Martin d'Hoffschmidt
On the importance of pre-training data volume for compact language models
Oct 09, 2020


Abstract:Recent advances in language modeling have led to computationally intensive and resource-demanding state-of-the-art models. In an effort towards sustainable practices, we study the impact of pre-training data volume on compact language models. Multiple BERT-based models are trained on gradually increasing amounts of French text. Through fine-tuning on the French Question Answering Dataset (FQuAD), we observe that well-performing models are obtained with as little as 100 MB of text. In addition, we show that past critically low amounts of pre-training data, an intermediate pre-training step on the task-specific corpus does not yield substantial improvements.
FQuAD: French Question Answering Dataset
Feb 14, 2020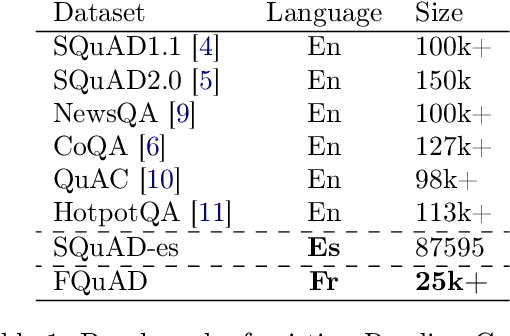
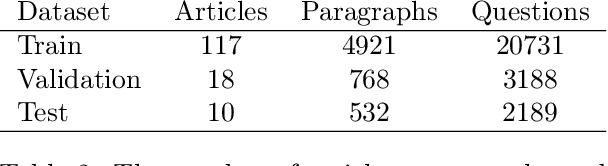

Abstract:Recent advances in the field of language modeling have improved state-of-the-art results on many Natural Language Processing tasks. Among them, the Machine Reading Comprehension task has made significant progress. However, most of the results are reported in English since labeled resources available in other languages, such as French, remain scarce. In the present work, we introduce the French Question Answering Dataset (FQuAD). FQuAD is French Native Reading Comprehension dataset that consists of 25,000+ questions on a set of Wikipedia articles. A baseline model is trained which achieves an F1 score of 88.0% and an exact match ratio of 77.9% on the test set. The dataset is made freely available at https://fquad.illuin.tech.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge