Meghana Verma
Can Population-based Engagement Improve Personalisation? A Novel Dataset and Experiments
Jun 22, 2022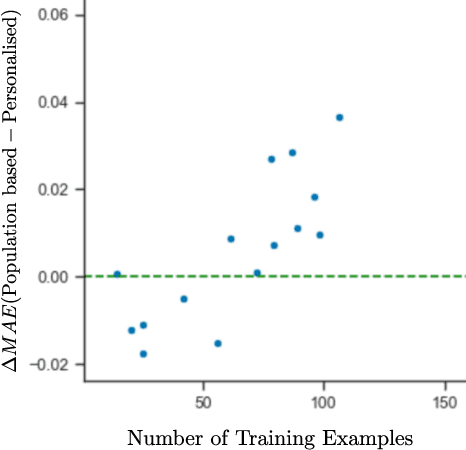
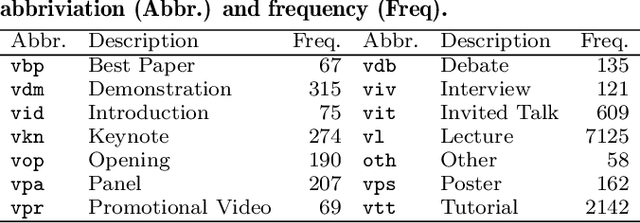
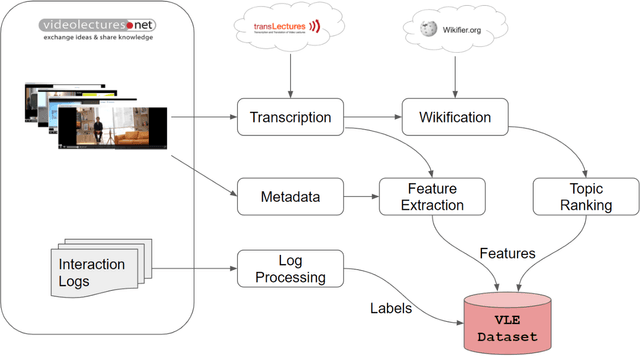
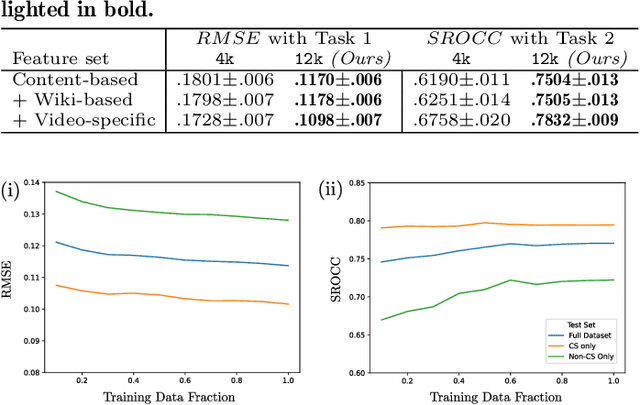
Abstract:This work explores how population-based engagement prediction can address cold-start at scale in large learning resource collections. The paper introduces i) VLE, a novel dataset that consists of content and video based features extracted from publicly available scientific video lectures coupled with implicit and explicit signals related to learner engagement, ii) two standard tasks related to predicting and ranking context-agnostic engagement in video lectures with preliminary baselines and iii) a set of experiments that validate the usefulness of the proposed dataset. Our experimental results indicate that the newly proposed VLE dataset leads to building context-agnostic engagement prediction models that are significantly performant than ones based on previous datasets, mainly attributing to the increase of training examples. VLE dataset's suitability in building models towards Computer Science/ Artificial Intelligence education focused on e-learning/ MOOC use-cases is also evidenced. Further experiments in combining the built model with a personalising algorithm show promising improvements in addressing the cold-start problem encountered in educational recommenders. This is the largest and most diverse publicly available dataset to our knowledge that deals with learner engagement prediction tasks. The dataset, helper tools, descriptive statistics and example code snippets are available publicly.
Watch Less and Uncover More: Could Navigation Tools Help Users Search and Explore Videos?
Jan 10, 2022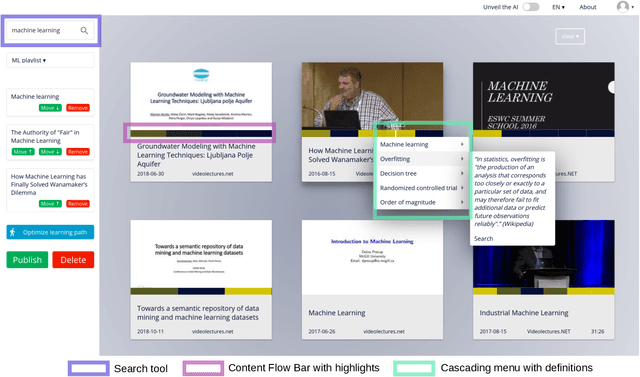
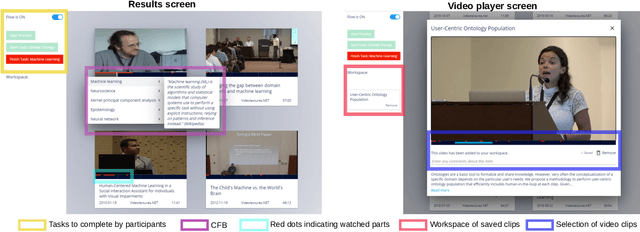
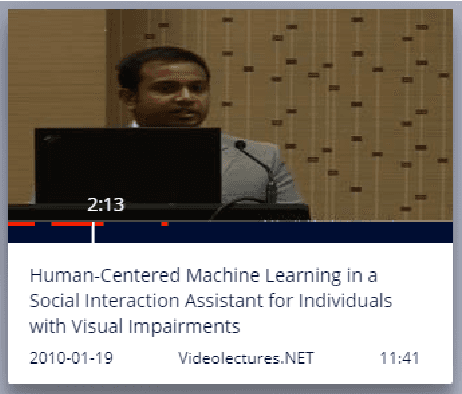
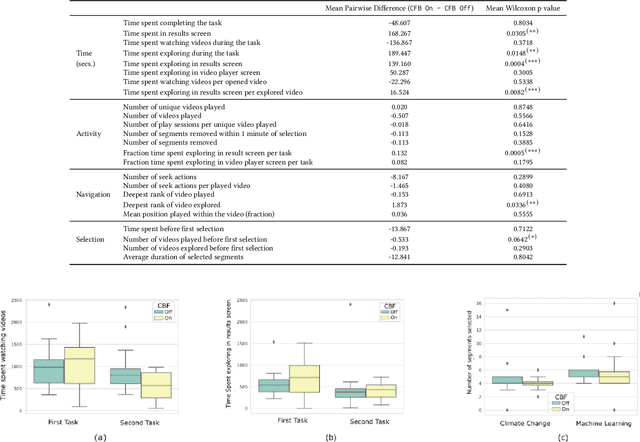
Abstract:Prior research has shown how 'content preview tools' improve speed and accuracy of user relevance judgements across different information retrieval tasks. This paper describes a novel user interface tool, the Content Flow Bar, designed to allow users to quickly identify relevant fragments within informational videos to facilitate browsing, through a cognitively augmented form of navigation. It achieves this by providing semantic "snippets" that enable the user to rapidly scan through video content. The tool provides visually-appealing pop-ups that appear in a time series bar at the bottom of each video, allowing to see in advance and at a glance how topics evolve in the content. We conducted a user study to evaluate how the tool changes the users search experience in video retrieval, as well as how it supports exploration and information seeking. The user questionnaire revealed that participants found the Content Flow Bar helpful and enjoyable for finding relevant information in videos. The interaction logs of the user study, where participants interacted with the tool for completing two informational tasks, showed that it holds promise for enhancing discoverability of content both across and within videos. This discovered potential could leverage a new generation of navigation tools in search and information retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge