Marek Rosa
Beyond Prompts: Dynamic Conversational Benchmarking of Large Language Models
Sep 30, 2024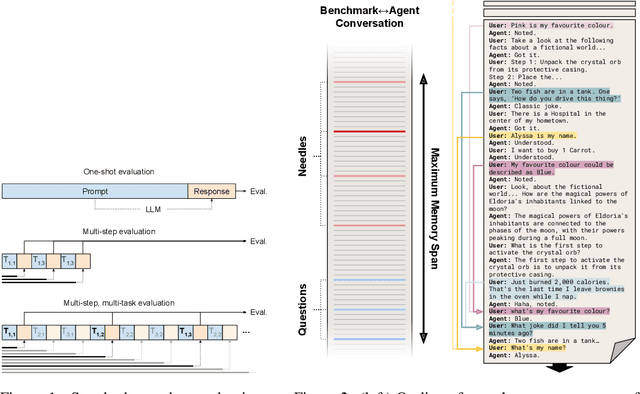
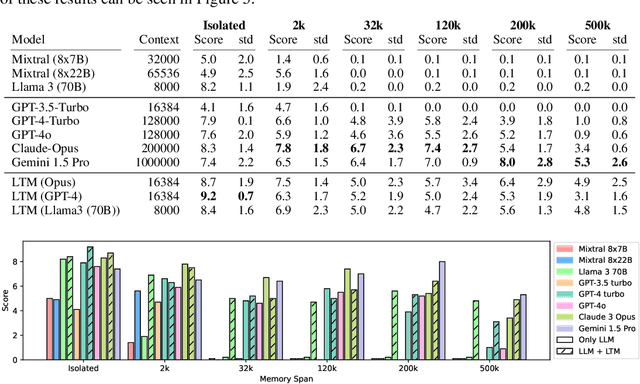


Abstract:We introduce a dynamic benchmarking system for conversational agents that evaluates their performance through a single, simulated, and lengthy user$\leftrightarrow$agent interaction. The interaction is a conversation between the user and agent, where multiple tasks are introduced and then undertaken concurrently. We context switch regularly to interleave the tasks, which constructs a realistic testing scenario in which we assess the Long-Term Memory, Continual Learning, and Information Integration capabilities of the agents. Results from both proprietary and open-source Large-Language Models show that LLMs in general perform well on single-task interactions, but they struggle on the same tasks when they are interleaved. Notably, short-context LLMs supplemented with an LTM system perform as well as or better than those with larger contexts. Our benchmark suggests that there are other challenges for LLMs responding to more natural interactions that contemporary benchmarks have heretofore not been able to capture.
Bootstrapping of memetic from genetic evolution via inter-agent selection pressures
Apr 07, 2021



Abstract:We create an artificial system of agents (attention-based neural networks) which selectively exchange messages with each-other in order to study the emergence of memetic evolution and how memetic evolutionary pressures interact with genetic evolution of the network weights. We observe that the ability of agents to exert selection pressures on each-other is essential for memetic evolution to bootstrap itself into a state which has both high-fidelity replication of memes, as well as continuing production of new memes over time. However, in this system there is very little interaction between this memetic 'ecology' and underlying tasks driving individual fitness - the emergent meme layer appears to be neither helpful nor harmful to agents' ability to learn to solve tasks. Sourcecode for these experiments is available at https://github.com/GoodAI/memes
BADGER: Learning to (Learn [Learning Algorithms] through Multi-Agent Communication)
Dec 03, 2019![Figure 1 for BADGER: Learning to (Learn [Learning Algorithms] through Multi-Agent Communication)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F2e8dd183207e83abdc653bc126189032d6b7ab5e%2F1-Figure1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 2 for BADGER: Learning to (Learn [Learning Algorithms] through Multi-Agent Communication)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F2e8dd183207e83abdc653bc126189032d6b7ab5e%2F1-Figure2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 3 for BADGER: Learning to (Learn [Learning Algorithms] through Multi-Agent Communication)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F2e8dd183207e83abdc653bc126189032d6b7ab5e%2F5-Figure6-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 4 for BADGER: Learning to (Learn [Learning Algorithms] through Multi-Agent Communication)](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F2e8dd183207e83abdc653bc126189032d6b7ab5e%2F5-Figure7-1.png&w=640&q=75)
Abstract:In this work, we propose a novel memory-based multi-agent meta-learning architecture and learning procedure that allows for learning of a shared communication policy that enables the emergence of rapid adaptation to new and unseen environments by learning to learn learning algorithms through communication. Behavior, adaptation and learning to adapt emerges from the interactions of homogeneous experts inside a single agent. The proposed architecture should allow for generalization beyond the level seen in existing methods, in part due to the use of a single policy shared by all experts within the agent as well as the inherent modularity of 'Badger'.
ToyArchitecture: Unsupervised Learning of Interpretable Models of the World
Apr 12, 2019



Abstract:Research in Artificial Intelligence (AI) has focused mostly on two extremes: either on small improvements in narrow AI domains, or on universal theoretical frameworks which are usually uncomputable, incompatible with theories of biological intelligence, or lack practical implementations. The goal of this work is to combine the main advantages of the two: to follow a big picture view, while providing a particular theory and its implementation. In contrast with purely theoretical approaches, the resulting architecture should be usable in realistic settings, but also form the core of a framework containing all the basic mechanisms, into which it should be easier to integrate additional required functionality. In this paper, we present a novel, purposely simple, and interpretable hierarchical architecture which combines multiple different mechanisms into one system: unsupervised learning of a model of the world, learning the influence of one's own actions on the world, model-based reinforcement learning, hierarchical planning and plan execution, and symbolic/sub-symbolic integration in general. The learned model is stored in the form of hierarchical representations with the following properties: 1) they are increasingly more abstract, but can retain details when needed, and 2) they are easy to manipulate in their local and symbolic-like form, thus also allowing one to observe the learning process at each level of abstraction. On all levels of the system, the representation of the data can be interpreted in both a symbolic and a sub-symbolic manner. This enables the architecture to learn efficiently using sub-symbolic methods and to employ symbolic inference.
A Framework for Searching for General Artificial Intelligence
Nov 02, 2016



Abstract:There is a significant lack of unified approaches to building generally intelligent machines. The majority of current artificial intelligence research operates within a very narrow field of focus, frequently without considering the importance of the 'big picture'. In this document, we seek to describe and unify principles that guide the basis of our development of general artificial intelligence. These principles revolve around the idea that intelligence is a tool for searching for general solutions to problems. We define intelligence as the ability to acquire skills that narrow this search, diversify it and help steer it to more promising areas. We also provide suggestions for studying, measuring, and testing the various skills and abilities that a human-level intelligent machine needs to acquire. The document aims to be both implementation agnostic, and to provide an analytic, systematic, and scalable way to generate hypotheses that we believe are needed to meet the necessary conditions in the search for general artificial intelligence. We believe that such a framework is an important stepping stone for bringing together definitions, highlighting open problems, connecting researchers willing to collaborate, and for unifying the arguably most significant search of this century.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge