Maral Zarvani
Attention Swin U-Net: Cross-Contextual Attention Mechanism for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Oct 30, 2022Abstract:Melanoma is caused by the abnormal growth of melanocytes in human skin. Like other cancers, this life-threatening skin cancer can be treated with early diagnosis. To support a diagnosis by automatic skin lesion segmentation, several Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) approaches, specifically the U-Net architecture, have been proposed. The U-Net model with a symmetrical architecture has exhibited superior performance in the segmentation task. However, the locality restriction of the convolutional operation incorporated in the U-Net architecture limits its performance in capturing long-range dependency, which is crucial for the segmentation task in medical images. To address this limitation, recently a Transformer based U-Net architecture that replaces the CNN blocks with the Swin Transformer module has been proposed to capture both local and global representation. In this paper, we propose Att-SwinU-Net, an attention-based Swin U-Net extension, for medical image segmentation. In our design, we seek to enhance the feature re-usability of the network by carefully designing the skip connection path. We argue that the classical concatenation operation utilized in the skip connection path can be further improved by incorporating an attention mechanism. By performing a comprehensive ablation study on several skin lesion segmentation datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed attention mechanism.
SnapMode: An Intelligent and Distributed Large-Scale Fashion Image Retrieval Platform Based On Big Data and Deep Generative Adversarial Network Technologies
Apr 08, 2022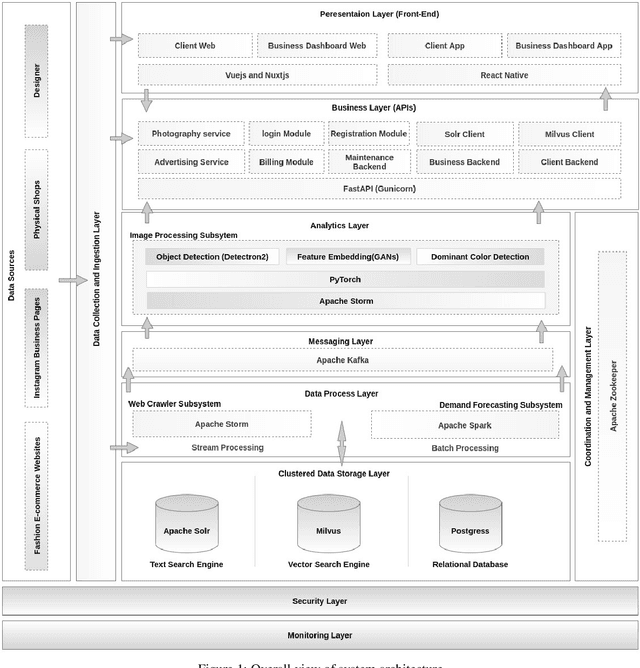
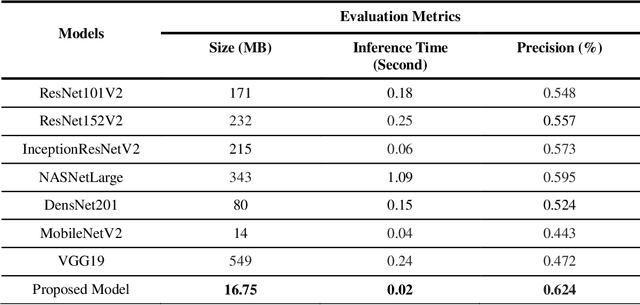
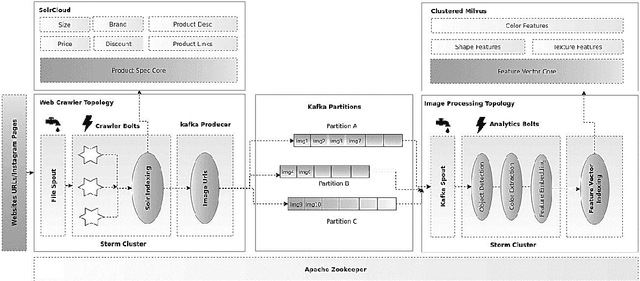
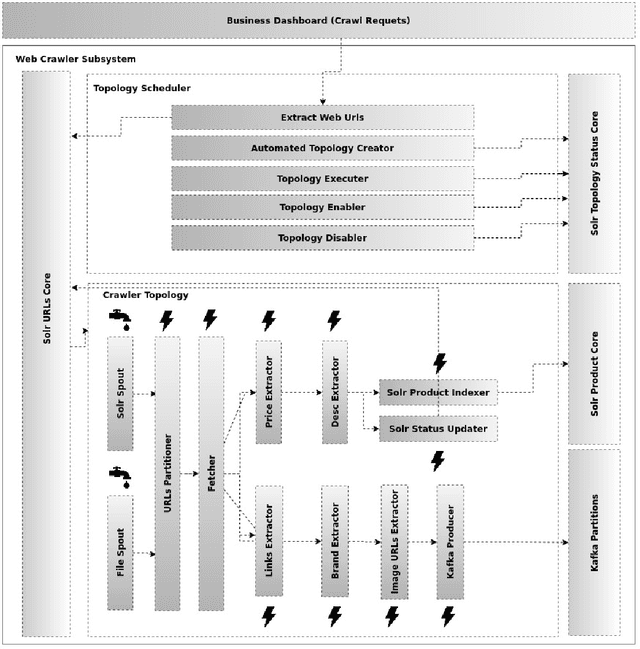
Abstract:Fashion is now among the largest industries worldwide, for it represents human history and helps tell the worlds story. As a result of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Internet has become an increasingly important source of fashion information. However, with a growing number of web pages and social data, it is nearly impossible for humans to manually catch up with the ongoing evolution and the continuously variable content in this domain. The proper management and exploitation of big data can pave the way for the substantial growth of the global economy as well as citizen satisfaction. Therefore, computer scientists have found it challenging to handle e-commerce fashion websites by using big data and machine learning technologies. This paper first proposes a scalable focused Web Crawler engine based on the distributed computing platforms to extract and process fashion data on e-commerce websites. The role of the proposed platform is then described in developing a disentangled feature extraction method by employing deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs) for content-based image indexing and retrieval. Finally, the state-of-the-art solutions are compared, and the results of the proposed approach are analyzed on a standard dataset. For the real-life implementation of the proposed solution, a Web-based application is developed on Apache Storm, Kafka, Solr, and Milvus platforms to create a fashion search engine called SnapMode.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge