Maximilian Kohlbrenner
Towards best practice in explaining neural network decisions with LRP
Oct 22, 2019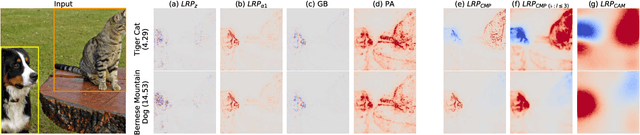

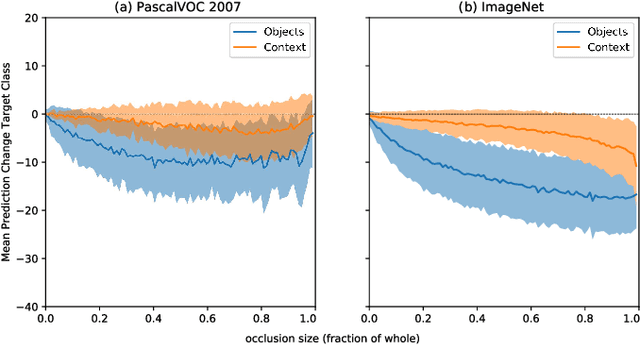
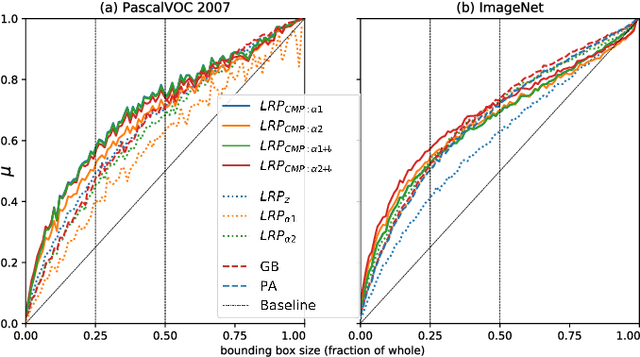
Abstract:Within the last decade, neural network based predictors have demonstrated impressive - and at times super-human - capabilities. This performance is often paid for with an intransparent prediction process and thus has sparked numerous contributions in the novel field of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). In this paper, we focus on a popular and widely used method of XAI, the Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP). Since its initial proposition LRP has evolved as a method, and a best practice for applying the method has tacitly emerged, based on humanly observed evidence. We investigate - and for the first time quantify - the effect of this current best practice on feedforward neural networks in a visual object detection setting. The results verify that the current, layer-dependent approach to LRP applied in recent literature better represents the model's reasoning, and at the same time increases the object localization and class discriminativity of LRP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge