Md. Sadekur Rahman
Breaking the Fake News Barrier: Deep Learning Approaches in Bangla Language
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:The rapid development of digital stages has greatly compounded the dispersal of untrue data, dissolving certainty and judgment in society, especially among the Bengali-speaking community. Our ponder addresses this critical issue by presenting an interesting strategy that utilizes a profound learning innovation, particularly the Gated Repetitive Unit (GRU), to recognize fake news within the Bangla dialect. The strategy of our proposed work incorporates intensive information preprocessing, which includes lemmatization, tokenization, and tending to course awkward nature by oversampling. This comes about in a dataset containing 58,478 passages. We appreciate the creation of a demonstration based on GRU (Gated Repetitive Unit) that illustrates remarkable execution with a noteworthy precision rate of 94%. This ponder gives an intensive clarification of the methods included in planning the information, selecting the show, preparing it, and assessing its execution. The performance of the model is investigated by reliable metrics like precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy. The commitment of the work incorporates making a huge fake news dataset in Bangla and a demonstration that has outperformed other Bangla fake news location models.
NeuroSym-BioCAT: Leveraging Neuro-Symbolic Methods for Biomedical Scholarly Document Categorization and Question Answering
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:The growing volume of biomedical scholarly document abstracts presents an increasing challenge in efficiently retrieving accurate and relevant information. To address this, we introduce a novel approach that integrates an optimized topic modelling framework, OVB-LDA, with the BI-POP CMA-ES optimization technique for enhanced scholarly document abstract categorization. Complementing this, we employ the distilled MiniLM model, fine-tuned on domain-specific data, for high-precision answer extraction. Our approach is evaluated across three configurations: scholarly document abstract retrieval, gold-standard scholarly documents abstract, and gold-standard snippets, consistently outperforming established methods such as RYGH and bio-answer finder. Notably, we demonstrate that extracting answers from scholarly documents abstracts alone can yield high accuracy, underscoring the sufficiency of abstracts for many biomedical queries. Despite its compact size, MiniLM exhibits competitive performance, challenging the prevailing notion that only large, resource-intensive models can handle such complex tasks. Our results, validated across various question types and evaluation batches, highlight the robustness and adaptability of our method in real-world biomedical applications. While our approach shows promise, we identify challenges in handling complex list-type questions and inconsistencies in evaluation metrics. Future work will focus on refining the topic model with more extensive domain-specific datasets, further optimizing MiniLM and utilizing large language models (LLM) to improve both precision and efficiency in biomedical question answering.
Comparative Performance Analysis of Transformer-Based Pre-Trained Models for Detecting Keratoconus Disease
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:This study compares eight pre-trained CNNs for diagnosing keratoconus, a degenerative eye disease. A carefully selected dataset of keratoconus, normal, and suspicious cases was used. The models tested include DenseNet121, EfficientNetB0, InceptionResNetV2, InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, ResNet50, VGG16, and VGG19. To maximize model training, bad sample removal, resizing, rescaling, and augmentation were used. The models were trained with similar parameters, activation function, classification function, and optimizer to compare performance. To determine class separation effectiveness, each model was evaluated on accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. MobileNetV2 was the best accurate model in identifying keratoconus and normal cases with few misclassifications. InceptionV3 and DenseNet121 both performed well in keratoconus detection, but they had trouble with questionable cases. In contrast, EfficientNetB0, ResNet50, and VGG19 had more difficulty distinguishing dubious cases from regular ones, indicating the need for model refining and development. A detailed comparison of state-of-the-art CNN architectures for automated keratoconus identification reveals each model's benefits and weaknesses. This study shows that advanced deep learning models can enhance keratoconus diagnosis and treatment planning. Future research should explore hybrid models and integrate clinical parameters to improve diagnostic accuracy and robustness in real-world clinical applications, paving the way for more effective AI-driven ophthalmology tools.
Convolutional Neural Network Based Partial Face Detection
Jun 29, 2022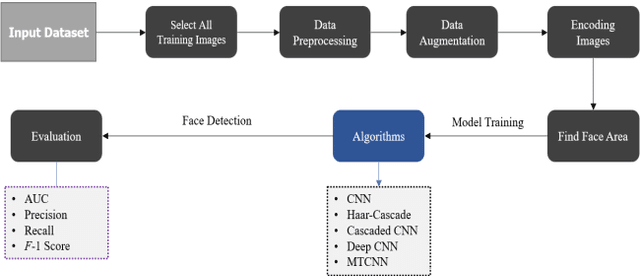

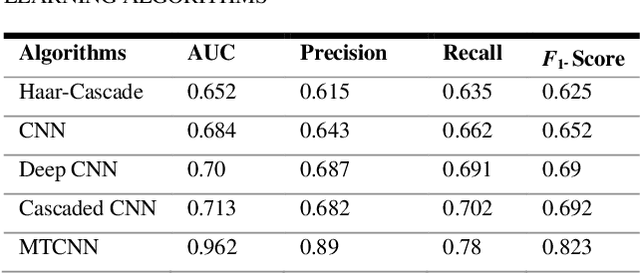
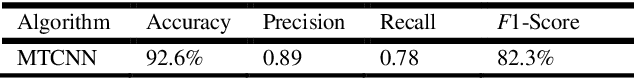
Abstract:Due to the massive explanation of artificial intelligence, machine learning technology is being used in various areas of our day-to-day life. In the world, there are a lot of scenarios where a simple crime can be prevented before it may even happen or find the person responsible for it. A face is one distinctive feature that we have and can differentiate easily among many other species. But not just different species, it also plays a significant role in determining someone from the same species as us, humans. Regarding this critical feature, a single problem occurs most often nowadays. When the camera is pointed, it cannot detect a person's face, and it becomes a poor image. On the other hand, where there was a robbery and a security camera installed, the robber's identity is almost indistinguishable due to the low-quality camera. But just making an excellent algorithm to work and detecting a face reduces the cost of hardware, and it doesn't cost that much to focus on that area. Facial recognition, widget control, and such can be done by detecting the face correctly. This study aims to create and enhance a machine learning model that correctly recognizes faces. Total 627 Data have been collected from different Bangladeshi people's faces on four angels. In this work, CNN, Harr Cascade, Cascaded CNN, Deep CNN & MTCNN are these five machine learning approaches implemented to get the best accuracy of our dataset. After creating and running the model, Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Network (MTCNN) achieved 96.2% best model accuracy with training data rather than other machine learning models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge