Hamid Bagheri
Toward Non-Expert Customized Congestion Control
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:General-purpose congestion control algorithms (CCAs) are designed to achieve general congestion control goals, but they may not meet the specific requirements of certain users. Customized CCAs can meet certain users' specific requirements; however, non-expert users often lack the expertise to implement them. In this paper, we present an exploratory non-expert customized CCA framework, named NECC, which enables non-expert users to easily model, implement, and deploy their customized CCAs by leveraging Large Language Models and the Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) interface. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to address the customized CCA implementation problem. Our evaluations using real-world CCAs show that the performance of NECC is very promising, and we discuss the insights that we find and possible future research directions.
* Accepted manuscript (AAM) of IEEE ICC 2025 paper. DOI: 10.1109/ICC52391.2025.11160790
Automated Repair of Declarative Software Specifications in the Era of Large Language Models
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:The growing adoption of declarative software specification languages, coupled with their inherent difficulty in debugging, has underscored the need for effective and automated repair techniques applicable to such languages. Researchers have recently explored various methods to automatically repair declarative software specifications, such as template-based repair, feedback-driven iterative repair, and bounded exhaustive approaches. The latest developments in large language models provide new opportunities for the automatic repair of declarative specifications. In this study, we assess the effectiveness of utilizing OpenAI's ChatGPT to repair software specifications written in the Alloy declarative language. Unlike imperative languages, specifications in Alloy are not executed but rather translated into logical formulas and evaluated using backend constraint solvers to identify specification instances and counterexamples to assertions. Our evaluation focuses on ChatGPT's ability to improve the correctness and completeness of Alloy declarative specifications through automatic repairs. We analyze the results produced by ChatGPT and compare them with those of leading automatic Alloy repair methods. Our study revealed that while ChatGPT falls short in comparison to existing techniques, it was able to successfully repair bugs that no other technique could address. Our analysis also identified errors in ChatGPT's generated repairs, including improper operator usage, type errors, higher-order logic misuse, and relational arity mismatches. Additionally, we observed instances of hallucinations in ChatGPT-generated repairs and inconsistency in its results. Our study provides valuable insights for software practitioners, researchers, and tool builders considering ChatGPT for declarative specification repairs.
Sentiment analysis of twitter data
Dec 16, 2017
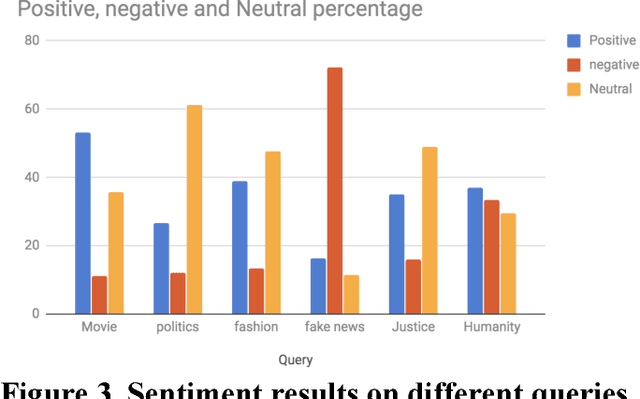
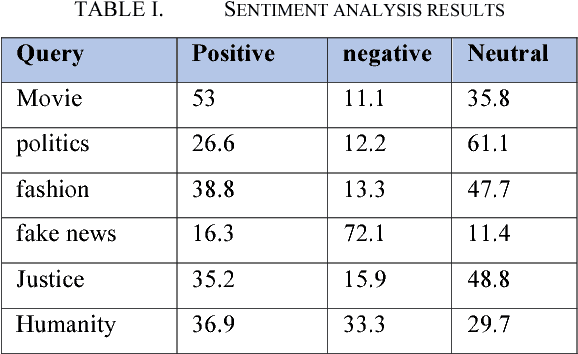
Abstract:Social networks are the main resources to gather information about people's opinion and sentiments towards different topics as they spend hours daily on social media and share their opinion. In this technical paper, we show the application of sentimental analysis and how to connect to Twitter and run sentimental analysis queries. We run experiments on different queries from politics to humanity and show the interesting results. We realized that the neutral sentiments for tweets are significantly high which clearly shows the limitations of the current works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge