Reza Azmi
PRFashion24: A Dataset for Sentiment Analysis of Fashion Products Reviews in Persian
May 28, 2024Abstract:The PRFashion24 dataset is a comprehensive Persian dataset collected from various online fashion stores, spanning from April 2020 to March 2024. With 767,272 reviews, it is the first dataset in its kind that encompasses diverse categories within the fashion industry in the Persian language. The goal of this study is to harness deep learning techniques, specifically Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and a combination of Bidirectional LSTM and Convolutional Neural Network (BiLSTM-CNN), to analyze and reveal sentiments towards online fashion shopping. The LSTM model yielded an accuracy of 81.23%, while the BiLSTM-CNN model reached 82.89%. This research aims not only to introduce a diverse dataset in the field of fashion but also to enhance the public's understanding of opinions on online fashion shopping, which predominantly reflect a positive sentiment. Upon publication, both the optimized models and the PRFashion24 dataset will be available on GitHub.
SnapMode: An Intelligent and Distributed Large-Scale Fashion Image Retrieval Platform Based On Big Data and Deep Generative Adversarial Network Technologies
Apr 08, 2022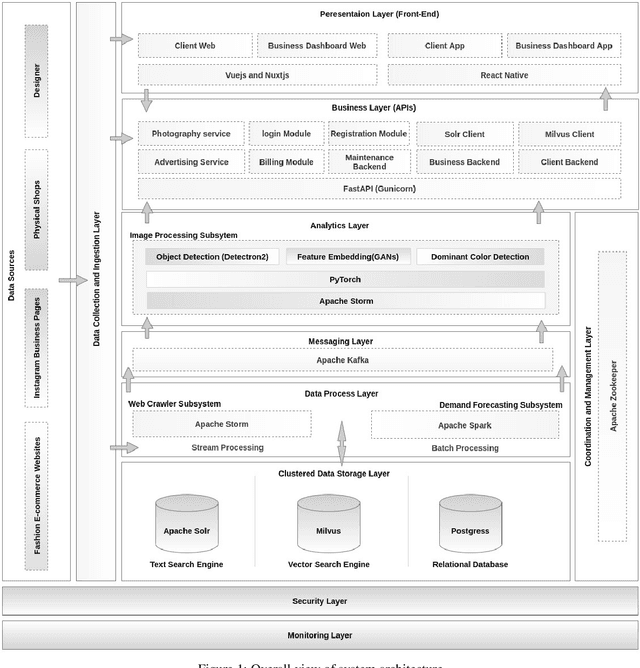
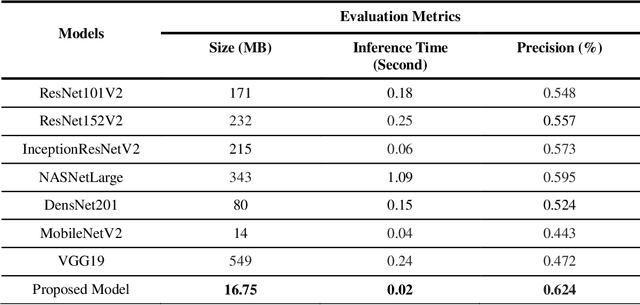
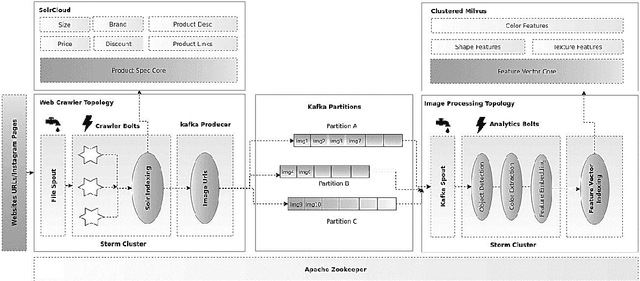
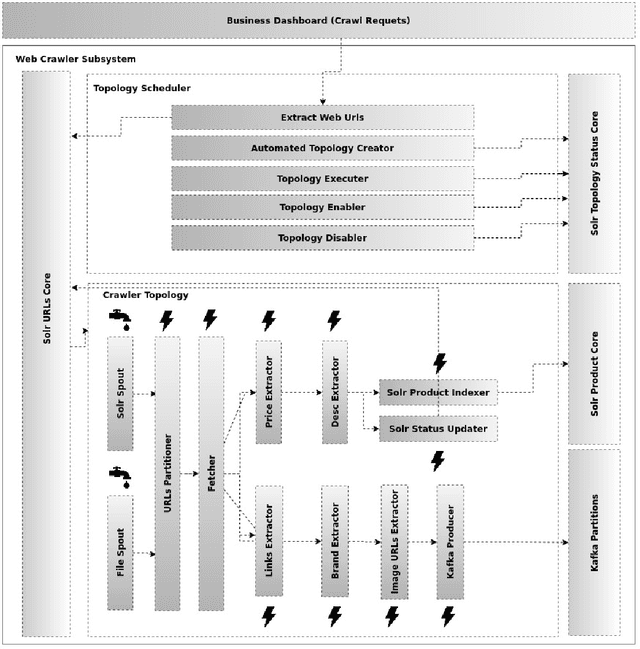
Abstract:Fashion is now among the largest industries worldwide, for it represents human history and helps tell the worlds story. As a result of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Internet has become an increasingly important source of fashion information. However, with a growing number of web pages and social data, it is nearly impossible for humans to manually catch up with the ongoing evolution and the continuously variable content in this domain. The proper management and exploitation of big data can pave the way for the substantial growth of the global economy as well as citizen satisfaction. Therefore, computer scientists have found it challenging to handle e-commerce fashion websites by using big data and machine learning technologies. This paper first proposes a scalable focused Web Crawler engine based on the distributed computing platforms to extract and process fashion data on e-commerce websites. The role of the proposed platform is then described in developing a disentangled feature extraction method by employing deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs) for content-based image indexing and retrieval. Finally, the state-of-the-art solutions are compared, and the results of the proposed approach are analyzed on a standard dataset. For the real-life implementation of the proposed solution, a Web-based application is developed on Apache Storm, Kafka, Solr, and Milvus platforms to create a fashion search engine called SnapMode.
A New Automatic Change Detection Frame-work Based on Region Growing and Weighted Local Mutual Information: Analysis of Breast Tumor Response to Chemotherapy in Serial MR Images
Oct 19, 2021



Abstract:The automatic analysis of subtle changes between longitudinal MR images is an important task as it is still a challenging issue in scope of the breast medical image processing. In this paper we propose an effective automatic change detection framework composed of two phases since previously used methods have features with low distinctive power. First, in the preprocessing phase an intensity normalization method is suggested based on Hierarchical Histogram Matching (HHM) that is more robust to noise than previous methods. To eliminate undesirable changes and extract the regions containing significant changes the proposed Extraction Region of Changes (EROC) method is applied based on intensity distribution and Hill-Climbing algorithm. Second, in the detection phase a region growing-based approach is suggested to differentiate significant changes from unreal ones. Due to using proposed Weighted Local Mutual Information (WLMI) method to extract high level features and also utilizing the principle of the local consistency of changes, the proposed approach enjoys reasonable performance. The experimental results on both simulated and real longitudinal Breast MR Images confirm the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Also, this framework outperforms the human expert in some cases which can detect many lesion evolutions that are missed by expert.
Hippocampus Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Detection using a Combination of Shape-based Features and Spherical Harmonics Representation
Dec 28, 2016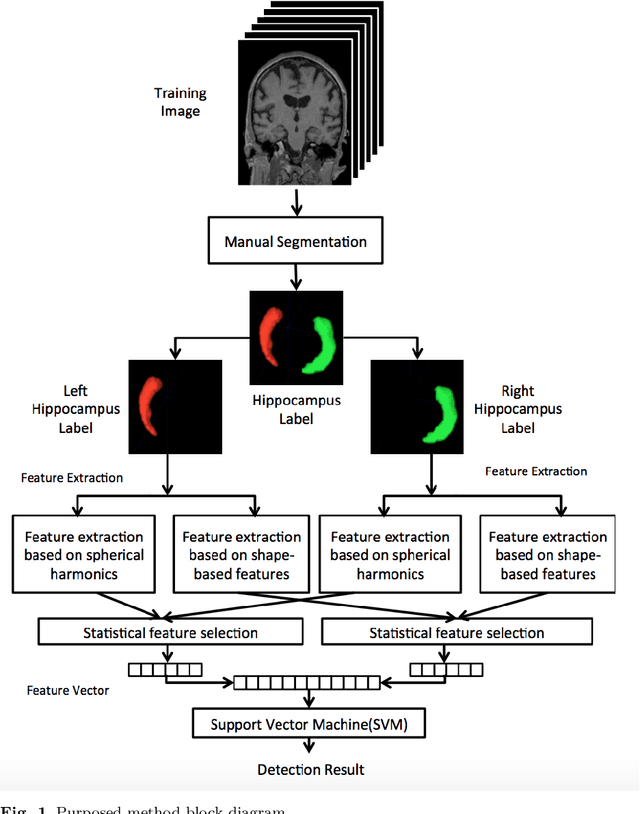
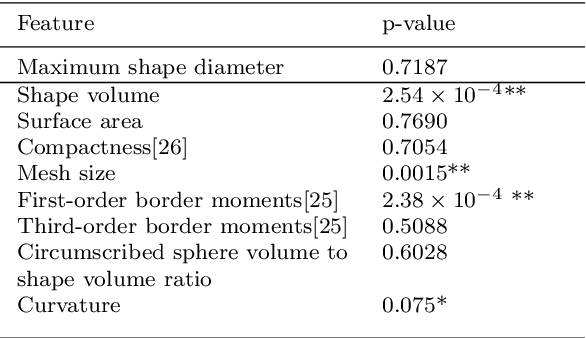
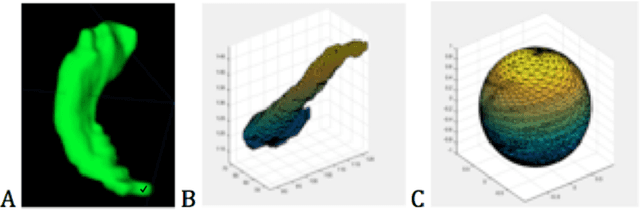
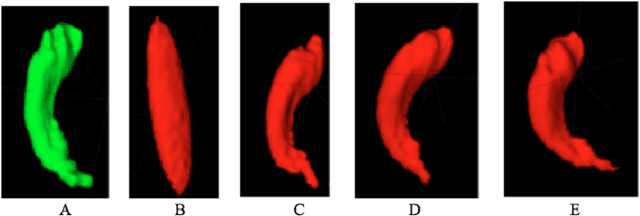
Abstract:Most of the temporal lobe epilepsy detection approaches are based on hippocampus deformation and use complicated features, resulting, detection is done with complicated features extraction and pre-processing task. In this paper, a new detection method based on shape-based features and spherical harmonics is proposed which can analysis the hippocampus shape anomaly and detection asymmetry. This method consisted of two main parts; (1) shape feature extraction, and (2) image classification. For evaluation, HFH database is used which is publicly available in this field. Nine different geometry and 256 spherical harmonic features are introduced then selected Eighteen of them that detect the asymmetry in hippocampus significantly in a randomly selected subset of the dataset. Then a support vector machine (SVM) classifier was employed to classify the remaining images of the dataset to normal and epileptic images using our selected features. On a dataset of 25 images, 12 images were used for feature extraction and the rest 13 for classification. The results show that the proposed method has accuracy, specificity and sensitivity of, respectively, 84%, 100%, and 80%. Therefore, the proposed approach shows acceptable result and is straightforward also; complicated pre-processing steps were omitted compared to other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge