Mark S. Krass
Pile of Law: Learning Responsible Data Filtering from the Law and a 256GB Open-Source Legal Dataset
Jul 01, 2022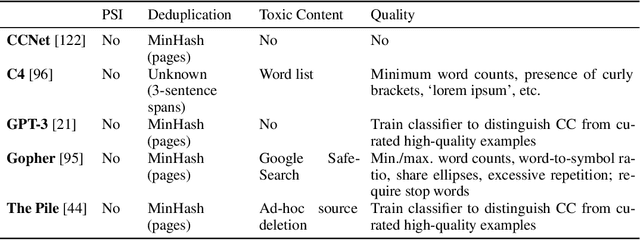
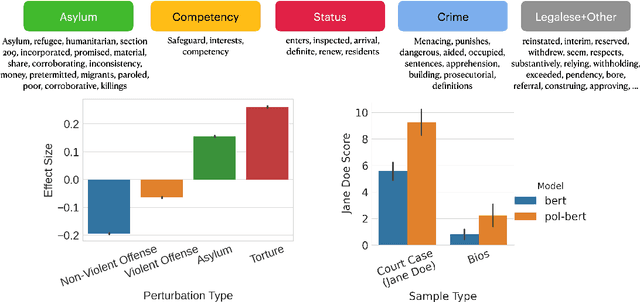
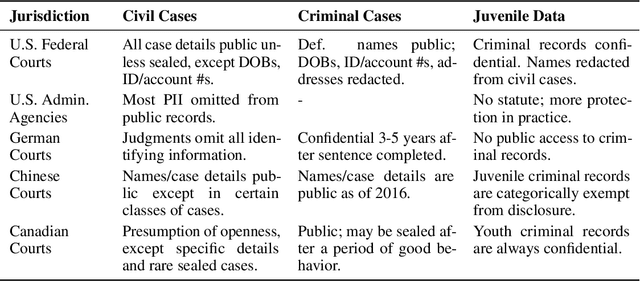
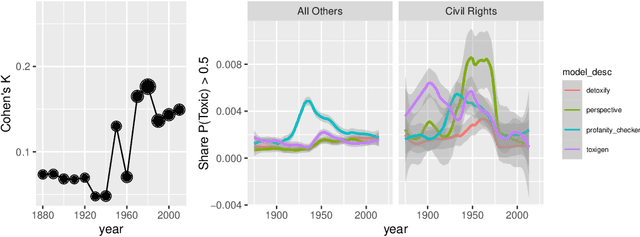
Abstract:One concern with the rise of large language models lies with their potential for significant harm, particularly from pretraining on biased, obscene, copyrighted, and private information. Emerging ethical approaches have attempted to filter pretraining material, but such approaches have been ad hoc and failed to take into account context. We offer an approach to filtering grounded in law, which has directly addressed the tradeoffs in filtering material. First, we gather and make available the Pile of Law, a 256GB (and growing) dataset of open-source English-language legal and administrative data, covering court opinions, contracts, administrative rules, and legislative records. Pretraining on the Pile of Law may potentially help with legal tasks that have the promise to improve access to justice. Second, we distill the legal norms that governments have developed to constrain the inclusion of toxic or private content into actionable lessons for researchers and discuss how our dataset reflects these norms. Third, we show how the Pile of Law offers researchers the opportunity to learn such filtering rules directly from the data, providing an exciting new research direction in model-based processing.
Context-Aware Legal Citation Recommendation using Deep Learning
Jun 20, 2021
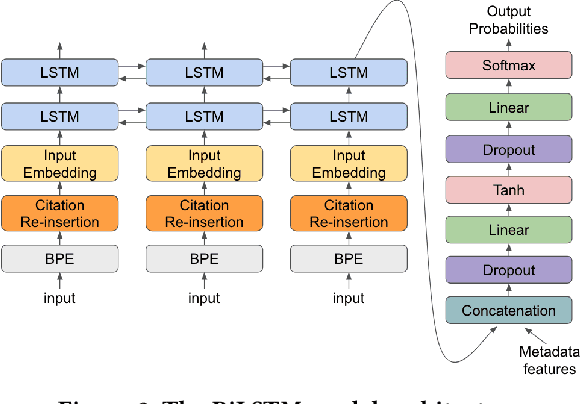

Abstract:Lawyers and judges spend a large amount of time researching the proper legal authority to cite while drafting decisions. In this paper, we develop a citation recommendation tool that can help improve efficiency in the process of opinion drafting. We train four types of machine learning models, including a citation-list based method (collaborative filtering) and three context-based methods (text similarity, BiLSTM and RoBERTa classifiers). Our experiments show that leveraging local textual context improves recommendation, and that deep neural models achieve decent performance. We show that non-deep text-based methods benefit from access to structured case metadata, but deep models only benefit from such access when predicting from context of insufficient length. We also find that, even after extensive training, RoBERTa does not outperform a recurrent neural model, despite its benefits of pretraining. Our behavior analysis of the RoBERTa model further shows that predictive performance is stable across time and citation classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge