Mikhail Chernoskutov
An Unsupervised Word Sense Disambiguation System for Under-Resourced Languages
Apr 27, 2018
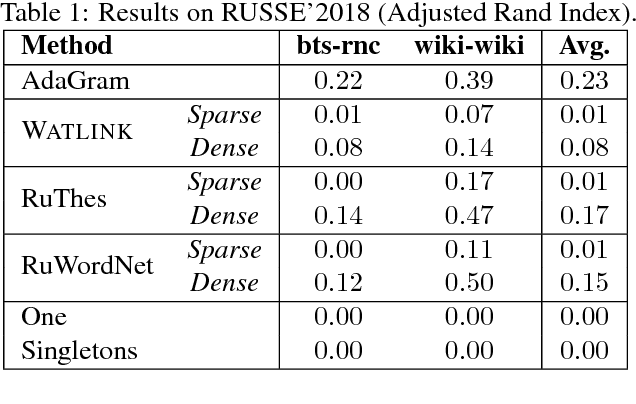
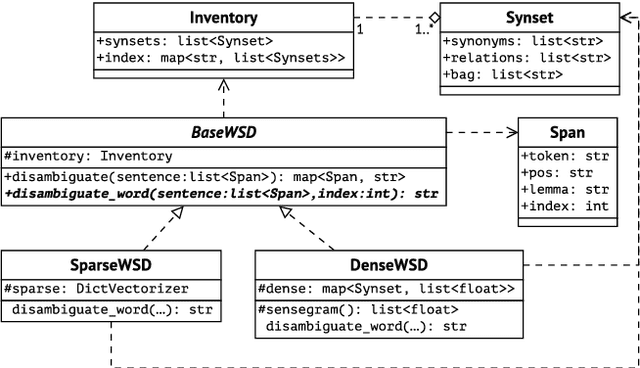
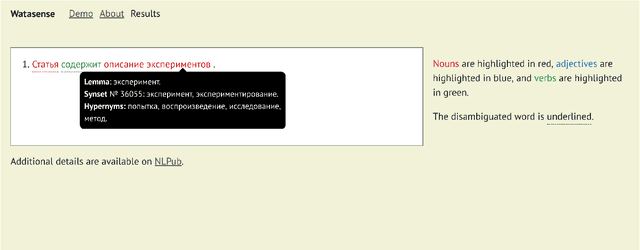
Abstract:In this paper, we present Watasense, an unsupervised system for word sense disambiguation. Given a sentence, the system chooses the most relevant sense of each input word with respect to the semantic similarity between the given sentence and the synset constituting the sense of the target word. Watasense has two modes of operation. The sparse mode uses the traditional vector space model to estimate the most similar word sense corresponding to its context. The dense mode, instead, uses synset embeddings to cope with the sparsity problem. We describe the architecture of the present system and also conduct its evaluation on three different lexical semantic resources for Russian. We found that the dense mode substantially outperforms the sparse one on all datasets according to the adjusted Rand index.
Fighting with the Sparsity of Synonymy Dictionaries
Aug 30, 2017



Abstract:Graph-based synset induction methods, such as MaxMax and Watset, induce synsets by performing a global clustering of a synonymy graph. However, such methods are sensitive to the structure of the input synonymy graph: sparseness of the input dictionary can substantially reduce the quality of the extracted synsets. In this paper, we propose two different approaches designed to alleviate the incompleteness of the input dictionaries. The first one performs a pre-processing of the graph by adding missing edges, while the second one performs a post-processing by merging similar synset clusters. We evaluate these approaches on two datasets for the Russian language and discuss their impact on the performance of synset induction methods. Finally, we perform an extensive error analysis of each approach and discuss prominent alternative methods for coping with the problem of the sparsity of the synonymy dictionaries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge