Milan Curcic
A Fortran-Keras Deep Learning Bridge for Scientific Computing
Apr 14, 2020
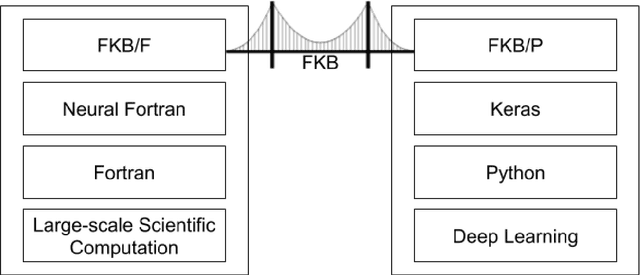
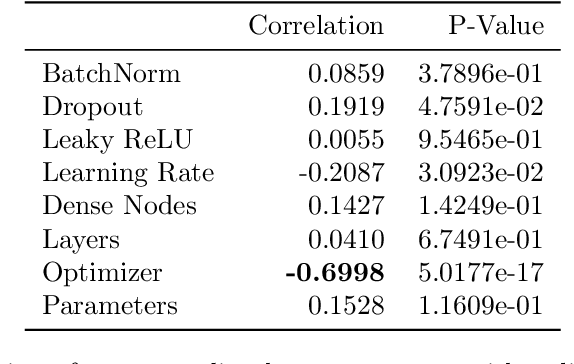
Abstract:Implementing artificial neural networks is commonly achieved via high-level programming languages like Python, and easy-to-use deep learning libraries like Keras. These software libraries come pre-loaded with a variety of network architectures, provide autodifferentiation, and support GPUs for fast and efficient computation. As a result, a deep learning practitioner will favor training a neural network model in Python where these tools are readily available. However, many large-scale scientific computation projects are written in Fortran, which makes them difficult to integrate with modern deep learning methods. To alleviate this problem, we introduce a software library, the Fortran-Keras Bridge (FKB). This two-way bridge connects environments where deep learning resources are plentiful, with those where they are scarce. The paper describes a number of unique features offered by FKB, such as customizable layers, loss functions, and network ensembles. The paper concludes with a case study that applies FKB to address open questions about the robustness of an experimental approach to global climate simulation, in which subgrid physics are outsourced to deep neural network emulators. In this context, FKB enables a hyperparameter search of one hundred plus candidate models of subgrid cloud and radiation physics, initially implemented in Keras, to then be transferred and used in Fortran to assess their emergent behavior, i.e. when fit imperfections are coupled to explicit planetary scale fluid dynamics. The results reveal a previously unrecognized strong relationship between offline validation error and online performance, in which the choice of optimizer proves unexpectedly critical; this in turn helps identify a new optimized NN that demonstrates a 500 fold improvement of model stability compared to previously published results for this application.
A parallel Fortran framework for neural networks and deep learning
Mar 25, 2019



Abstract:This paper describes neural-fortran, a parallel Fortran framework for neural networks and deep learning. It features a simple interface to construct feed-forward neural networks of arbitrary structure and size, several activation functions, and stochastic gradient descent as the default optimization algorithm. Neural-fortran also leverages the Fortran 2018 standard collective subroutines to achieve data-based parallelism on shared- or distributed-memory machines. First, I describe the implementation of neural networks with Fortran derived types, whole-array arithmetic, and collective sum and broadcast operations to achieve parallelism. Second, I demonstrate the use of neural-fortran in an example of recognizing hand-written digits from images. Finally, I evaluate the computational performance in both serial and parallel modes. Ease of use and computational performance are similar to an existing popular machine learning framework, making neural-fortran a viable candidate for further development and use in production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge