Md Johirul Islam
A Comprehensive Study on Deep Learning Bug Characteristics
Jun 03, 2019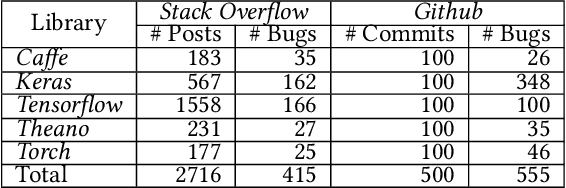
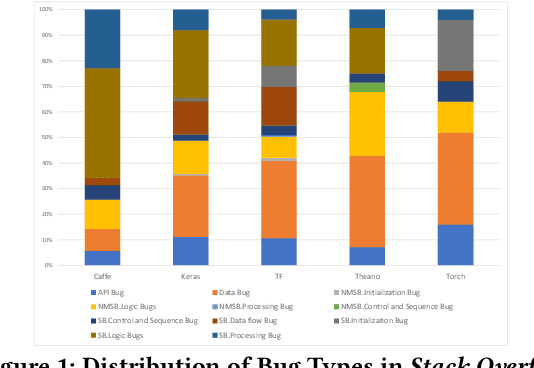
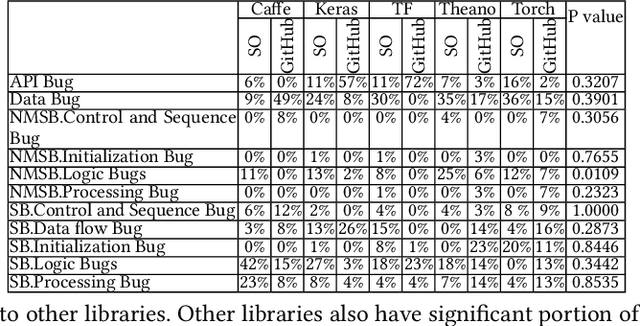
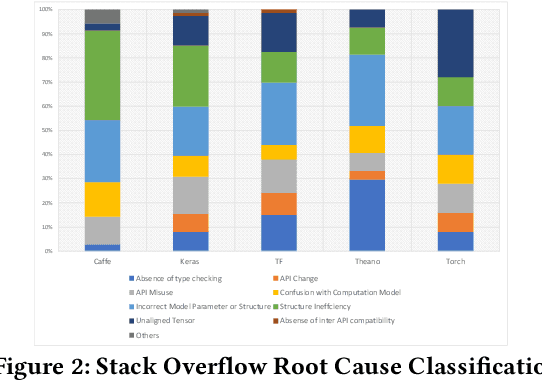
Abstract:Deep learning has gained substantial popularity in recent years. Developers mainly rely on libraries and tools to add deep learning capabilities to their software. What kinds of bugs are frequently found in such software? What are the root causes of such bugs? What impacts do such bugs have? Which stages of deep learning pipeline are more bug prone? Are there any antipatterns? Understanding such characteristics of bugs in deep learning software has the potential to foster the development of better deep learning platforms, debugging mechanisms, development practices, and encourage the development of analysis and verification frameworks. Therefore, we study 2716 high-quality posts from Stack Overflow and 500 bug fix commits from Github about five popular deep learning libraries Caffe, Keras, Tensorflow, Theano, and Torch to understand the types of bugs, root causes of bugs, impacts of bugs, bug-prone stage of deep learning pipeline as well as whether there are some common antipatterns found in this buggy software. The key findings of our study include: data bug and logic bug are the most severe bug types in deep learning software appearing more than 48% of the times, major root causes of these bugs are Incorrect Model Parameter (IPS) and Structural Inefficiency (SI) showing up more than 43% of the times. We have also found that the bugs in the usage of deep learning libraries have some common antipatterns that lead to a strong correlation of bug types among the libraries.
Identifying Classes Susceptible to Adversarial Attacks
May 30, 2019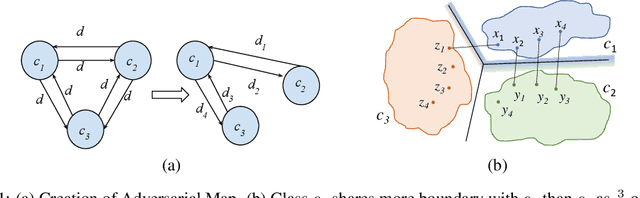
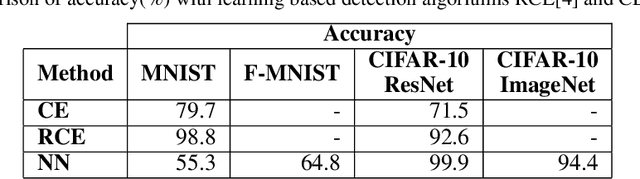
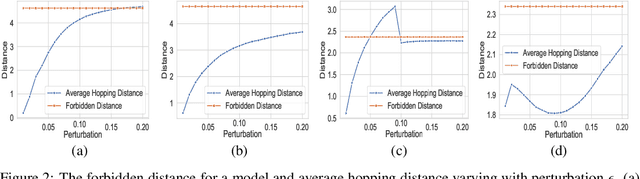
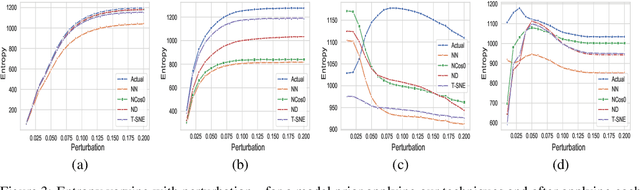
Abstract:Despite numerous attempts to defend deep learning based image classifiers, they remain susceptible to the adversarial attacks. This paper proposes a technique to identify susceptible classes, those classes that are more easily subverted. To identify the susceptible classes we use distance-based measures and apply them on a trained model. Based on the distance among original classes, we create mapping among original classes and adversarial classes that helps to reduce the randomness of a model to a significant amount in an adversarial setting. We analyze the high dimensional geometry among the feature classes and identify the k most susceptible target classes in an adversarial attack. We conduct experiments using MNIST, Fashion MNIST, CIFAR-10 (ImageNet and ResNet-32) datasets. Finally, we evaluate our techniques in order to determine which distance-based measure works best and how the randomness of a model changes with perturbation.
Sentiment analysis of twitter data
Dec 16, 2017
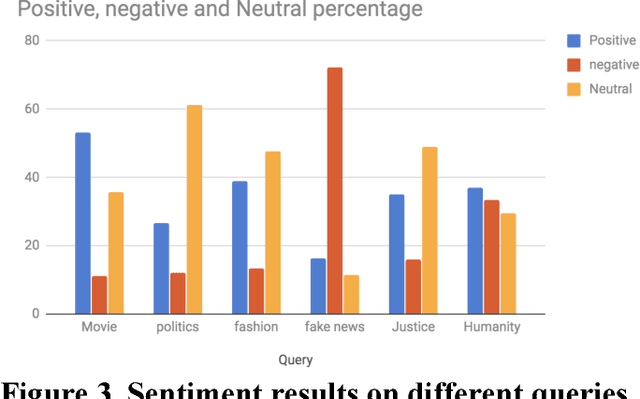
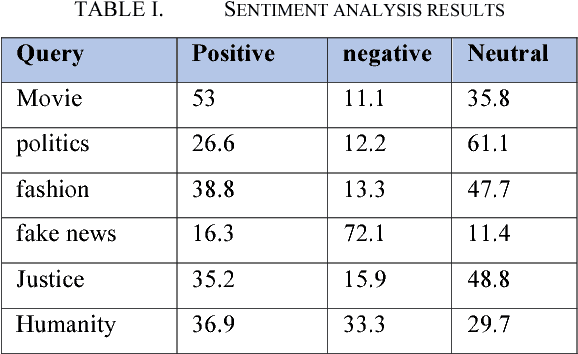
Abstract:Social networks are the main resources to gather information about people's opinion and sentiments towards different topics as they spend hours daily on social media and share their opinion. In this technical paper, we show the application of sentimental analysis and how to connect to Twitter and run sentimental analysis queries. We run experiments on different queries from politics to humanity and show the interesting results. We realized that the neutral sentiments for tweets are significantly high which clearly shows the limitations of the current works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge