Md Sakib Ullah Sourav
IoMT-Blockchain based Secured Remote Patient Monitoring Framework for Neuro-Stimulation Device
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:Biomedical Engineering's Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is helping to improve the accuracy, dependability, and productivity of electronic equipment in the healthcare business. Real-time sensory data from patients may be delivered and subsequently analyzed through rapid development of wearable IoMT devices, such as neuro-stimulation devices with a range of functions. Data from the Internet of Things is gathered, analyzed, and stored in a single location. However, single-point failure, data manipulation, privacy difficulties, and other challenges might arise as a result of centralization. Due to its decentralized nature, blockchain (BC) can alleviate these issues. The viability of establishing a non-invasive remote neurostimulation system employing IoMT-based transcranial Direct Current Stimulation is investigated in this work (tDCS). A hardware-based prototype tDCS device has been developed that can be operated over the internet using an android application. Our suggested framework addresses the problems of IoMTBC-based systems, meets the criteria of real-time remote patient monitoring systems, and incorporates literature best practices in the relevant fields.
The Role of Digital Agriculture in Transforming Rural Areas into Smart Villages
Jan 07, 2023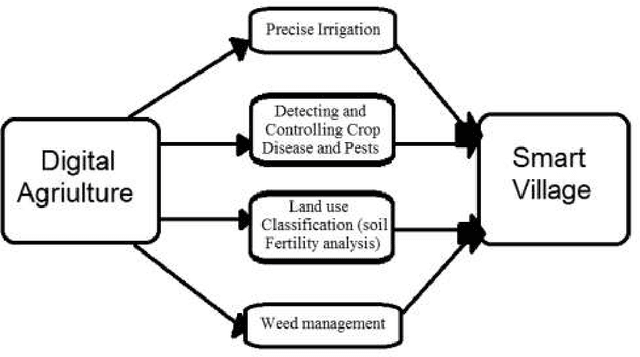
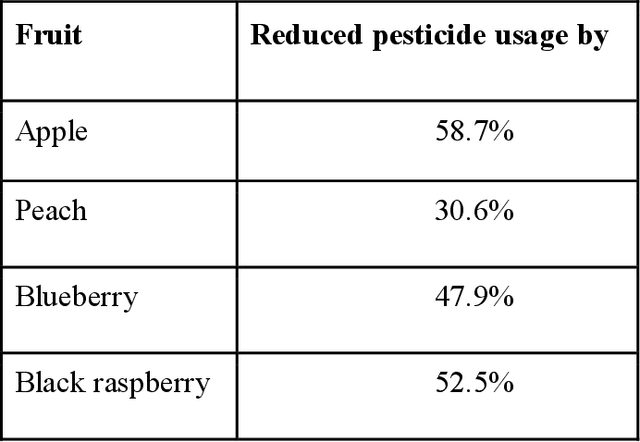
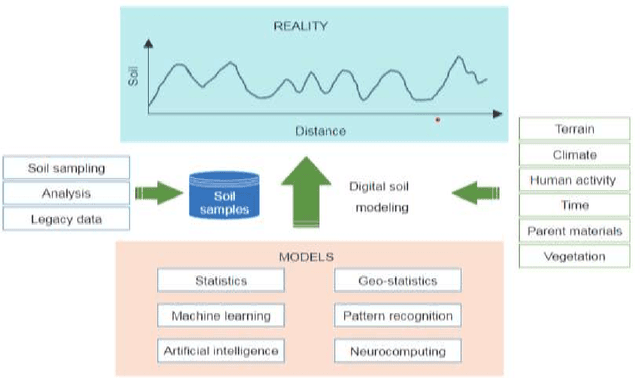
Abstract:From the perspective of any nation, rural areas generally present a comparable set of problems, such as a lack of proper health care, education, living conditions, wages, and market opportunities. Some nations have created and developed the concept of smart villages during the previous few decades, which effectively addresses these issues. The landscape of traditional agriculture has been radically altered by digital agriculture, which has also had a positive economic impact on farmers and those who live in rural regions by ensuring an increase in agricultural production. We explored current issues in rural areas, and the consequences of smart village applications, and then illustrate our concept of smart village from recent examples of how emerging digital agriculture trends contribute to improving agricultural production in this chapter.
Classifying Mental-Disorders through Clinicians Subjective Approach based on Three-way Decision
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:In psychiatric diagnosis, a contemporary data-driven, manual-based method for mental disorders classification is the most popular technique; however, it has several inevitable flaws. Using the three-way decision as a framework, we propose a unified model that stands for clinicians' subjective approach (CSA) analysis consisting of three parts: quantitative analysis, quantitative analysis, and evaluation-based analysis. A ranking list and a set of numerical weights based on illness magnitude levels according to the clinician's greatest degree of assumptions are the findings of the qualitative and quantitative investigation. We further create a comparative classification of illnesses into three groups with varying important levels; a three-way evaluation-based model is utilized in this study for the aim of understanding and portraying these results in a more clear way. This proposed method might be integrated with the manual-based process as a complementary tool to improve precision while diagnosing mental disorders
Transformer-based Text Classification on Unified Bangla Multi-class Emotion Corpus
Oct 12, 2022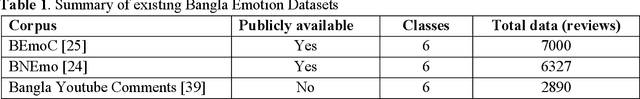
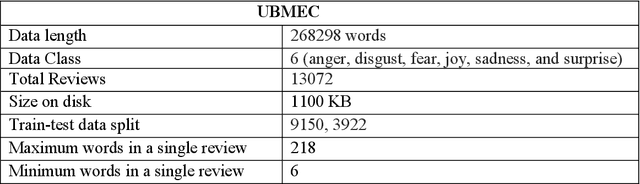
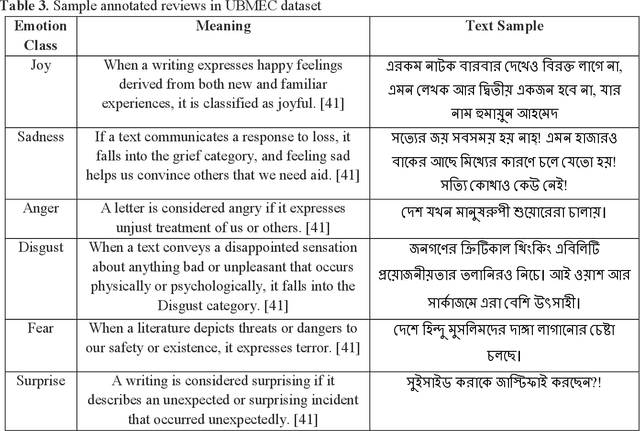
Abstract:Because of its importance in studying people's thoughts on various Web 2.0 services, emotion classification (EC) is an important undertaking. Existing research, on the other hand, is mostly focused on the English language, with little work on low-resource languages. Though sentiment analysis, particularly the EC in English, has received a lot of attention in recent years, little study has been done in the context of Bangla, one of the world's most widely spoken languages. We propose a complete set of approaches for identifying and extracting emotions from Bangla texts in this research. We provide a Bangla emotion classifier for six classes (anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, and surprise) from Bangla words, using transformer-based models which exhibit phenomenal results in recent days, especially for high resource languages. The "Unified Bangla Multi-class Emotion Corpus (UBMEC)" is used to assess the performance of our models. UBMEC was created by combining two previously released manually labeled datasets of Bangla comments on 6-emotion classes with fresh manually tagged Bangla comments created by us. The corpus dataset and code we used in this work is publicly available.
Efficient approach of using CNN based pretrained model in Bangla handwritten digit recognition
Sep 19, 2022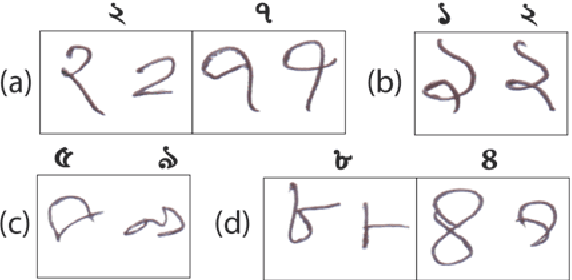
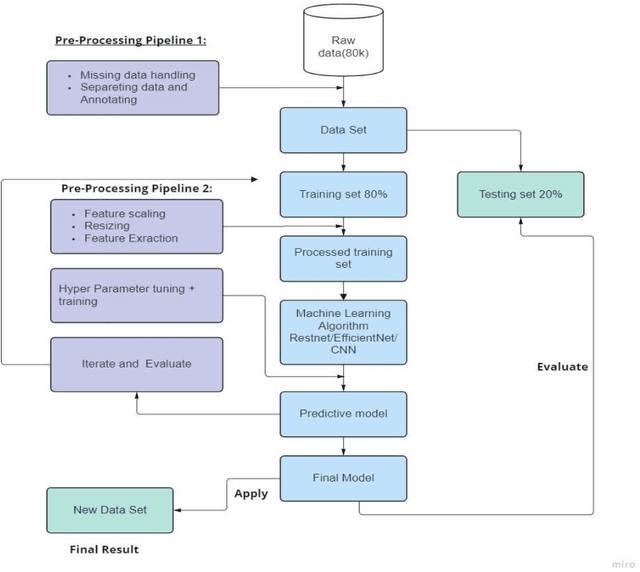
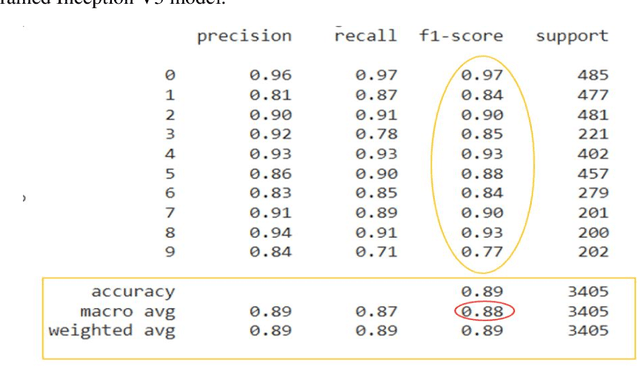
Abstract:Due to digitalization in everyday life, the need for automatically recognizing handwritten digits is increasing. Handwritten digit recognition is essential for numerous applications in various industries. Bengali ranks the fifth largest language in the world with 265 million speakers (Native and non-native combined) and 4 percent of the world population speaks Bengali. Due to the complexity of Bengali writing in terms of variety in shape, size, and writing style, researchers did not get better accuracy using Supervised machine learning algorithms to date. Moreover, fewer studies have been done on Bangla handwritten digit recognition (BHwDR). In this paper, we proposed a novel CNN-based pre-trained handwritten digit recognition model which includes Resnet-50, Inception-v3, and EfficientNetB0 on NumtaDB dataset of 17 thousand instances with 10 classes.. The Result outperformed the performance of other models to date with 97% accuracy in the 10-digit classes. Furthermore, we have evaluated the result or our model with other research studies while suggesting future study
Energy Efficient Automatic Streetlight Controlling System using Semantic Segmentation
Sep 18, 2022Abstract:This study aims to develop a novel streetlight management system powered by computer vision technology mounted with the close circuit television (CCTV) camera that allows the light emitting diode (LED) streetlight to automatically light up with proper brightness by recognizing the presence of pedestrians or vehicles and reversely dimming the streetlight in their absence by semantic image segmentation from video.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge