Masaya Tsunokake
Is Micro Domain-Adaptive Pre-Training Effective for Real-World Operations? Multi-Step Evaluation Reveals Potential and Bottlenecks
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:When applying LLMs to real-world enterprise operations, LLMs need to handle proprietary knowledge in small domains of specific operations ($\textbf{micro domains}$). A previous study shows micro domain-adaptive pre-training ($\textbf{mDAPT}$) with fewer documents is effective, similarly to DAPT in larger domains. However, it evaluates mDAPT only on multiple-choice questions; thus, its effectiveness for generative tasks in real-world operations remains unknown. We aim to reveal the potential and bottlenecks of mDAPT for generative tasks. To this end, we disentangle the answering process into three subtasks and evaluate the performance of each subtask: (1) $\textbf{eliciting}$ facts relevant to questions from an LLM's own knowledge, (2) $\textbf{reasoning}$ over the facts to obtain conclusions, and (3) $\textbf{composing}$ long-form answers based on the conclusions. We verified mDAPT on proprietary IT product knowledge for real-world questions in IT technical support operations. As a result, mDAPT resolved the elicitation task that the base model struggled with but did not resolve other subtasks. This clarifies mDAPT's effectiveness in the knowledge aspect and its bottlenecks in other aspects. Further analysis empirically shows that resolving the elicitation and reasoning tasks ensures sufficient performance (over 90%), emphasizing the need to enhance reasoning capability.
Agent Fine-tuning through Distillation for Domain-specific LLMs in Microdomains
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Agentic large language models (LLMs) have become prominent for autonomously interacting with external environments and performing multi-step reasoning tasks. Most approaches leverage these capabilities via in-context learning with few-shot prompts, but this often results in lengthy inputs and higher computational costs. Agent fine-tuning offers an alternative by enabling LLMs to internalize procedural reasoning and domain-specific knowledge through training on relevant data and demonstration trajectories. While prior studies have focused on general domains, their effectiveness in specialized technical microdomains remains unclear. This paper explores agent fine-tuning for domain adaptation within Hitachi's JP1 middleware, a microdomain for specialized IT operations. We fine-tuned LLMs using JP1-specific datasets derived from domain manuals and distilled reasoning trajectories generated by LLMs themselves, enhancing decision making accuracy and search efficiency. During inference, we used an agentic prompt with retrieval-augmented generation and introduced a context-answer extractor to improve information relevance. On JP1 certification exam questions, our method achieved a 14% performance improvement over the base model, demonstrating the potential of agent fine-tuning for domain-specific reasoning in complex microdomains.
GFlowNet Fine-tuning for Diverse Correct Solutions in Mathematical Reasoning Tasks
Oct 26, 2024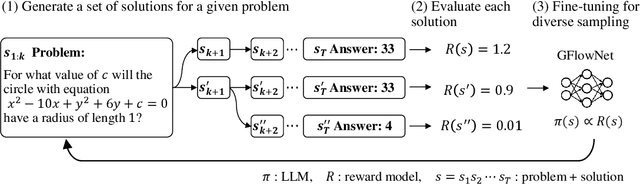
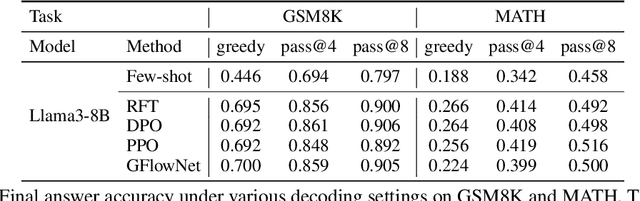
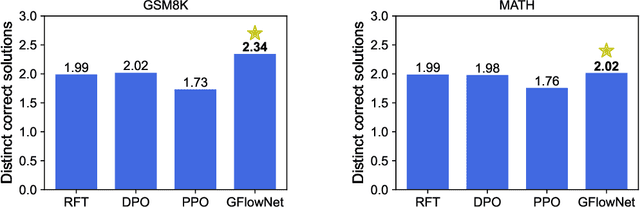
Abstract:Mathematical reasoning problems are among the most challenging, as they typically require an understanding of fundamental laws to solve. The laws are universal, but the derivation of the final answer changes depending on how a problem is approached. When training large language models (LLMs), learning the capability of generating such multiple solutions is essential to accelerate their use in mathematical education. To this end, we train LLMs using generative flow network (GFlowNet). Different from reward-maximizing reinforcement learning (RL), GFlowNet fine-tuning seeks to find diverse solutions by training the LLM whose distribution is proportional to a reward function. In numerical experiments, we evaluate GFlowNet fine-tuning and reward-maximizing RL in terms of accuracy and diversity. The results show that GFlowNet fine-tuning derives correct final answers from diverse intermediate reasoning steps, indicating the improvement of the capability of alternative solution generation.
Team Hitachi at SemEval-2023 Task 3: Exploring Cross-lingual Multi-task Strategies for Genre and Framing Detection in Online News
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:This paper explains the participation of team Hitachi to SemEval-2023 Task 3 "Detecting the genre, the framing, and the persuasion techniques in online news in a multi-lingual setup." Based on the multilingual, multi-task nature of the task and the setting that training data is limited, we investigated different strategies for training the pretrained language models under low resource settings. Through extensive experiments, we found that (a) cross-lingual/multi-task training, and (b) collecting an external balanced dataset, can benefit the genre and framing detection. We constructed ensemble models from the results and achieved the highest macro-averaged F1 scores in Italian and Russian genre categorization subtasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge