Niranda Perera
In-depth Analysis On Parallel Processing Patterns for High-Performance Dataframes
Jul 03, 2023

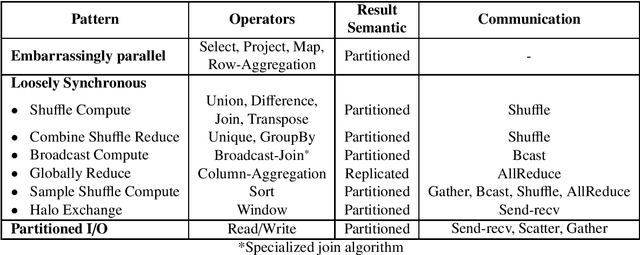

Abstract:The Data Science domain has expanded monumentally in both research and industry communities during the past decade, predominantly owing to the Big Data revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are bringing more complexities to data engineering applications, which are now integrated into data processing pipelines to process terabytes of data. Typically, a significant amount of time is spent on data preprocessing in these pipelines, and hence improving its e fficiency directly impacts the overall pipeline performance. The community has recently embraced the concept of Dataframes as the de-facto data structure for data representation and manipulation. However, the most widely used serial Dataframes today (R, pandas) experience performance limitations while working on even moderately large data sets. We believe that there is plenty of room for improvement by taking a look at this problem from a high-performance computing point of view. In a prior publication, we presented a set of parallel processing patterns for distributed dataframe operators and the reference runtime implementation, Cylon [1]. In this paper, we are expanding on the initial concept by introducing a cost model for evaluating the said patterns. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of Cylon on the ORNL Summit supercomputer.
HPTMT Parallel Operators for High Performance Data Science & Data Engineering
Aug 13, 2021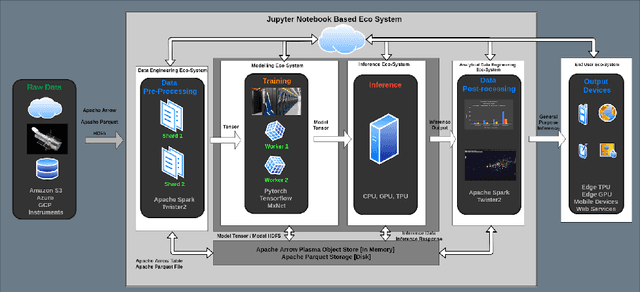


Abstract:Data-intensive applications are becoming commonplace in all science disciplines. They are comprised of a rich set of sub-domains such as data engineering, deep learning, and machine learning. These applications are built around efficient data abstractions and operators that suit the applications of different domains. Often lack of a clear definition of data structures and operators in the field has led to other implementations that do not work well together. The HPTMT architecture that we proposed recently, identifies a set of data structures, operators, and an execution model for creating rich data applications that links all aspects of data engineering and data science together efficiently. This paper elaborates and illustrates this architecture using an end-to-end application with deep learning and data engineering parts working together.
HPTMT: Operator-Based Architecture for Scalable High-Performance Data-Intensive Frameworks
Jul 30, 2021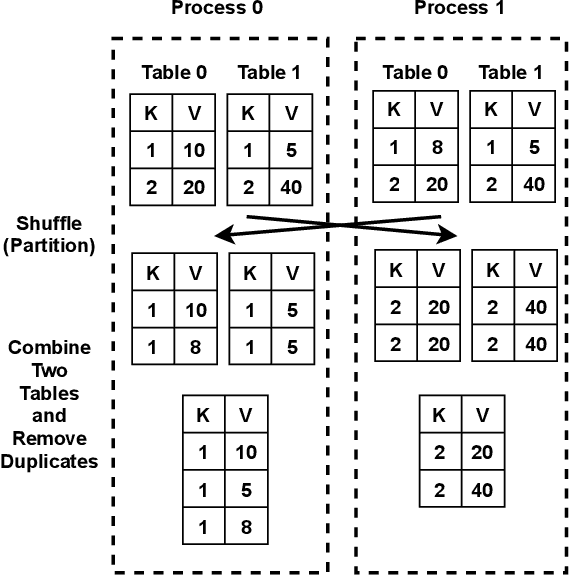
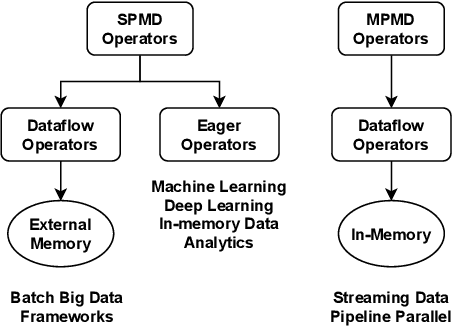
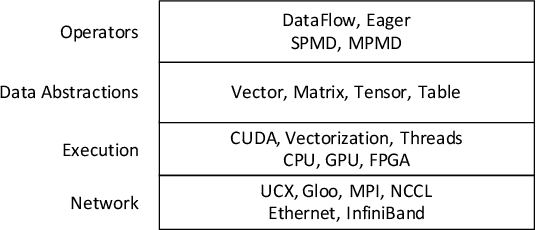
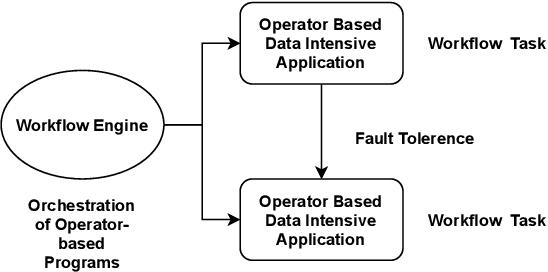
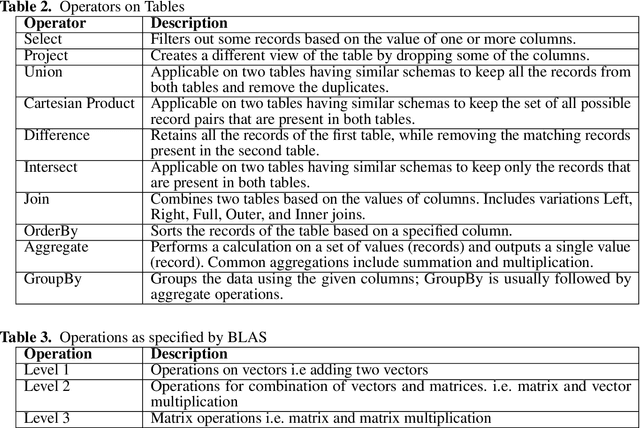
Abstract:Data-intensive applications impact many domains, and their steadily increasing size and complexity demands high-performance, highly usable environments. We integrate a set of ideas developed in various data science and data engineering frameworks. They employ a set of operators on specific data abstractions that include vectors, matrices, tensors, graphs, and tables. Our key concepts are inspired from systems like MPI, HPF (High-Performance Fortran), NumPy, Pandas, Spark, Modin, PyTorch, TensorFlow, RAPIDS(NVIDIA), and OneAPI (Intel). Further, it is crucial to support different languages in everyday use in the Big Data arena, including Python, R, C++, and Java. We note the importance of Apache Arrow and Parquet for enabling language agnostic high performance and interoperability. In this paper, we propose High-Performance Tensors, Matrices and Tables (HPTMT), an operator-based architecture for data-intensive applications, and identify the fundamental principles needed for performance and usability success. We illustrate these principles by a discussion of examples using our software environments, Cylon and Twister2 that embody HPTMT.
High Performance Data Engineering Everywhere
Jul 19, 2020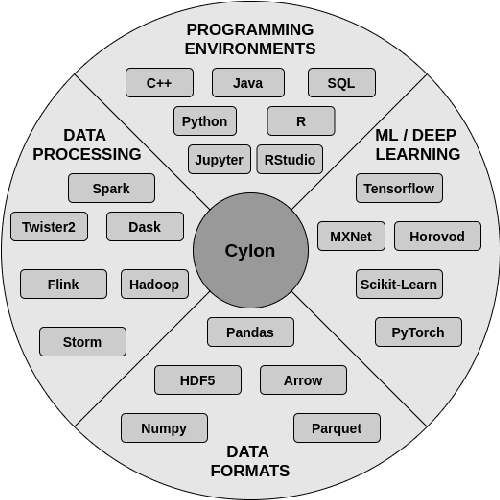
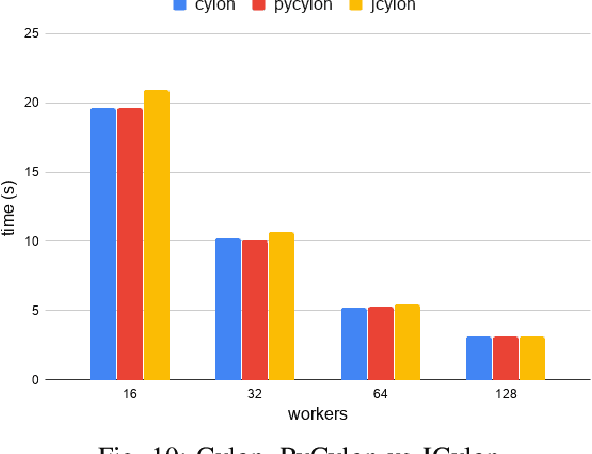
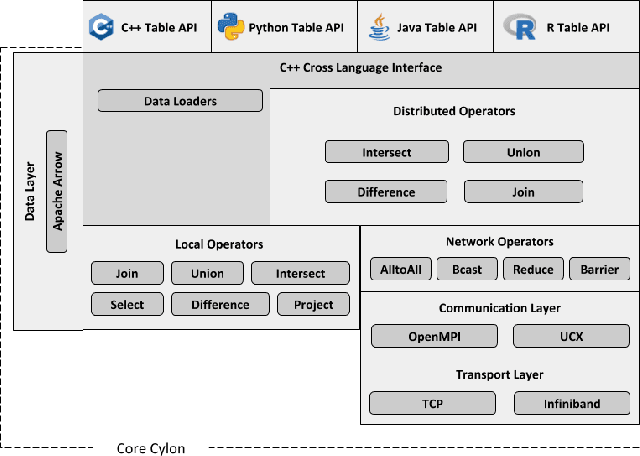
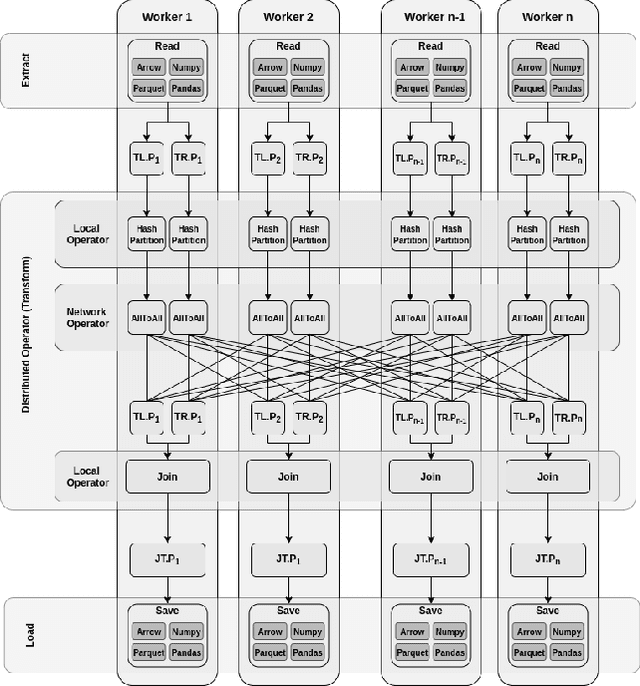
Abstract:The amazing advances being made in the fields of machine and deep learning are a highlight of the Big Data era for both enterprise and research communities. Modern applications require resources beyond a single node's ability to provide. However this is just a small part of the issues facing the overall data processing environment, which must also support a raft of data engineering for pre- and post-data processing, communication, and system integration. An important requirement of data analytics tools is to be able to easily integrate with existing frameworks in a multitude of languages, thereby increasing user productivity and efficiency. All this demands an efficient and highly distributed integrated approach for data processing, yet many of today's popular data analytics tools are unable to satisfy all these requirements at the same time. In this paper we present Cylon, an open-source high performance distributed data processing library that can be seamlessly integrated with existing Big Data and AI/ML frameworks. It is developed with a flexible C++ core on top of a compact data structure and exposes language bindings to C++, Java, and Python. We discuss Cylon's architecture in detail, and reveal how it can be imported as a library to existing applications or operate as a standalone framework. Initial experiments show that Cylon enhances popular tools such as Apache Spark and Dask with major performance improvements for key operations and better component linkages. Finally, we show how its design enables Cylon to be used cross-platform with minimum overhead, which includes popular AI tools such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, and Jupyter notebooks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge