Mehrab Beikzadeh
Leveraging ChatGPT and Other NLP Methods for Identifying Risk and Protective Behaviors in MSM: Social Media and Dating apps Text Analysis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Men who have sex with men (MSM) are at elevated risk for sexually transmitted infections and harmful drinking compared to heterosexual men. Text data collected from social media and dating applications may provide new opportunities for personalized public health interventions by enabling automatic identification of risk and protective behaviors. In this study, we evaluated whether text from social media and dating apps can be used to predict sexual risk behaviors, alcohol use, and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) uptake among MSM. With participant consent, we collected textual data and trained machine learning models using features derived from ChatGPT embeddings, BERT embeddings, LIWC, and a dictionary-based risk term approach. The models achieved strong performance in predicting monthly binge drinking and having more than five sexual partners, with F1 scores of 0.78, and moderate performance in predicting PrEP use and heavy drinking, with F1 scores of 0.64 and 0.63. These findings demonstrate that social media and dating app text data can provide valuable insights into risk and protective behaviors and highlight the potential of large language model-based methods to support scalable and personalized public health interventions for MSM.
A Self-supervised Framework for Improved Data-Driven Monitoring of Stress via Multi-modal Passive Sensing
Mar 24, 2023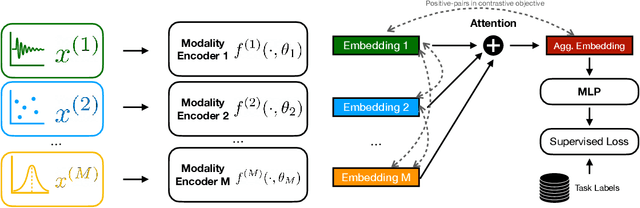

Abstract:Recent advances in remote health monitoring systems have significantly benefited patients and played a crucial role in improving their quality of life. However, while physiological health-focused solutions have demonstrated increasing success and maturity, mental health-focused applications have seen comparatively limited success in spite of the fact that stress and anxiety disorders are among the most common issues people deal with in their daily lives. In the hopes of furthering progress in this domain through the development of a more robust analytic framework for the measurement of indicators of mental health, we propose a multi-modal semi-supervised framework for tracking physiological precursors of the stress response. Our methodology enables utilizing multi-modal data of differing domains and resolutions from wearable devices and leveraging them to map short-term episodes to semantically efficient embeddings for a given task. Additionally, we leverage an inter-modality contrastive objective, with the advantages of rendering our framework both modular and scalable. The focus on optimizing both local and global aspects of our embeddings via a hierarchical structure renders transferring knowledge and compatibility with other devices easier to achieve. In our pipeline, a task-specific pooling based on an attention mechanism, which estimates the contribution of each modality on an instance level, computes the final embeddings for observations. This additionally provides a thorough diagnostic insight into the data characteristics and highlights the importance of signals in the broader view of predicting episodes annotated per mental health status. We perform training experiments using a corpus of real-world data on perceived stress, and our results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach in performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge