Matthias Kohl
BACH: Grand Challenge on Breast Cancer Histology Images
Aug 13, 2018
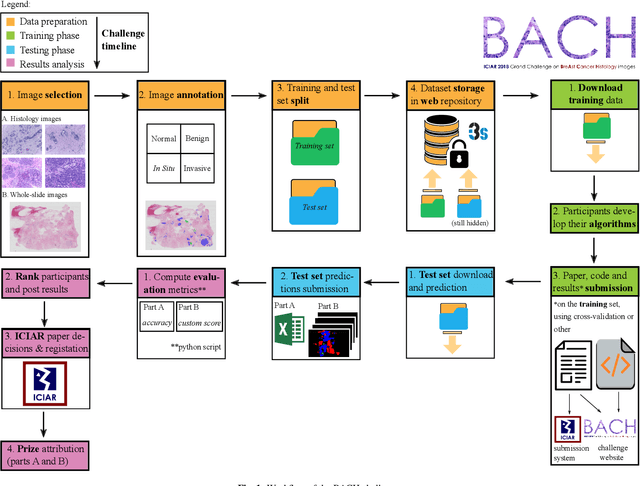
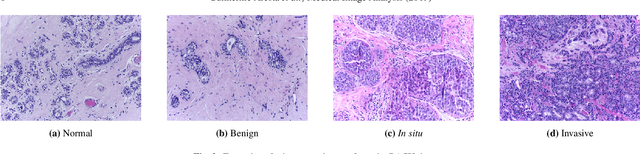
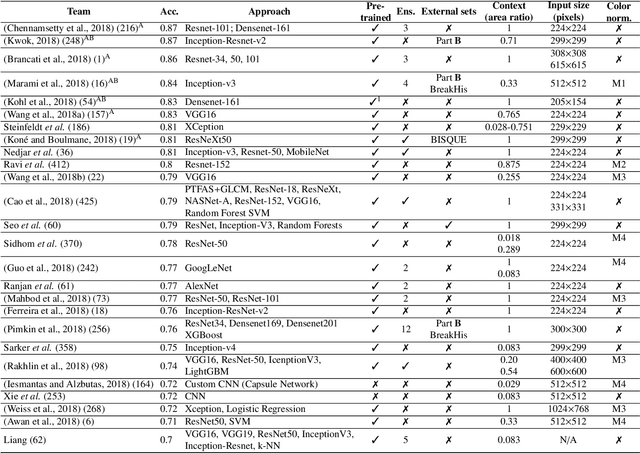
Abstract:Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women, affecting more than 10% of women worldwide. Microscopic analysis of a biopsy remains one of the most important methods to diagnose the type of breast cancer. This requires specialized analysis by pathologists, in a task that i) is highly time- and cost-consuming and ii) often leads to nonconsensual results. The relevance and potential of automatic classification algorithms using hematoxylin-eosin stained histopathological images has already been demonstrated, but the reported results are still sub-optimal for clinical use. With the goal of advancing the state-of-the-art in automatic classification, the Grand Challenge on BreAst Cancer Histology images (BACH) was organized in conjunction with the 15th International Conference on Image Analysis and Recognition (ICIAR 2018). A large annotated dataset, composed of both microscopy and whole-slide images, was specifically compiled and made publicly available for the BACH challenge. Following a positive response from the scientific community, a total of 64 submissions, out of 677 registrations, effectively entered the competition. From the submitted algorithms it was possible to push forward the state-of-the-art in terms of accuracy (87%) in automatic classification of breast cancer with histopathological images. Convolutional neuronal networks were the most successful methodology in the BACH challenge. Detailed analysis of the collective results allowed the identification of remaining challenges in the field and recommendations for future developments. The BACH dataset remains publically available as to promote further improvements to the field of automatic classification in digital pathology.
Understanding Regularization to Visualize Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 20, 2018
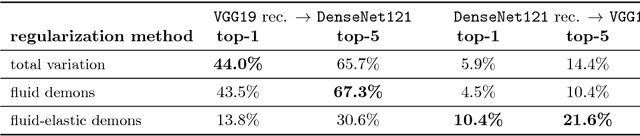

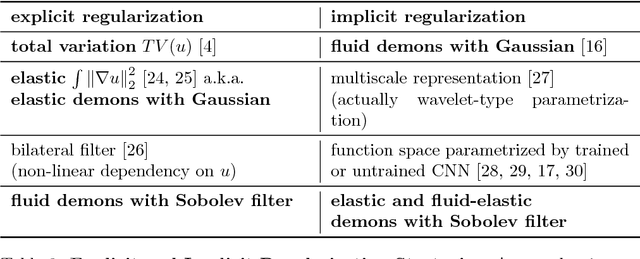
Abstract:Variational methods for revealing visual concepts learned by convolutional neural networks have gained significant attention during the last years. Being based on noisy gradients obtained via back-propagation such methods require the application of regularization strategies. We present a mathematical framework unifying previously employed regularization methods. Within this framework, we propose a novel technique based on Sobolev gradients which can be implemented via convolutions and does not require specialized numerical treatment, such as total variation regularization. The experiments performed on feature inversion and activation maximization demonstrate the benefit of a unified approach to regularization, such as sharper reconstructions via the proposed Sobolev filters and a better control over reconstructed scales.
Assessment of Breast Cancer Histology using Densely Connected Convolutional Networks
Apr 09, 2018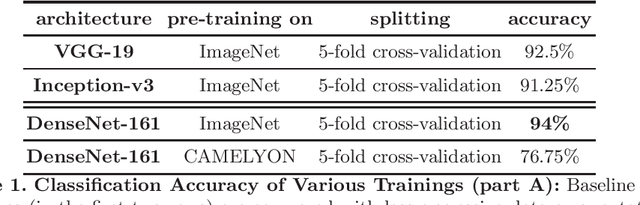
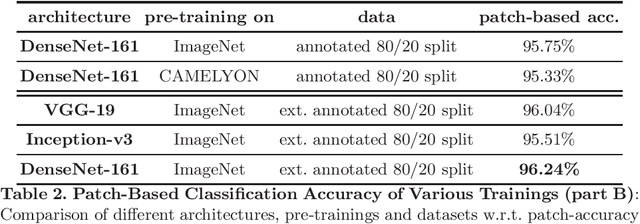
Abstract:Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and leading cause of cancer-related death among females worldwide. In this article, we investigate the applicability of densely connected convolutional neural networks to the problems of histology image classification and whole slide image segmentation in the area of computer-aided diagnoses for breast cancer. To this end, we study various approaches for transfer learning and apply them to the data set from the 2018 grand challenge on breast cancer histology images (BACH).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge