Mathé T. Zeegers
A tomographic workflow to enable deep learning for X-ray based foreign object detection
Jan 28, 2022
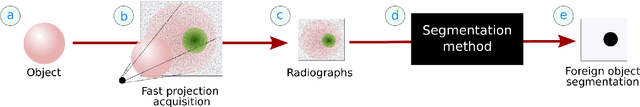
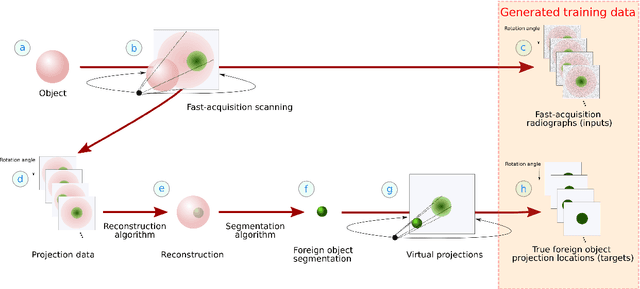
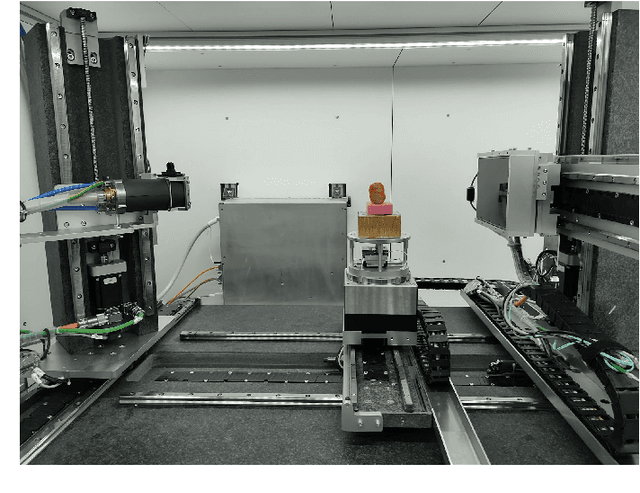
Abstract:Detection of unwanted (`foreign') objects within products is a common procedure in many branches of industry for maintaining production quality. X-ray imaging is a fast, non-invasive and widely applicable method for foreign object detection. Deep learning has recently emerged as a powerful approach for recognizing patterns in radiographs (i.e., X-ray images), enabling automated X-ray based foreign object detection. However, these methods require a large number of training examples and manual annotation of these examples is a subjective and laborious task. In this work, we propose a Computed Tomography (CT) based method for producing training data for supervised learning of foreign object detection, with minimal labour requirements. In our approach, a few representative objects are CT scanned and reconstructed in 3D. The radiographs that have been acquired as part of the CT-scan data serve as input for the machine learning method. High-quality ground truth locations of the foreign objects are obtained through accurate 3D reconstructions and segmentations. Using these segmented volumes, corresponding 2D segmentations are obtained by creating virtual projections. We outline the benefits of objectively and reproducibly generating training data in this way compared to conventional radiograph annotation. In addition, we show how the accuracy depends on the number of objects used for the CT reconstructions. The results show that in this workflow generally only a relatively small number of representative objects (i.e., fewer than 10) are needed to achieve adequate detection performance in an industrial setting. Moreover, for real experimental data we show that the workflow leads to higher foreign object detection accuracies than with standard radiograph annotation.
ADJUST: A Dictionary-Based Joint Reconstruction and Unmixing Method for Spectral Tomography
Dec 21, 2021



Abstract:Advances in multi-spectral detectors are causing a paradigm shift in X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). Spectral information acquired from these detectors can be used to extract volumetric material composition maps of the object of interest. If the materials and their spectral responses are known a priori, the image reconstruction step is rather straightforward. If they are not known, however, the maps as well as the responses need to be estimated jointly. A conventional workflow in spectral CT involves performing volume reconstruction followed by material decomposition, or vice versa. However, these methods inherently suffer from the ill-posedness of the joint reconstruction problem. To resolve this issue, we propose `A Dictionary-based Joint reconstruction and Unmixing method for Spectral Tomography' (ADJUST). Our formulation relies on forming a dictionary of spectral signatures of materials common in CT and prior knowledge of the number of materials present in an object. In particular, we decompose the spectral volume linearly in terms of spatial material maps, a spectral dictionary, and the indicator of materials for the dictionary elements. We propose a memory-efficient accelerated alternating proximal gradient method to find an approximate solution to the resulting bi-convex problem. From numerical demonstrations on several synthetic phantoms, we observe that ADJUST performs exceedingly well when compared to other state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we address the robustness of ADJUST against limited measurement patterns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge