Mills Staylor
Scalable Cosmic AI Inference using Cloud Serverless Computing with FMI
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Large-scale astronomical image data processing and prediction is essential for astronomers, providing crucial insights into celestial objects, the universe's history, and its evolution. While modern deep learning models offer high predictive accuracy, they often demand substantial computational resources, making them resource-intensive and limiting accessibility. We introduce the Cloud-based Astronomy Inference (CAI) framework to address these challenges. This scalable solution integrates pre-trained foundation models with serverless cloud infrastructure through a Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) Message Interface (FMI). CAI enables efficient and scalable inference on astronomical images without extensive hardware. Using a foundation model for redshift prediction as a case study, our extensive experiments cover user devices, HPC (High-Performance Computing) servers, and Cloud. CAI's significant scalability improvement on large data sizes provides an accessible and effective tool for the astronomy community. The code is accessible at https://github.com/UVA-MLSys/AI-for-Astronomy.
In-depth Analysis On Parallel Processing Patterns for High-Performance Dataframes
Jul 03, 2023

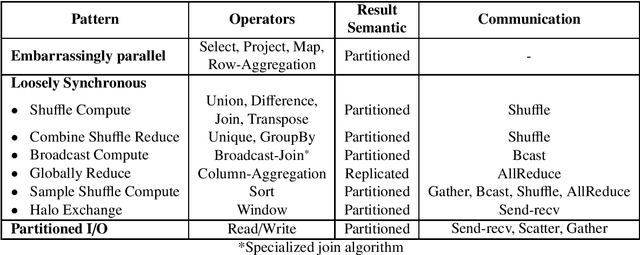

Abstract:The Data Science domain has expanded monumentally in both research and industry communities during the past decade, predominantly owing to the Big Data revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are bringing more complexities to data engineering applications, which are now integrated into data processing pipelines to process terabytes of data. Typically, a significant amount of time is spent on data preprocessing in these pipelines, and hence improving its e fficiency directly impacts the overall pipeline performance. The community has recently embraced the concept of Dataframes as the de-facto data structure for data representation and manipulation. However, the most widely used serial Dataframes today (R, pandas) experience performance limitations while working on even moderately large data sets. We believe that there is plenty of room for improvement by taking a look at this problem from a high-performance computing point of view. In a prior publication, we presented a set of parallel processing patterns for distributed dataframe operators and the reference runtime implementation, Cylon [1]. In this paper, we are expanding on the initial concept by introducing a cost model for evaluating the said patterns. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of Cylon on the ORNL Summit supercomputer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge