Mengyu Ye
Relaxing Positional Alignment in Masked Diffusion Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Masked diffusion language models (MDLMs) have emerged as a promising alternative to dominant autoregressive approaches. Although they achieve competitive performance on several tasks, a substantial gap remains in open-ended text generation. We hypothesize that one cause of this gap is that strict positional prediction makes MDLM decoding highly sensitive to token misalignment, and we show through controlled interventions that a one-position shift can severely disrupt semantics. This observation suggests that enforcing strict positional supervision during training is misaligned with the irreversible denoising dynamics of MDLM decoding. Motivated by this mismatch, we adopt an alignment-flexible supervision strategy during fine-tuning. Specifically, we introduce a special token <slack> via the connectionist temporal classification objective. We apply this approach to the widely used MDLM model and conduct experiments on five open-ended text generation benchmarks. Our method consistently outperforms the original model and improves robustness to positional shifts, indicating that relaxing strict positional supervision is an important factor in improving generation quality in MDLMs.
An Open and Reproducible Deep Research Agent for Long-Form Question Answering
Dec 15, 2025



Abstract:We present an open deep research system for long-form question answering, selected as a winning system in the text-to-text track of the MMU-RAG competition at NeurIPS 2025. The system combines an open-source large language model (LLM) with an open web search API to perform iterative retrieval, reasoning, and synthesis in real-world open-domain settings. To enhance reasoning quality, we apply preference tuning based on LLM-as-a-judge feedback that evaluates multiple aspects, including clarity, insightfulness, and factuality. Our experimental results show that the proposed method consistently improves answer quality across all three aspects. Our source code is publicly available at https://github.com/efficient-deep-research/efficient-deep-research.
Transformer Key-Value Memories Are Nearly as Interpretable as Sparse Autoencoders
Oct 25, 2025



Abstract:Recent interpretability work on large language models (LLMs) has been increasingly dominated by a feature-discovery approach with the help of proxy modules. Then, the quality of features learned by, e.g., sparse auto-encoders (SAEs), is evaluated. This paradigm naturally raises a critical question: do such learned features have better properties than those already represented within the original model parameters, and unfortunately, only a few studies have made such comparisons systematically so far. In this work, we revisit the interpretability of feature vectors stored in feed-forward (FF) layers, given the perspective of FF as key-value memories, with modern interpretability benchmarks. Our extensive evaluation revealed that SAE and FFs exhibits a similar range of interpretability, although SAEs displayed an observable but minimal improvement in some aspects. Furthermore, in certain aspects, surprisingly, even vanilla FFs yielded better interpretability than the SAEs, and features discovered in SAEs and FFs diverged. These bring questions about the advantage of SAEs from both perspectives of feature quality and faithfulness, compared to directly interpreting FF feature vectors, and FF key-value parameters serve as a strong baseline in modern interpretability research.
Can Input Attributions Interpret the Inductive Reasoning Process Elicited in In-Context Learning?
Dec 20, 2024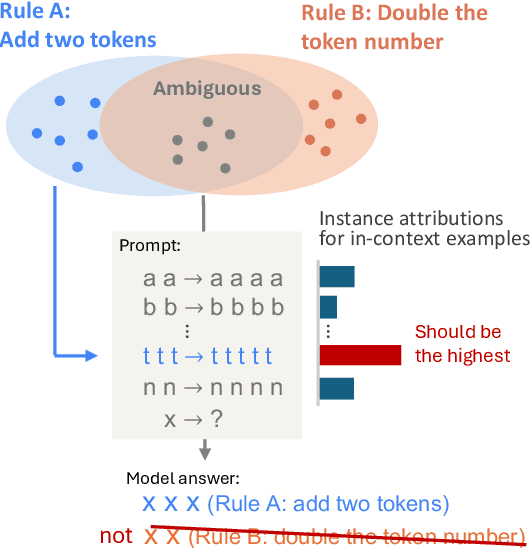
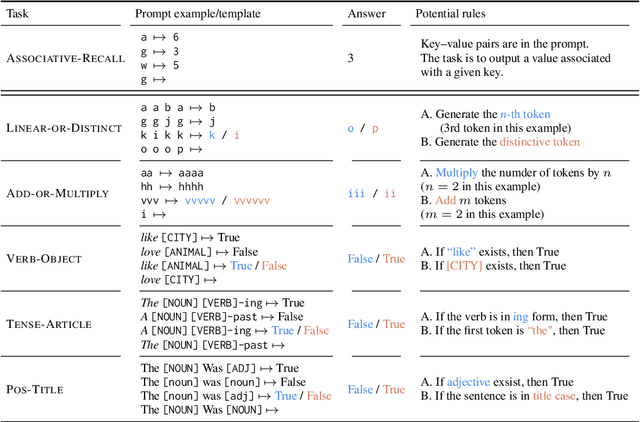
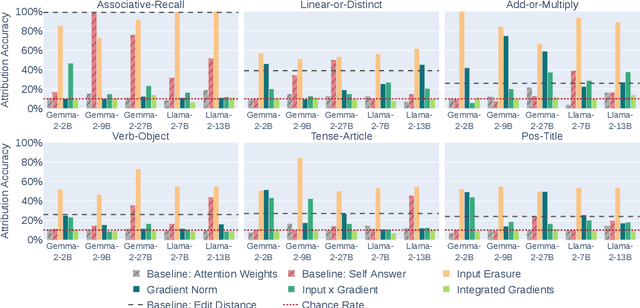
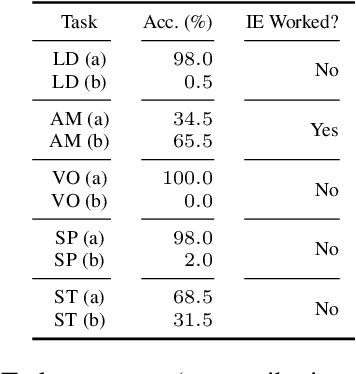
Abstract:Elucidating the rationale behind neural models' outputs has been challenging in the machine learning field, which is indeed applicable in this age of large language models (LLMs) and in-context learning (ICL). When it comes to estimating input attributions (IA), ICL poses a new issue of interpreting which example in the prompt, consisting of a set of examples, contributed to identifying the task/rule to be solved. To this end, in this paper, we introduce synthetic diagnostic tasks inspired by the poverty of the stimulus design in inductive reasoning; here, most in-context examples are ambiguous w.r.t. their underlying rule, and one critical example disambiguates the task demonstrated. The question is whether conventional IA methods can identify such an example in interpreting the inductive reasoning process in ICL. Our experiments provide several practical findings; for example, a certain simple IA method works the best, and the larger the model, the generally harder it is to interpret the ICL with gradient-based IA methods.
Assessing Step-by-Step Reasoning against Lexical Negation: A Case Study on Syllogism
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) take advantage of step-by-step reasoning instructions, e.g., chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. Building on this, their ability to perform CoT-style reasoning robustly is of interest from a probing perspective. In this study, we inspect the step-by-step reasoning ability of LLMs with a focus on negation, which is a core linguistic phenomenon that is difficult to process. In particular, we introduce several controlled settings (e.g., reasoning in case of fictional entities) to evaluate the logical reasoning abilities of the models. We observed that dozens of modern LLMs were not robust against lexical negation (e.g., plausible ->implausible) when performing CoT-style reasoning, and the results highlight unique limitations in each LLM family.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge