Mia Taige Li
University of British Columbia
Building the Intent Landscape of Real-World Conversational Corpora with Extractive Question-Answering Transformers
Aug 30, 2022
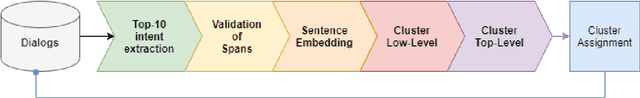

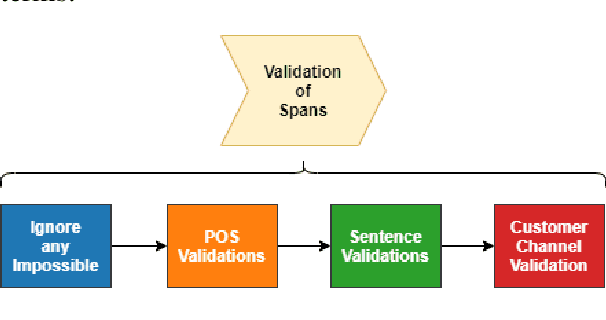
Abstract:For companies with customer service, mapping intents inside their conversational data is crucial in building applications based on natural language understanding (NLU). Nevertheless, there is no established automated technique to gather the intents from noisy online chats or voice transcripts. Simple clustering approaches are not suited to intent-sparse dialogues. To solve this intent-landscape task, we propose an unsupervised pipeline that extracts the intents and the taxonomy of intents from real-world dialogues. Our pipeline mines intent-span candidates with an extractive Question-Answering Electra model and leverages sentence embeddings to apply a low-level density clustering followed by a top-level hierarchical clustering. Our results demonstrate the generalization ability of an ELECTRA large model fine-tuned on the SQuAD2 dataset to understand dialogues. With the right prompting question, this model achieves a rate of linguistic validation on intent spans beyond 85%. We furthermore reconstructed the intent schemes of five domains from the MultiDoGo dataset with an average recall of 94.3%.
Speech Technology for Everyone: Automatic Speech Recognition for Non-Native English with Transfer Learning
Oct 15, 2021

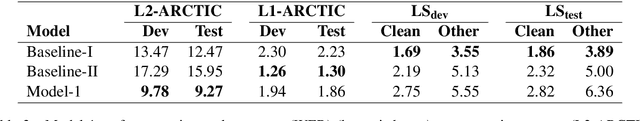

Abstract:To address the performance gap of English ASR models on L2 English speakers, we evaluate fine-tuning of pretrained wav2vec 2.0 models (Baevski et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021) on L2-ARCTIC, a non-native English speech corpus (Zhao et al., 2018) under different training settings. We compare \textbf{(a)} models trained with a combination of diverse accents to ones trained with only specific accents and \textbf{(b)} results from different single-accent models. Our experiments demonstrate the promise of developing ASR models for non-native English speakers, even with small amounts of L2 training data and even without a language model. Our models also excel in the zero-shot setting where we train on multiple L2 datasets and test on a blind L2 test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge