Masoud Ataei
Modeling Regime Structure and Informational Drivers of Stock Market Volatility via the Financial Chaos Index
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the structural dynamics of stock market volatility through the Financial Chaos Index, a tensor- and eigenvalue-based measure designed to capture realized volatility via mutual fluctuations among asset prices. Motivated by empirical evidence of regime-dependent volatility behavior and perceptual time dilation during financial crises, we develop a regime-switching framework based on the Modified Lognormal Power-Law distribution. Analysis of the FCIX from January 1990 to December 2023 identifies three distinct market regimes, low-chaos, intermediate-chaos, and high-chaos, each characterized by differing levels of systemic stress, statistical dispersion and persistence characteristics. Building upon the segmented regime structure, we further examine the informational forces that shape forward-looking market expectations. Using sentiment-based predictors derived from the Equity Market Volatility tracker, we employ an elastic net regression model to forecast implied volatility, as proxied by the VIX index. Our findings indicate that shifts in macroeconomic, financial, policy, and geopolitical uncertainty exhibit strong predictive power for volatility dynamics across regimes. Together, these results offer a unified empirical perspective on how systemic uncertainty governs both the realized evolution of financial markets and the anticipatory behavior embedded in implied volatility measures.
Generalized Derangetropy Functionals for Modeling Cyclical Information Flow
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a framework for modeling cyclical and feedback-driven information flow through a generalized family of entropy-modulated transformations called derangetropy functionals. Unlike scalar and static entropy measures such as Shannon entropy, these functionals act directly on probability densities and provide a topographical representation of information structure across the support of the distribution. The framework captures periodic and self-referential aspects of information distribution and encodes them through functional operators governed by nonlinear differential equations. When applied recursively, these operators induce a spectral diffusion process governed by the heat equation, leading to convergence toward a Gaussian characteristic function. This convergence theorem provides a unified analytical foundation for describing the long-term dynamics of information under cyclic modulation. The proposed framework offers new tools for analyzing the temporal evolution of information in systems characterized by periodic structure, stochastic feedback, and delayed interaction, with applications in artificial neural networks, communication theory, and non-equilibrium statistical mechanics.
Mathematical Programming Models for Exact and Interpretable Formulation of Neural Networks
Apr 19, 2025

Abstract:This paper presents a unified mixed-integer programming framework for training sparse and interpretable neural networks. We develop exact formulations for both fully connected and convolutional architectures by modeling nonlinearities such as ReLU activations through binary variables and encoding structural sparsity via filter- and layer-level pruning constraints. The resulting models integrate parameter learning, architecture selection, and structural regularization within a single optimization problem, yielding globally optimal solutions with respect to a composite objective that balances prediction accuracy, weight sparsity, and architectural compactness. The mixed-integer programming formulation accommodates piecewise-linear operations, including max pooling and activation gating, and permits precise enforcement of logic-based or domain-specific constraints. By incorporating considerations of interpretability, sparsity, and verifiability directly into the training process, the proposed framework bridges a range of research areas including explainable artificial intelligence, symbolic reasoning, and formal verification.
Efficient and Interpretable Neural Networks Using Complex Lehmer Transform
Jan 25, 2025
Abstract:We propose an efficient and interpretable neural network with a novel activation function called the weighted Lehmer transform. This new activation function enables adaptive feature selection and extends to the complex domain, capturing phase-sensitive and hierarchical relationships within data. Notably, it provides greater interpretability and transparency compared to existing machine learning models, facilitating a deeper understanding of its functionality and decision-making processes. We analyze the mathematical properties of both real-valued and complex-valued Lehmer activation units and demonstrate their applications in modeling nonlinear interactions. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our proposed neural network achieves competitive accuracy on benchmark datasets with significantly improved computational efficiency. A single layer of real-valued or complex-valued Lehmer activation units is shown to deliver state-of-the-art performance, balancing efficiency with interpretability.
DAREK -- Distance Aware Error for Kolmogorov Networks
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we provide distance-aware error bounds for Kolmogorov Arnold Networks (KANs). We call our new error bounds estimator DAREK -- Distance Aware Error for Kolmogorov networks. Z. Liu et al. provide error bounds, which may be loose, lack distance-awareness, and are defined only up to an unknown constant of proportionality. We review the error bounds for Newton's polynomial, which is then generalized to an arbitrary spline, under Lipschitz continuity assumptions. We then extend these bounds to nested compositions of splines, arriving at error bounds for KANs. We evaluate our method by estimating an object's shape from sparse laser scan points. We use KAN to fit a smooth function to the scans and provide error bounds for the fit. We find that our method is faster than Monte Carlo approaches, and that our error bounds enclose the true obstacle shape reliably.
Omobot: a low-cost mobile robot for autonomous search and fall detection
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Detecting falls among the elderly and alerting their community responders can save countless lives. We design and develop a low-cost mobile robot that periodically searches the house for the person being monitored and sends an email to a set of designated responders if a fall is detected. In this project, we make three novel design decisions and contributions. First, our custom-designed low-cost robot has advanced features like omnidirectional wheels, the ability to run deep learning models, and autonomous wireless charging. Second, we improve the accuracy of fall detection for the YOLOv8-Pose-nano object detection network by 6% and YOLOv8-Pose-large by 12%. We do so by transforming the images captured from the robot viewpoint (camera height 0.15m from the ground) to a typical human viewpoint (1.5m above the ground) using a principally computed Homography matrix. This improves network accuracy because the training dataset MS-COCO on which YOLOv8-Pose is trained is captured from a human-height viewpoint. Lastly, we improve the robot controller by learning a model that predicts the robot velocity from the input signal to the motor controller.
DADEE: Well-calibrated uncertainty quantification in neural networks for barriers-based robot safety
Jun 30, 2024Abstract:Uncertainty-aware controllers that guarantee safety are critical for safety critical applications. Among such controllers, Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) based approaches are popular because they are fast, yet safe. However, most such works depend on Gaussian Processes (GPs) or MC-Dropout for learning and uncertainty estimation, and both approaches come with drawbacks: GPs are non-parametric methods that are slow, while MC-Dropout does not capture aleatoric uncertainty. On the other hand, modern Bayesian learning algorithms have shown promise in uncertainty quantification. The application of modern Bayesian learning methods to CBF-based controllers has not yet been studied. We aim to fill this gap by surveying uncertainty quantification algorithms and evaluating them on CBF-based safe controllers. We find that model variance-based algorithms (for example, Deep ensembles, MC-dropout, etc.) and direct estimation-based algorithms (such as DEUP) have complementary strengths. Algorithms in the former category can only estimate uncertainty accurately out-of-domain, while those in the latter category can only do so in-domain. We combine the two approaches to obtain more accurate uncertainty estimates both in- and out-of-domain. As measured by the failure rate of a simulated robot, this results in a safer CBF-based robot controller.
Lehmer Transform and its Theoretical Properties
May 13, 2018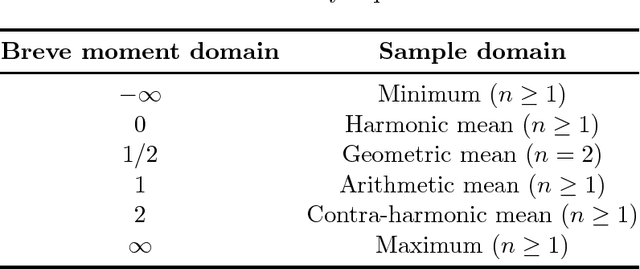
Abstract:We propose a new class of transforms that we call {\it Lehmer Transform} which is motivated by the {\it Lehmer mean function}. The proposed {\it Lehmer transform} decomposes a function of a sample into their constituting statistical moments. Theoretical properties of the proposed transform are presented. This transform could be very useful to provide an alternative method in analyzing non-stationary signals such as brain wave EEG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge