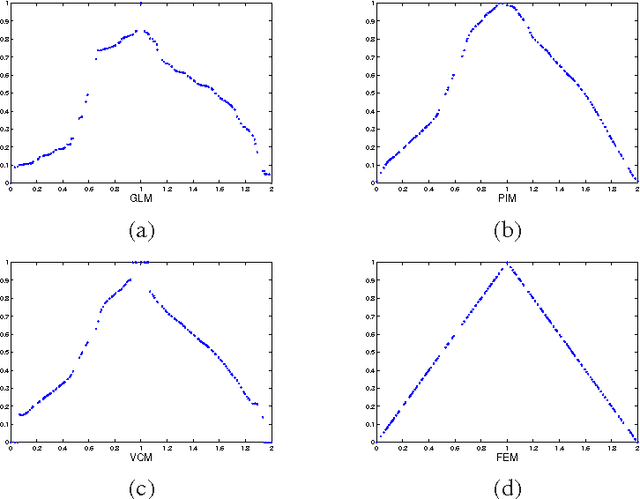
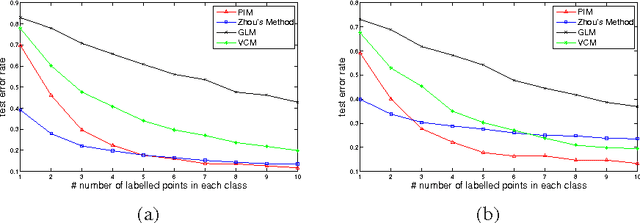
Abstract:In this paper, we consider the harmonic extension problem, which is widely used in many applications of machine learning. We find that the transitional method of graph Laplacian fails to produce a good approximation of the classical harmonic function. To tackle this problem, we propose a new method called the point integral method (PIM). We consider the harmonic extension problem from the point of view of solving PDEs on manifolds. The basic idea of the PIM method is to approximate the harmonicity using an integral equation, which is easy to be discretized from points. Based on the integral equation, we explain the reason why the transitional graph Laplacian may fail to approximate the harmonicity in the classical sense and propose a different approach which we call the volume constraint method (VCM). Theoretically, both the PIM and the VCM computes a harmonic function with convergence guarantees, and practically, they are both simple, which amount to solve a linear system. One important application of the harmonic extension in machine learning is semi-supervised learning. We run a popular semi-supervised learning algorithm by Zhu et al. over a couple of well-known datasets and compare the performance of the aforementioned approaches. Our experiments show the PIM performs the best.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge