Mark Eramian
TGraphX: Tensor-Aware Graph Neural Network for Multi-Dimensional Feature Learning
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:TGraphX presents a novel paradigm in deep learning by unifying convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with graph neural networks (GNNs) to enhance visual reasoning tasks. Traditional CNNs excel at extracting rich spatial features from images but lack the inherent capability to model inter-object relationships. Conversely, conventional GNNs typically rely on flattened node features, thereby discarding vital spatial details. TGraphX overcomes these limitations by employing CNNs to generate multi-dimensional node features (e.g., (3*128*128) tensors) that preserve local spatial semantics. These spatially aware nodes participate in a graph where message passing is performed using 1*1 convolutions, which fuse adjacent features while maintaining their structure. Furthermore, a deep CNN aggregator with residual connections is used to robustly refine the fused messages, ensuring stable gradient flow and end-to-end trainability. Our approach not only bridges the gap between spatial feature extraction and relational reasoning but also demonstrates significant improvements in object detection refinement and ensemble reasoning.
A Novel Technique Combining Image Processing, Plant Development Properties, and the Hungarian Algorithm, to Improve Leaf Detection in Maize
May 18, 2020
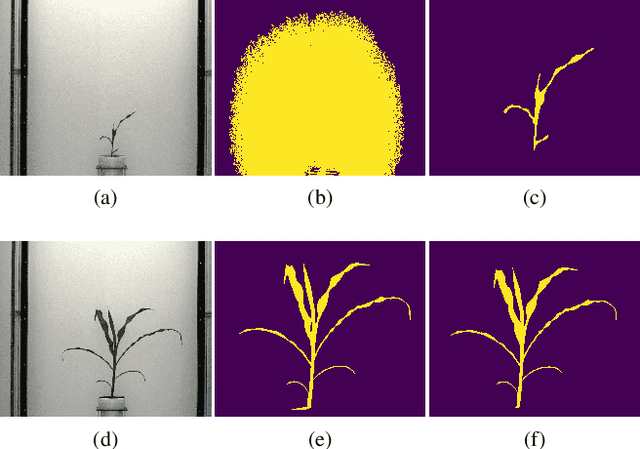
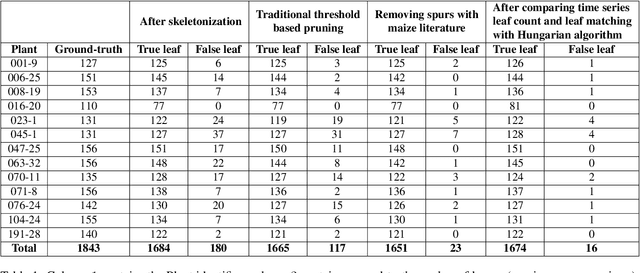

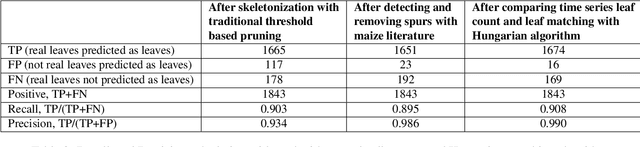
Abstract:Manual determination of plant phenotypic properties such as plant architecture, growth, and health is very time consuming and sometimes destructive. Automatic image analysis has become a popular approach. This research aims to identify the position (and number) of leaves from a temporal sequence of high-quality indoor images consisting of multiple views, focussing in particular of images of maize. The procedure used a segmentation on the images, using the convex hull to pick the best view at each time step, followed by a skeletonization of the corresponding image. To remove skeleton spurs, a discrete skeleton evolution pruning process was applied. Pre-existing statistics regarding maize development was incorporated to help differentiate between true leaves and false leaves. Furthermore, for each time step, leaves were matched to those of the previous and next three days using the graph-theoretic Hungarian algorithm. This matching algorithm can be used to both remove false positives, and also to predict true leaves, even if they were completely occluded from the image itself. The algorithm was evaluated using an open dataset consisting of 13 maize plants across 27 days from two different views. The total number of true leaves from the dataset was 1843, and our proposed techniques detect a total of 1690 leaves including 1674 true leaves, and only 16 false leaves, giving a recall of 90.8%, and a precision of 99.0%.
Crop Lodging Prediction from UAV-Acquired Images of Wheat and Canola using a DCNN Augmented with Handcrafted Texture Features
Jun 18, 2019
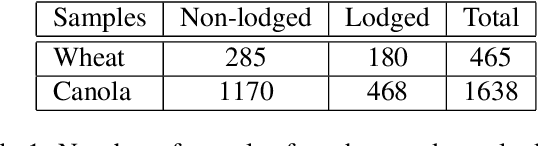
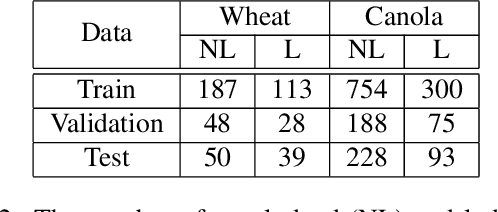

Abstract:Lodging, the permanent bending over of food crops, leads to poor plant growth and development. Consequently, lodging results in reduced crop quality, lowers crop yield, and makes harvesting difficult. Plant breeders routinely evaluate several thousand breeding lines, and therefore, automatic lodging detection and prediction is of great value aid in selection. In this paper, we propose a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) architecture for lodging classification using five spectral channel orthomosaic images from canola and wheat breeding trials. Also, using transfer learning, we trained 10 lodging detection models using well-established deep convolutional neural network architectures. Our proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art lodging detection methods in the literature that use only handcrafted features. In comparison to 10 DCNN lodging detection models, our proposed model achieves comparable results while having a substantially lower number of parameters. This makes the proposed model suitable for applications such as real-time classification using inexpensive hardware for high-throughput phenotyping pipelines. The GitHub repository at https://github.com/FarhadMaleki/LodgedNet contains code and models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge