Huidong Wang
Classifying Mental-Disorders through Clinicians Subjective Approach based on Three-way Decision
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:In psychiatric diagnosis, a contemporary data-driven, manual-based method for mental disorders classification is the most popular technique; however, it has several inevitable flaws. Using the three-way decision as a framework, we propose a unified model that stands for clinicians' subjective approach (CSA) analysis consisting of three parts: quantitative analysis, quantitative analysis, and evaluation-based analysis. A ranking list and a set of numerical weights based on illness magnitude levels according to the clinician's greatest degree of assumptions are the findings of the qualitative and quantitative investigation. We further create a comparative classification of illnesses into three groups with varying important levels; a three-way evaluation-based model is utilized in this study for the aim of understanding and portraying these results in a more clear way. This proposed method might be integrated with the manual-based process as a complementary tool to improve precision while diagnosing mental disorders
Transformer-based Text Classification on Unified Bangla Multi-class Emotion Corpus
Oct 12, 2022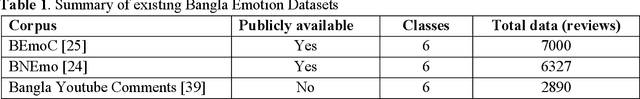
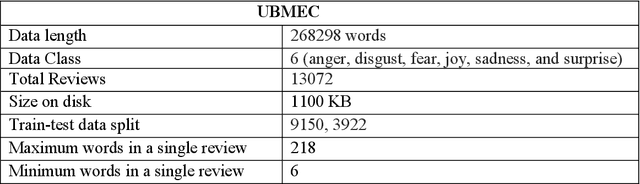
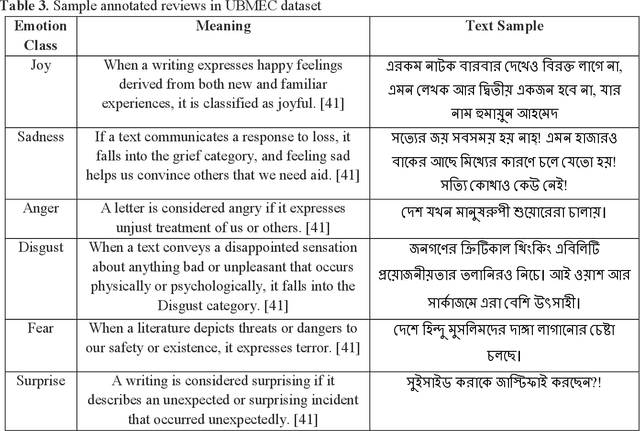
Abstract:Because of its importance in studying people's thoughts on various Web 2.0 services, emotion classification (EC) is an important undertaking. Existing research, on the other hand, is mostly focused on the English language, with little work on low-resource languages. Though sentiment analysis, particularly the EC in English, has received a lot of attention in recent years, little study has been done in the context of Bangla, one of the world's most widely spoken languages. We propose a complete set of approaches for identifying and extracting emotions from Bangla texts in this research. We provide a Bangla emotion classifier for six classes (anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, and surprise) from Bangla words, using transformer-based models which exhibit phenomenal results in recent days, especially for high resource languages. The "Unified Bangla Multi-class Emotion Corpus (UBMEC)" is used to assess the performance of our models. UBMEC was created by combining two previously released manually labeled datasets of Bangla comments on 6-emotion classes with fresh manually tagged Bangla comments created by us. The corpus dataset and code we used in this work is publicly available.
Energy Efficient Automatic Streetlight Controlling System using Semantic Segmentation
Sep 18, 2022Abstract:This study aims to develop a novel streetlight management system powered by computer vision technology mounted with the close circuit television (CCTV) camera that allows the light emitting diode (LED) streetlight to automatically light up with proper brightness by recognizing the presence of pedestrians or vehicles and reversely dimming the streetlight in their absence by semantic image segmentation from video.
Supervised Enhanced Soft Subspace Clustering (SESSC) for TSK Fuzzy Classifiers
Feb 27, 2020



Abstract:Fuzzy c-means based clustering algorithms are frequently used for Takagi-Sugeno-Kang (TSK) fuzzy classifier antecedent parameter estimation. One rule is initialized from each cluster. However, most of these clustering algorithms are unsupervised, which waste valuable label information in the training data. This paper proposes a supervised enhanced soft subspace clustering (SESSC) algorithm, which considers simultaneously the within-cluster compactness, between-cluster separation, and label information in clustering. It can effectively deal with high-dimensional data, be used as a classifier alone, or be integrated into a TSK fuzzy classifier to further improve its performance. Experiments on nine UCI datasets from various application domains demonstrated that SESSC based initialization outperformed other clustering approaches, especially when the number of rules is small.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge