Mateusz Grzyb
Mining United Nations General Assembly Debates
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:This project explores the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to analyse United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) speeches. Using NLP allows for the efficient processing and analysis of large volumes of textual data, enabling the extraction of semantic patterns, sentiment analysis, and topic modelling. Our goal is to deliver a comprehensive dataset and a tool (interface with descriptive statistics and automatically extracted topics) from which political scientists can derive insights into international relations and have the opportunity to have a nuanced understanding of global diplomatic discourse.
Consolidated learning -- a domain-specific model-free optimization strategy with examples for XGBoost and MIMIC-IV
Jan 27, 2022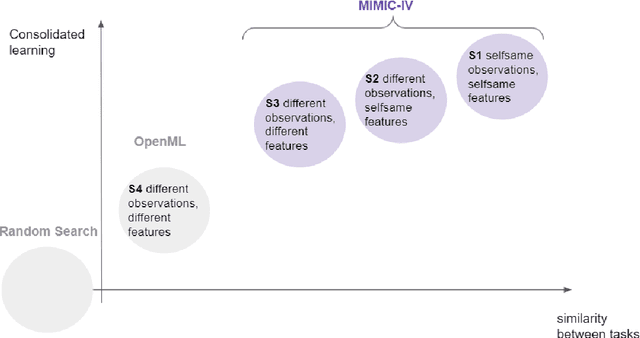
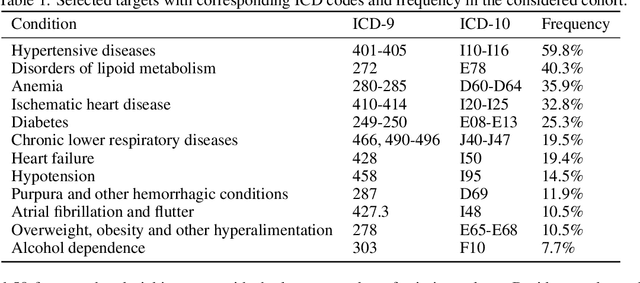
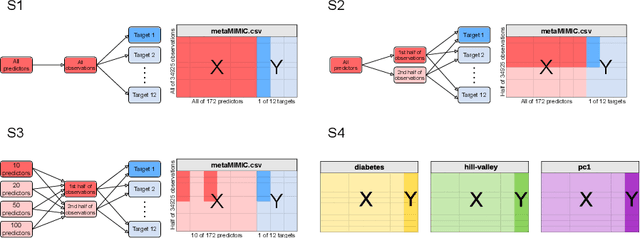
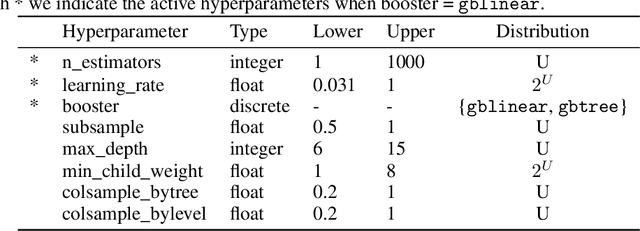
Abstract:For many machine learning models, a choice of hyperparameters is a crucial step towards achieving high performance. Prevalent meta-learning approaches focus on obtaining good hyperparameters configurations with a limited computational budget for a completely new task based on the results obtained from the prior tasks. This paper proposes a new formulation of the tuning problem, called consolidated learning, more suited to practical challenges faced by model developers, in which a large number of predictive models are created on similar data sets. In such settings, we are interested in the total optimization time rather than tuning for a single task. We show that a carefully selected static portfolio of hyperparameters yields good results for anytime optimization, maintaining ease of use and implementation. Moreover, we point out how to construct such a portfolio for specific domains. The improvement in the optimization is possible due to more efficient transfer of hyperparameter configurations between similar tasks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach through an empirical study for XGBoost algorithm and the collection of predictive tasks extracted from the MIMIC-IV medical database; however, consolidated learning is applicable in many others fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge