Shabbir Ahmed Shuvo
Offenburg University of Applied Sciences, Germany, Noakhali Science and Technology University, Bangladesh
Unleashing Modified Deep Learning Models in Efficient COVID19 Detection
Oct 21, 2023

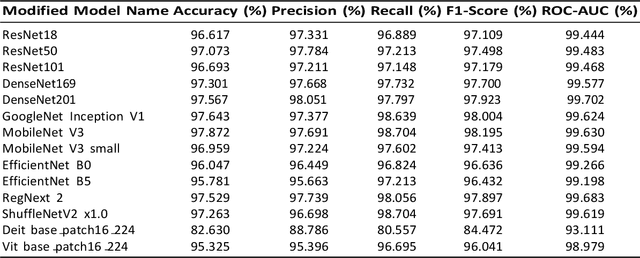

Abstract:The COVID19 pandemic, a unique and devastating respiratory disease outbreak, has affected global populations as the disease spreads rapidly. Recent Deep Learning breakthroughs may improve COVID19 prediction and forecasting as a tool of precise and fast detection, however, current methods are still being examined to achieve higher accuracy and precision. This study analyzed the collection contained 8055 CT image samples, 5427 of which were COVID cases and 2628 non COVID. The 9544 Xray samples included 4044 COVID patients and 5500 non COVID cases. The most accurate models are MobileNet V3 (97.872 percent), DenseNet201 (97.567 percent), and GoogleNet Inception V1 (97.643 percent). High accuracy indicates that these models can make many accurate predictions, as well as others, are also high for MobileNetV3 and DenseNet201. An extensive evaluation using accuracy, precision, and recall allows a comprehensive comparison to improve predictive models by combining loss optimization with scalable batch normalization in this study. Our analysis shows that these tactics improve model performance and resilience for advancing COVID19 prediction and detection and shows how Deep Learning can improve disease handling. The methods we suggest would strengthen healthcare systems, policymakers, and researchers to make educated decisions to reduce COVID19 and other contagious diseases. CCS CONCEPTS Covid,Deep Learning, Image Processing KEYWORDS Covid, Deep Learning, DenseNet201, MobileNet, ResNet, DenseNet, GoogleNet, Image Processing, Disease Detection.
Comparative study of Deep Learning Models for Binary Classification on Combined Pulmonary Chest X-ray Dataset
Sep 16, 2023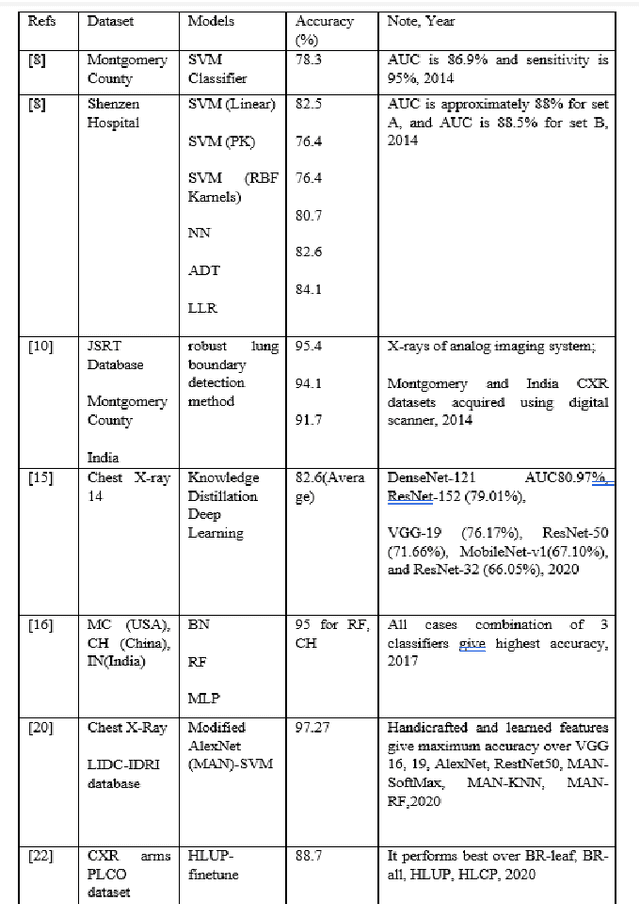
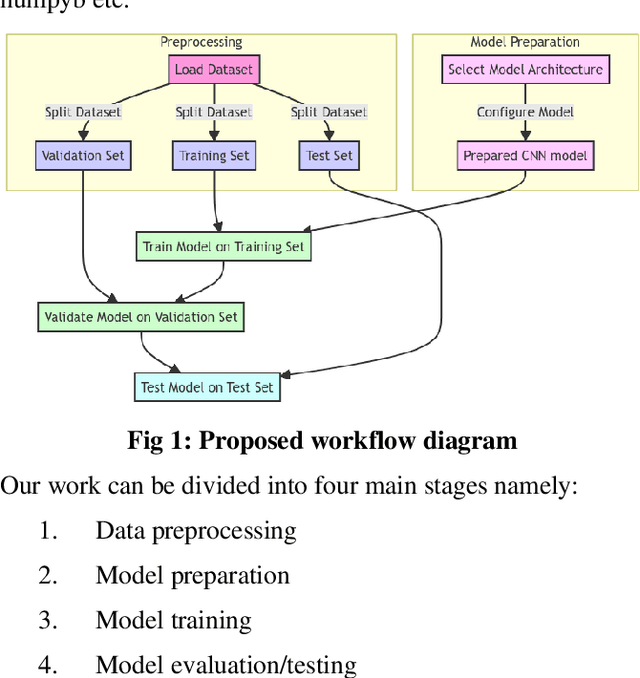
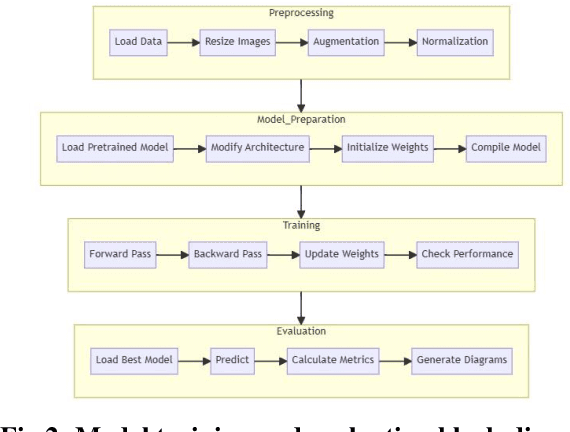
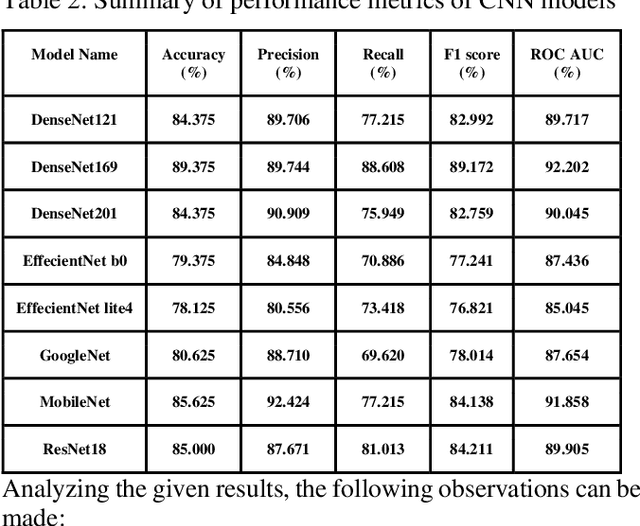
Abstract:CNN-based deep learning models for disease detection have become popular recently. We compared the binary classification performance of eight prominent deep learning models: DenseNet 121, DenseNet 169, DenseNet 201, EffecientNet b0, EffecientNet lite4, GoogleNet, MobileNet, and ResNet18 for their binary classification performance on combined Pulmonary Chest Xrays dataset. Despite the widespread application in different fields in medical images, there remains a knowledge gap in determining their relative performance when applied to the same dataset, a gap this study aimed to address. The dataset combined Shenzhen, China (CH) and Montgomery, USA (MC) data. We trained our model for binary classification, calculated different parameters of the mentioned models, and compared them. The models were trained to keep in mind all following the same training parameters to maintain a controlled comparison environment. End of the study, we found a distinct difference in performance among the other models when applied to the pulmonary chest Xray image dataset, where DenseNet169 performed with 89.38 percent and MobileNet with 92.2 percent precision. Keywords: Pulmonary, Deep Learning, Tuberculosis, Disease detection, Xray
Efficient approach of using CNN based pretrained model in Bangla handwritten digit recognition
Sep 19, 2022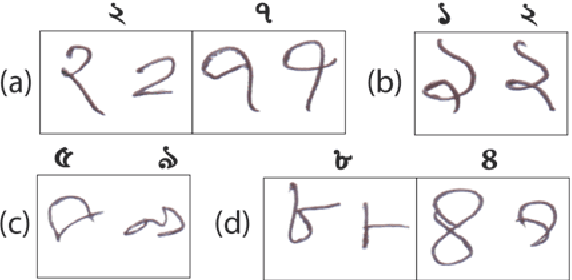
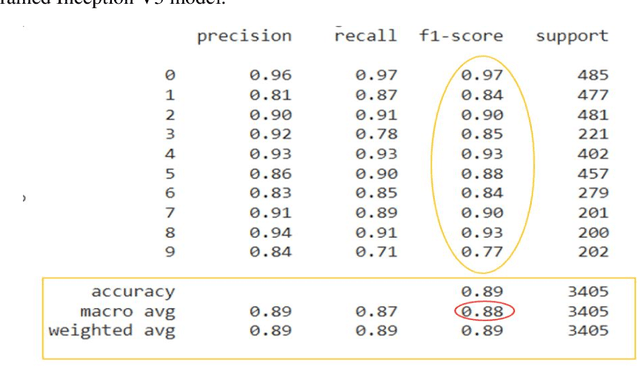
Abstract:Due to digitalization in everyday life, the need for automatically recognizing handwritten digits is increasing. Handwritten digit recognition is essential for numerous applications in various industries. Bengali ranks the fifth largest language in the world with 265 million speakers (Native and non-native combined) and 4 percent of the world population speaks Bengali. Due to the complexity of Bengali writing in terms of variety in shape, size, and writing style, researchers did not get better accuracy using Supervised machine learning algorithms to date. Moreover, fewer studies have been done on Bangla handwritten digit recognition (BHwDR). In this paper, we proposed a novel CNN-based pre-trained handwritten digit recognition model which includes Resnet-50, Inception-v3, and EfficientNetB0 on NumtaDB dataset of 17 thousand instances with 10 classes.. The Result outperformed the performance of other models to date with 97% accuracy in the 10-digit classes. Furthermore, we have evaluated the result or our model with other research studies while suggesting future study
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge