Md Athikul Islam
Risks, Causes, and Mitigations of Widespread Deployments of Large Language Models (LLMs): A Survey
Aug 01, 2024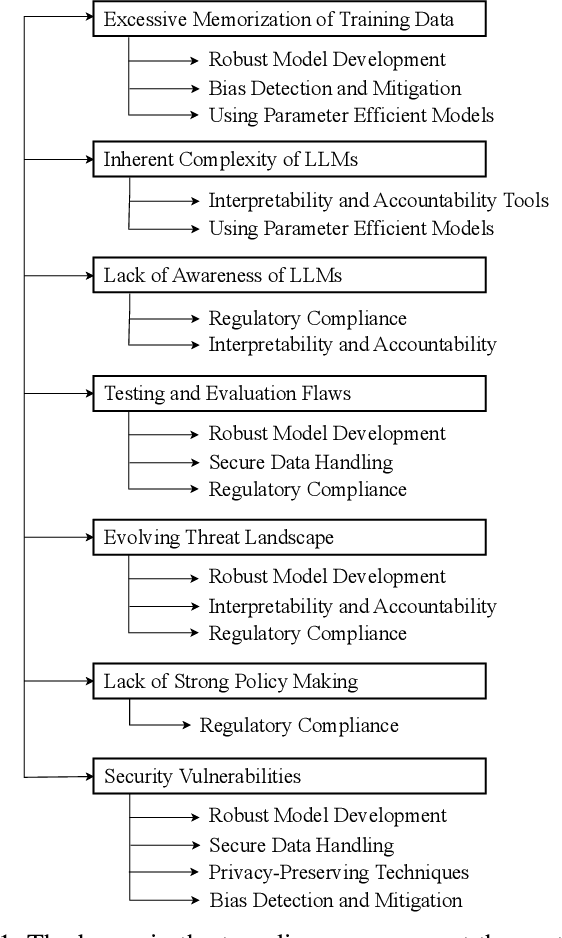
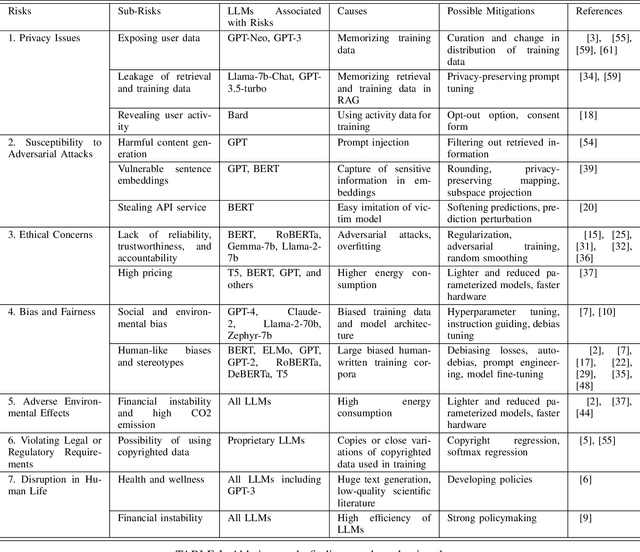
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT and LLaMA, have significantly transformed Natural Language Processing (NLP) with their outstanding abilities in text generation, summarization, and classification. Nevertheless, their widespread adoption introduces numerous challenges, including issues related to academic integrity, copyright, environmental impacts, and ethical considerations such as data bias, fairness, and privacy. The rapid evolution of LLMs also raises concerns regarding the reliability and generalizability of their evaluations. This paper offers a comprehensive survey of the literature on these subjects, systematically gathered and synthesized from Google Scholar. Our study provides an in-depth analysis of the risks associated with specific LLMs, identifying sub-risks, their causes, and potential solutions. Furthermore, we explore the broader challenges related to LLMs, detailing their causes and proposing mitigation strategies. Through this literature analysis, our survey aims to deepen the understanding of the implications and complexities surrounding these powerful models.
Automatic Pull Request Description Generation Using LLMs: A T5 Model Approach
Aug 01, 2024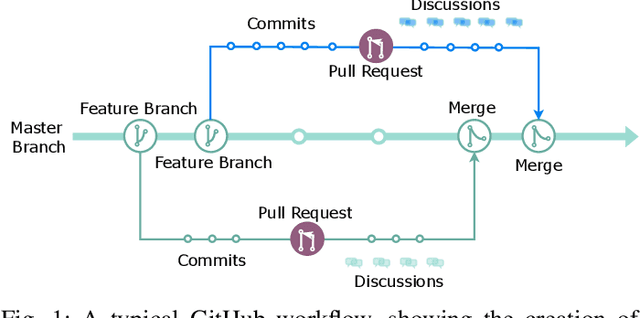
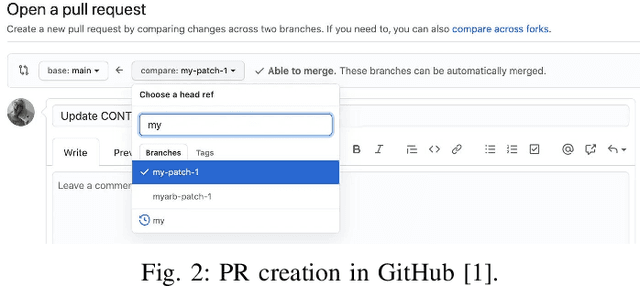
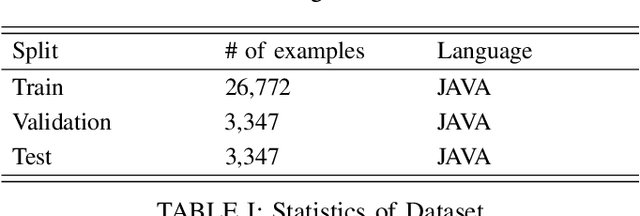
Abstract:Developers create pull request (PR) descriptions to provide an overview of their changes and explain the motivations behind them. These descriptions help reviewers and fellow developers quickly understand the updates. Despite their importance, some developers omit these descriptions. To tackle this problem, we propose an automated method for generating PR descriptions based on commit messages and source code comments. This method frames the task as a text summarization problem, for which we utilized the T5 text-to-text transfer model. We fine-tuned a pre-trained T5 model using a dataset containing 33,466 PRs. The model's effectiveness was assessed using ROUGE metrics, which are recognized for their strong alignment with human evaluations. Our findings reveal that the T5 model significantly outperforms LexRank, which served as our baseline for comparison.
GenFighter: A Generative and Evolutive Textual Attack Removal
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:Adversarial attacks pose significant challenges to deep neural networks (DNNs) such as Transformer models in natural language processing (NLP). This paper introduces a novel defense strategy, called GenFighter, which enhances adversarial robustness by learning and reasoning on the training classification distribution. GenFighter identifies potentially malicious instances deviating from the distribution, transforms them into semantically equivalent instances aligned with the training data, and employs ensemble techniques for a unified and robust response. By conducting extensive experiments, we show that GenFighter outperforms state-of-the-art defenses in accuracy under attack and attack success rate metrics. Additionally, it requires a high number of queries per attack, making the attack more challenging in real scenarios. The ablation study shows that our approach integrates transfer learning, a generative/evolutive procedure, and an ensemble method, providing an effective defense against NLP adversarial attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge