Matthias H. Hennig
Capturing cross-session neural population variability through self-supervised identification of consistent neuron ensembles
May 19, 2022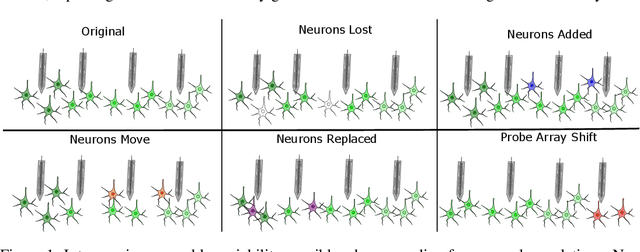
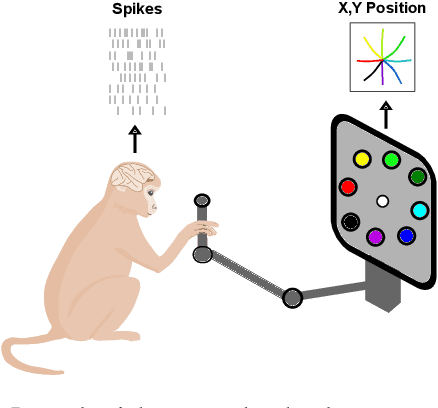

Abstract:Decoding stimuli or behaviour from recorded neural activity is a common approach to interrogate brain function in research, and an essential part of brain-computer and brain-machine interfaces. Reliable decoding even from small neural populations is possible because high dimensional neural population activity typically occupies low dimensional manifolds that are discoverable with suitable latent variable models. Over time however, drifts in activity of individual neurons and instabilities in neural recording devices can be substantial, making stable decoding over days and weeks impractical. While this drift cannot be predicted on an individual neuron level, population level variations over consecutive recording sessions such as differing sets of neurons and varying permutations of consistent neurons in recorded data may be learnable when the underlying manifold is stable over time. Classification of consistent versus unfamiliar neurons across sessions and accounting for deviations in the order of consistent recording neurons in recording datasets over sessions of recordings may then maintain decoding performance. In this work we show that self-supervised training of a deep neural network can be used to compensate for this inter-session variability. As a result, a sequential autoencoding model can maintain state-of-the-art behaviour decoding performance for completely unseen recording sessions several days into the future. Our approach only requires a single recording session for training the model, and is a step towards reliable, recalibration-free brain computer interfaces.
Building population models for large-scale neural recordings: opportunities and pitfalls
Feb 03, 2021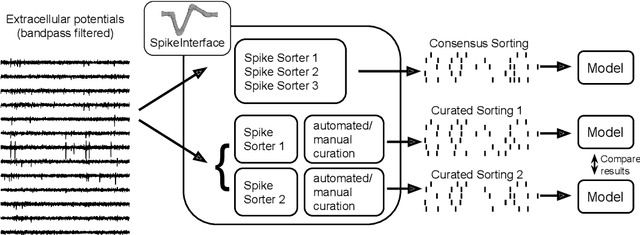
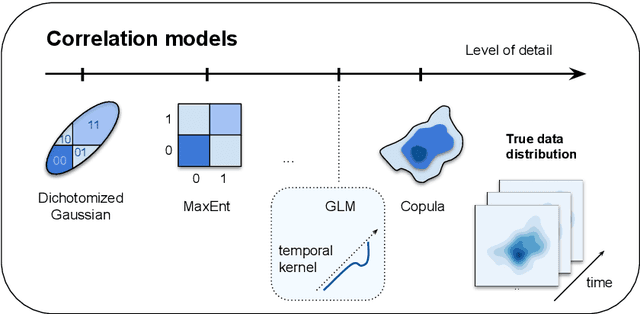
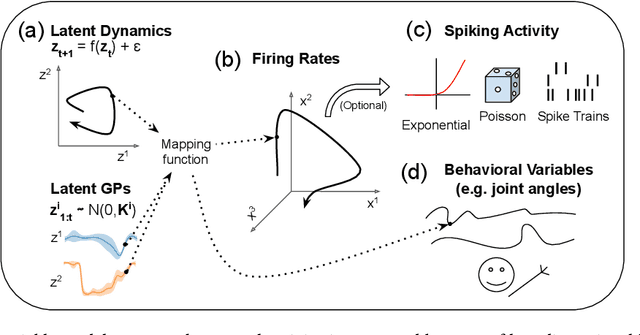
Abstract:Modern extracellular recording technologies now enable simultaneous recording from large numbers of neurons. This has driven the development of new statistical models for analyzing and interpreting neural population activity. Here we provide a broad overview of recent developments in this area. We compare and contrast different approaches, highlight strengths and limitations, and discuss biological and mechanistic insights that these methods provide. While still an area of active development, there are already a number of powerful models for interpreting large scale neural recordings even in complex experimental settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge