Md Aminul Islam
Oxford Brookes University, UK
Correcting for Position Bias in Learning to Rank: A Control Function Approach
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Implicit feedback data, such as user clicks, is commonly used in learning-to-rank (LTR) systems because it is easy to collect and it often reflects user preferences. However, this data is prone to various biases, and training an LTR system directly on biased data can result in suboptimal ranking performance. One of the most prominent and well-studied biases in implicit feedback data is position bias, which occurs because users are more likely to interact with higher-ranked documents regardless of their true relevance. In this paper, we propose a novel control function-based method that accounts for position bias in a two-stage process. The first stage uses exogenous variation from the residuals of the ranking process to correct for position bias in the second stage click equation. Unlike previous position bias correction methods, our method does not require knowledge of the click or propensity model and allows for nonlinearity in the underlying ranking model. Moreover, our method is general and allows for debiasing any state-of-the-art ranking algorithm by plugging it into the second stage. We also introduce a technique to debias validation clicks for hyperparameter tuning to select the optimal model in the absence of unbiased validation data. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in correcting for position bias.
Prompt-Based LLMs for Position Bias-Aware Reranking in Personalized Recommendations
May 08, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems are essential for delivering personalized content across digital platforms by modeling user preferences and behaviors. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have been adopted for prompt-based recommendation due to their ability to generate personalized outputs without task-specific training. However, LLM-based methods face limitations such as limited context window size, inefficient pointwise and pairwise prompting, and difficulty handling listwise ranking due to token constraints. LLMs can also be sensitive to position bias, as they may overemphasize earlier items in the prompt regardless of their true relevance. To address and investigate these issues, we propose a hybrid framework that combines a traditional recommendation model with an LLM for reranking top-k items using structured prompts. We evaluate the effects of user history reordering and instructional prompts for mitigating position bias. Experiments on MovieLens-100K show that randomizing user history improves ranking quality, but LLM-based reranking does not outperform the base model. Explicit instructions to reduce position bias are also ineffective. Our evaluations reveal limitations in LLMs' ability to model ranking context and mitigate bias. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/aminul7506/LLMForReRanking.
Unleashing Modified Deep Learning Models in Efficient COVID19 Detection
Oct 21, 2023

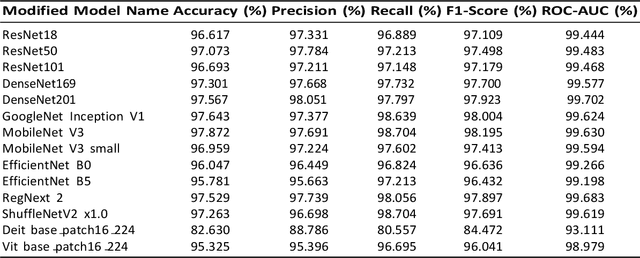

Abstract:The COVID19 pandemic, a unique and devastating respiratory disease outbreak, has affected global populations as the disease spreads rapidly. Recent Deep Learning breakthroughs may improve COVID19 prediction and forecasting as a tool of precise and fast detection, however, current methods are still being examined to achieve higher accuracy and precision. This study analyzed the collection contained 8055 CT image samples, 5427 of which were COVID cases and 2628 non COVID. The 9544 Xray samples included 4044 COVID patients and 5500 non COVID cases. The most accurate models are MobileNet V3 (97.872 percent), DenseNet201 (97.567 percent), and GoogleNet Inception V1 (97.643 percent). High accuracy indicates that these models can make many accurate predictions, as well as others, are also high for MobileNetV3 and DenseNet201. An extensive evaluation using accuracy, precision, and recall allows a comprehensive comparison to improve predictive models by combining loss optimization with scalable batch normalization in this study. Our analysis shows that these tactics improve model performance and resilience for advancing COVID19 prediction and detection and shows how Deep Learning can improve disease handling. The methods we suggest would strengthen healthcare systems, policymakers, and researchers to make educated decisions to reduce COVID19 and other contagious diseases. CCS CONCEPTS Covid,Deep Learning, Image Processing KEYWORDS Covid, Deep Learning, DenseNet201, MobileNet, ResNet, DenseNet, GoogleNet, Image Processing, Disease Detection.
Autonomous Vehicles an overview on system, cyber security, risks, issues, and a way forward
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:This chapter explores the complex realm of autonomous cars, analyzing their fundamental components and operational characteristics. The initial phase of the discussion is elucidating the internal mechanics of these automobiles, encompassing the crucial involvement of sensors, artificial intelligence (AI) identification systems, control mechanisms, and their integration with cloud-based servers within the framework of the Internet of Things (IoT). It delves into practical implementations of autonomous cars, emphasizing their utilization in forecasting traffic patterns and transforming the dynamics of transportation. The text also explores the topic of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), illustrating the impact of autonomous cars on different businesses through the automation of tasks. The primary focus of this investigation lies in the realm of cybersecurity, specifically in the context of autonomous vehicles. A comprehensive analysis will be conducted to explore various risk management solutions aimed at protecting these vehicles from potential threats including ethical, environmental, legal, professional, and social dimensions, offering a comprehensive perspective on their societal implications. A strategic plan for addressing the challenges and proposing strategies for effectively traversing the complex terrain of autonomous car systems, cybersecurity, hazards, and other concerns are some resources for acquiring an understanding of the intricate realm of autonomous cars and their ramifications in contemporary society, supported by a comprehensive compilation of resources for additional investigation. Keywords: RPA, Cyber Security, AV, Risk, Smart Cars
Comparative study of Deep Learning Models for Binary Classification on Combined Pulmonary Chest X-ray Dataset
Sep 16, 2023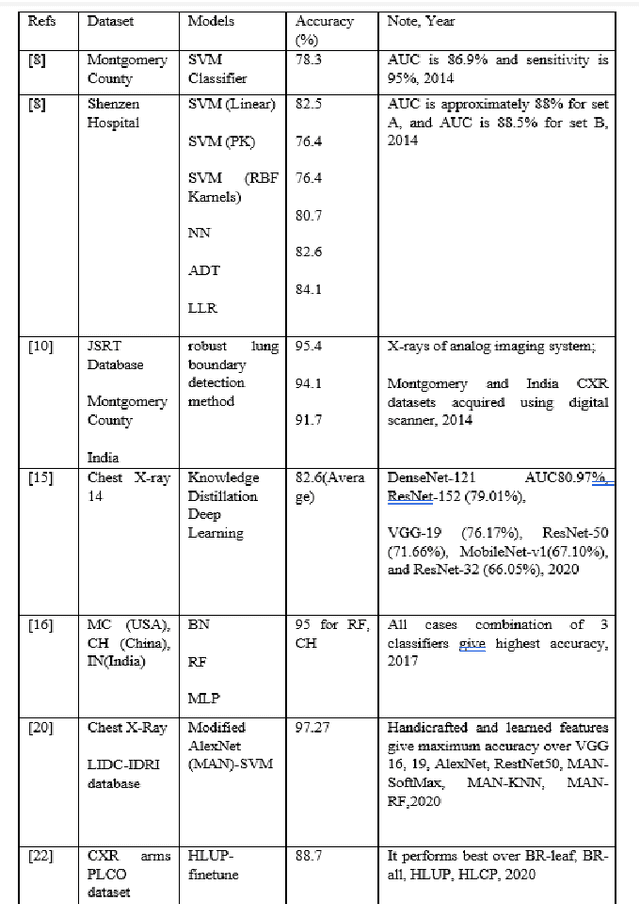
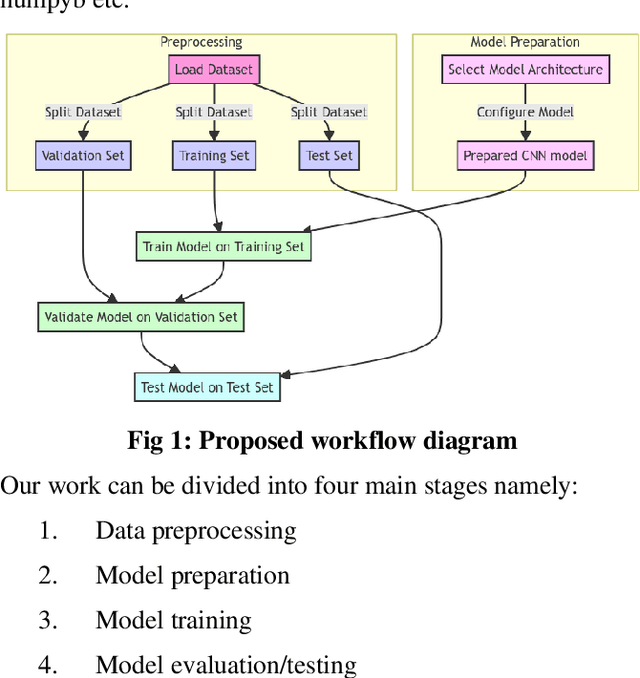
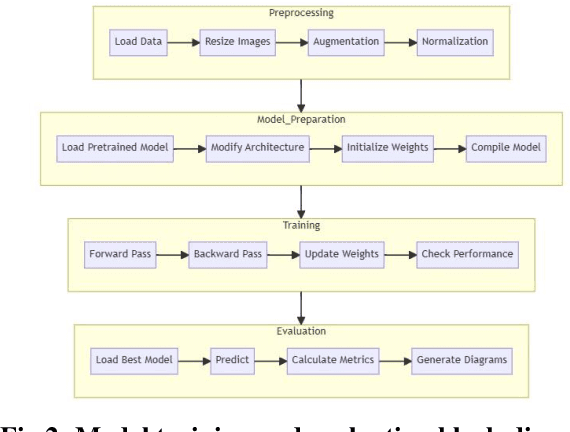
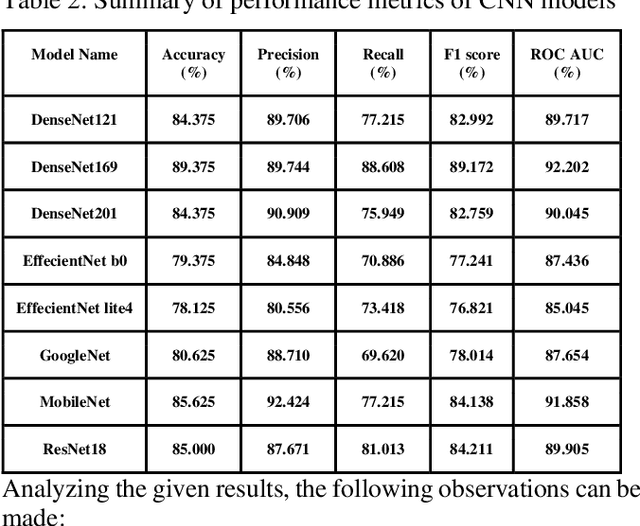
Abstract:CNN-based deep learning models for disease detection have become popular recently. We compared the binary classification performance of eight prominent deep learning models: DenseNet 121, DenseNet 169, DenseNet 201, EffecientNet b0, EffecientNet lite4, GoogleNet, MobileNet, and ResNet18 for their binary classification performance on combined Pulmonary Chest Xrays dataset. Despite the widespread application in different fields in medical images, there remains a knowledge gap in determining their relative performance when applied to the same dataset, a gap this study aimed to address. The dataset combined Shenzhen, China (CH) and Montgomery, USA (MC) data. We trained our model for binary classification, calculated different parameters of the mentioned models, and compared them. The models were trained to keep in mind all following the same training parameters to maintain a controlled comparison environment. End of the study, we found a distinct difference in performance among the other models when applied to the pulmonary chest Xray image dataset, where DenseNet169 performed with 89.38 percent and MobileNet with 92.2 percent precision. Keywords: Pulmonary, Deep Learning, Tuberculosis, Disease detection, Xray
AI & Blockchain as sustainable teaching and learning tools to cope with the 4IR
May 01, 2023Abstract:The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) is transforming the way we live and work, and education is no exception. To cope with the challenges of 4IR, there is a need for innovative and sustainable teaching and learning tools. AI and block chain technologies hold great promise in this regard, with potential benefits such as personalized learning, secure credentialing, and decentralized learning networks. This paper presents a review of existing research on AI and block chain in education, analyzing case studies and exploring the potential benefits and challenges of these technologies. The paper also suggests a unique model for integrating AI and block chain into sustainable teaching and learning practices. Future research directions are discussed, including the need for more empirical studies and the exploration of ethical and social implications. The key summary of this discussion is that, by enhancing accessibility, efficacy, and security in education, AI and blockchain have the potential to revolutionise the field. In order to ensure that students can benefit from these potentially game-changing technologies as technology develops, it will be crucial to find ways to harness its power while minimising hazards. Overall, this paper highlights the potential of AI and block chain as sustainable tools for teaching and learning in the 4IR era and their respective advantages, issues and future prospects have been discussed in this writing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge