Marek Kurdej
HEUDIASYC
Enhancing Mobile Object Classification Using Geo-referenced Maps and Evidential Grids
Jan 22, 2014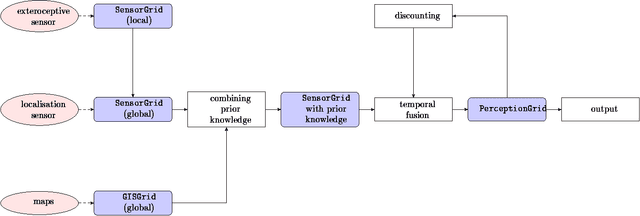
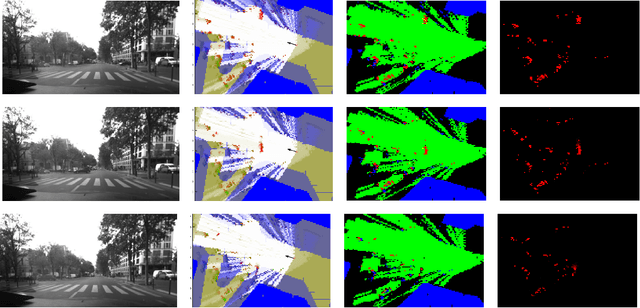
Abstract:Evidential grids have recently shown interesting properties for mobile object perception. Evidential grids are a generalisation of Bayesian occupancy grids using Dempster- Shafer theory. In particular, these grids can handle efficiently partial information. The novelty of this article is to propose a perception scheme enhanced by geo-referenced maps used as an additional source of information, which is fused with a sensor grid. The paper presents the key stages of such a data fusion process. An adaptation of conjunctive combination rule is presented to refine the analysis of the conflicting information. The method uses temporal accumulation to make the distinction between stationary and mobile objects, and applies contextual discounting for modelling information obsolescence. As a result, the method is able to better characterise the occupied cells by differentiating, for instance, moving objects, parked cars, urban infrastructure and buildings. Experiments carried out on real- world data illustrate the benefits of such an approach.
* 6 pp. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1207.1016
Conservative, Proportional and Optimistic Contextual Discounting in the Belief Functions Theory
Dec 19, 2013
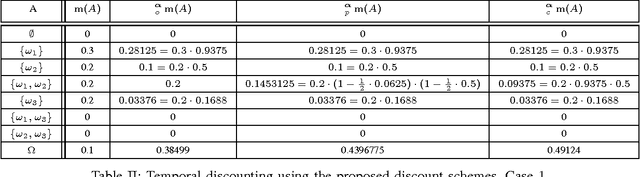
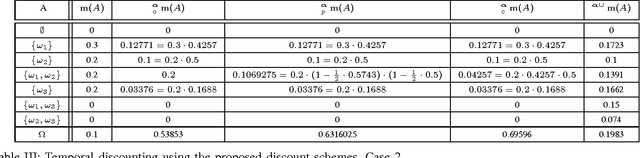
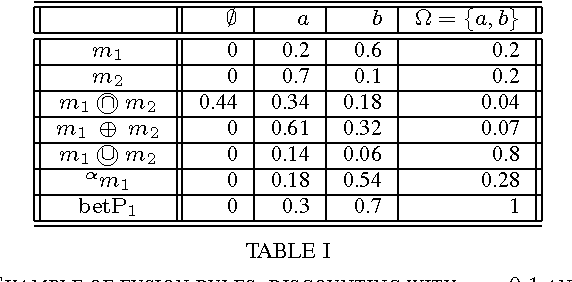
Abstract:Information discounting plays an important role in the theory of belief functions and, generally, in information fusion. Nevertheless, neither classical uniform discounting nor contextual cannot model certain use cases, notably temporal discounting. In this article, new contextual discounting schemes, conservative, proportional and optimistic, are proposed. Some properties of these discounting operations are examined. Classical discounting is shown to be a special case of these schemes. Two motivating cases are discussed: modelling of source reliability and application to temporal discounting.
* 7 pages
Map-aided Fusion Using Evidential Grids for Mobile Perception in Urban Environment
Jul 04, 2012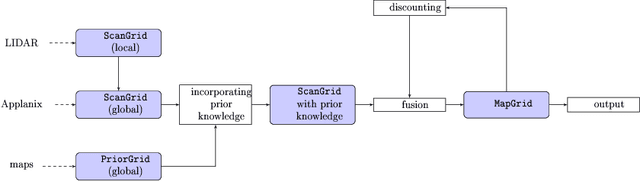
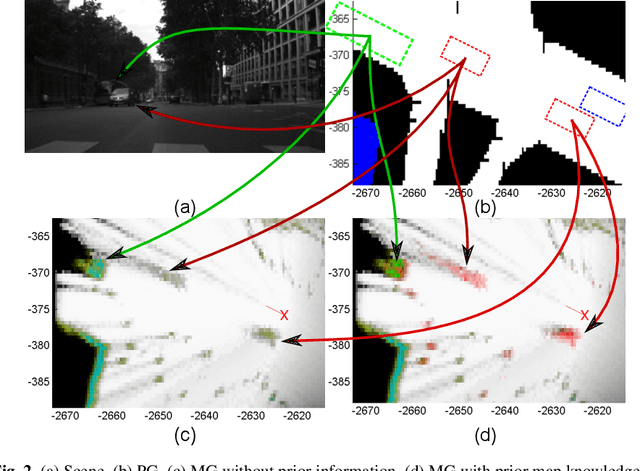

Abstract:Evidential grids have been recently used for mobile object perception. The novelty of this article is to propose a perception scheme using prior map knowledge. A geographic map is considered an additional source of information fused with a grid representing sensor data. Yager's rule is adapted to exploit the Dempster-Shafer conflict information at large. In order to distinguish stationary and mobile objects, a counter is introduced and used as a factor for mass function specialisation. Contextual discounting is used, since we assume that different pieces of information become obsolete at different rates. Tests on real-world data are also presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge