Md Zia Uddin
A Computer Vision Based Approach for Stalking Detection Using a CNN-LSTM-MLP Hybrid Fusion Model
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Criminal and suspicious activity detection has become a popular research topic in recent years. The rapid growth of computer vision technologies has had a crucial impact on solving this issue. However, physical stalking detection is still a less explored area despite the evolution of modern technology. Nowadays, stalking in public places has become a common occurrence with women being the most affected. Stalking is a visible action that usually occurs before any criminal activity begins as the stalker begins to follow, loiter, and stare at the victim before committing any criminal activity such as assault, kidnapping, rape, and so on. Therefore, it has become a necessity to detect stalking as all of these criminal activities can be stopped in the first place through stalking detection. In this research, we propose a novel deep learning-based hybrid fusion model to detect potential stalkers from a single video with a minimal number of frames. We extract multiple relevant features, such as facial landmarks, head pose estimation, and relative distance, as numerical values from video frames. This data is fed into a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to perform a classification task between a stalking and a non-stalking scenario. Simultaneously, the video frames are fed into a combination of convolutional and LSTM models to extract the spatio-temporal features. We use a fusion of these numerical and spatio-temporal features to build a classifier to detect stalking incidents. Additionally, we introduce a dataset consisting of stalking and non-stalking videos gathered from various feature films and television series, which is also used to train the model. The experimental results show the efficiency and dynamism of our proposed stalker detection system, achieving 89.58% testing accuracy with a significant improvement as compared to the state-of-the-art approaches.
Sketch2FullStack: Generating Skeleton Code of Full Stack Website and Application from Sketch using Deep Learning and Computer Vision
Nov 26, 2022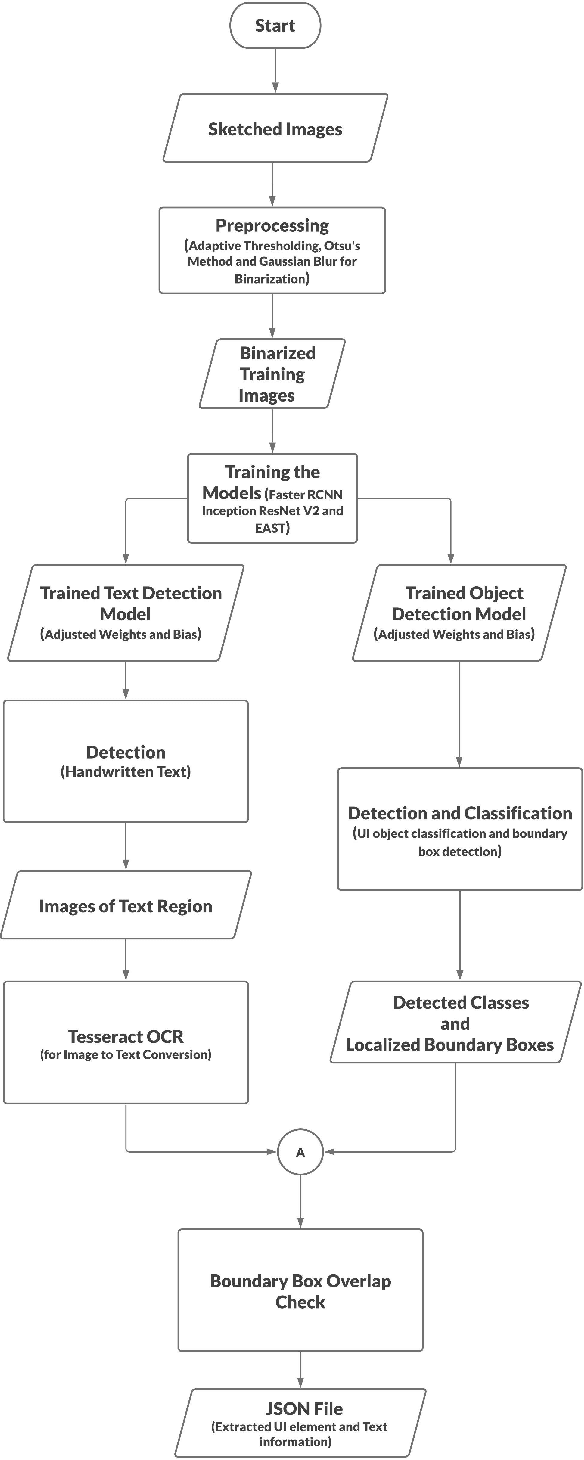

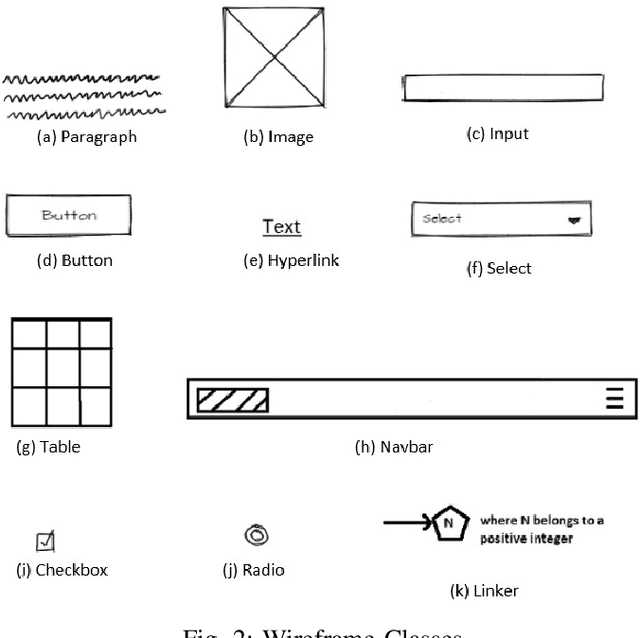
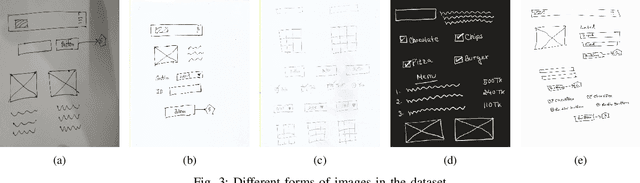
Abstract:For a full-stack web or app development, it requires a software firm or more specifically a team of experienced developers to contribute a large portion of their time and resources to design the website and then convert it to code. As a result, the efficiency of the development team is significantly reduced when it comes to converting UI wireframes and database schemas into an actual working system. It would save valuable resources and fasten the overall workflow if the clients or developers can automate this process of converting the pre-made full-stack website design to get a partially working if not fully working code. In this paper, we present a novel approach of generating the skeleton code from sketched images using Deep Learning and Computer Vision approaches. The dataset for training are first-hand sketched images of low fidelity wireframes, database schemas and class diagrams. The approach consists of three parts. First, the front-end or UI elements detection and extraction from custom-made UI wireframes. Second, individual database table creation from schema designs and lastly, creating a class file from class diagrams.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge