Michael Stein
Daimler Benz Research and Technology
DeepMIDE: A Multivariate Spatio-Temporal Method for Ultra-Scale Offshore Wind Energy Forecasting
Oct 26, 2024Abstract:To unlock access to stronger winds, the offshore wind industry is advancing with significantly larger and taller wind turbines. This massive upscaling motivates a departure from univariate wind forecasting methods that traditionally focused on a single representative height. To fill this gap, we propose DeepMIDE--a statistical deep learning method which jointly models the offshore wind speeds across space, time, and height. DeepMIDE is formulated as a multi-output integro-difference equation model with a multivariate, nonstationary, and state-dependent kernel characterized by a set of advection vectors that encode the physics of wind field formation and propagation. Embedded within DeepMIDE, an advanced deep learning architecture learns these advection vectors from high dimensional streams of exogenous weather information, which, along with other parameters, are plugged back into the statistical model for probabilistic multi-height space-time forecasting. Tested on real-world data from future offshore wind energy sites in the Northeastern United States, the wind speed and power forecasts from DeepMIDE are shown to outperform those from prevalent time series, spatio-temporal, and deep learning methods.
Domain and Language Independent Feature Extraction for Statistical Text Categorization
Jul 02, 1996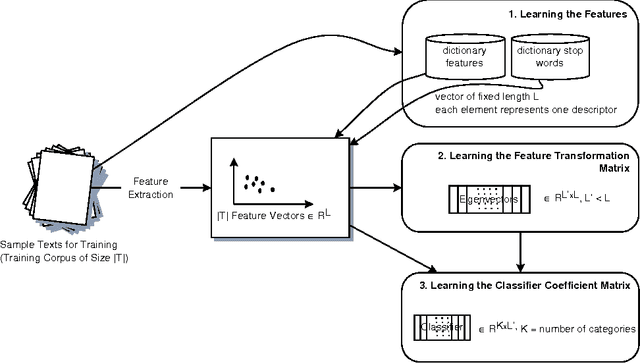
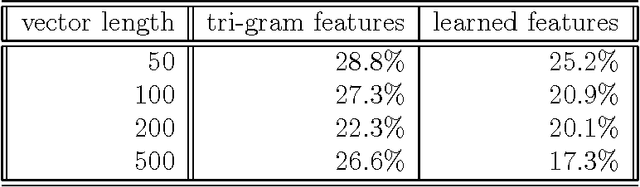
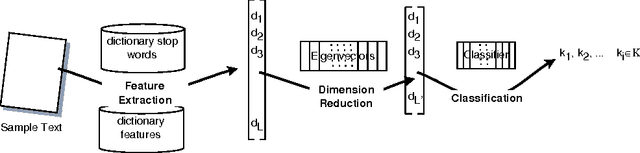

Abstract:A generic system for text categorization is presented which uses a representative text corpus to adapt the processing steps: feature extraction, dimension reduction, and classification. Feature extraction automatically learns features from the corpus by reducing actual word forms using statistical information of the corpus and general linguistic knowledge. The dimension of feature vector is then reduced by linear transformation keeping the essential information. The classification principle is a minimum least square approach based on polynomials. The described system can be readily adapted to new domains or new languages. In application, the system is reliable, fast, and processes completely automatically. It is shown that the text categorizer works successfully both on text generated by document image analysis - DIA and on ground truth data.
* 12 pages, TeX file, 9 Postscript figures, uses epsf.sty
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge