Magdalena Baratsits
U-Net with spatial pyramid pooling for drusen segmentation in optical coherence tomography
Dec 11, 2019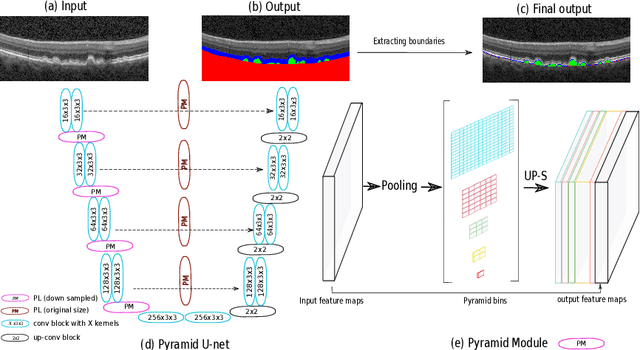

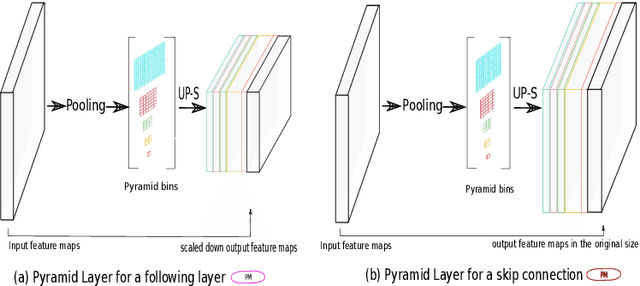
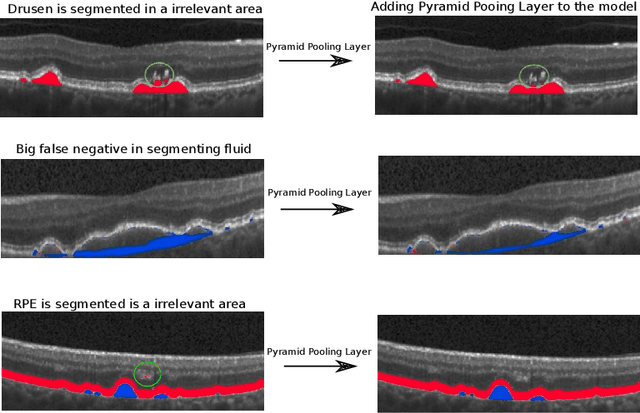
Abstract:The presence of drusen is the main hallmark of early/intermediate age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Therefore, automated drusen segmentation is an important step in image-guided management of AMD. There are two common approaches to drusen segmentation. In the first, the drusen are segmented directly as a binary classification task. In the second approach, the surrounding retinal layers (outer boundary retinal pigment epithelium (OBRPE) and Bruch's membrane (BM)) are segmented and the remaining space between these two layers is extracted as drusen. In this work, we extend the standard U-Net architecture with spatial pyramid pooling components to introduce global feature context. We apply the model to the task of segmenting drusen together with BM and OBRPE. The proposed network was trained and evaluated on a longitudinal OCT dataset of 425 scans from 38 patients with early/intermediate AMD. This preliminary study showed that the proposed network consistently outperformed the standard U-net model.
Multiclass segmentation as multitask learning for drusen segmentation in retinal optical coherence tomography
Jul 24, 2019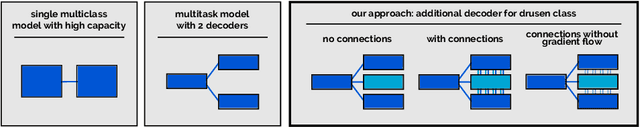
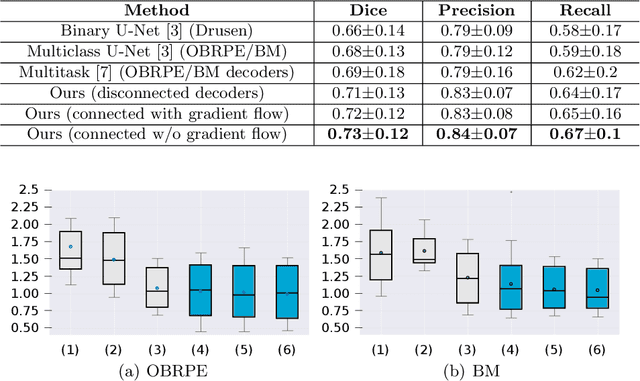
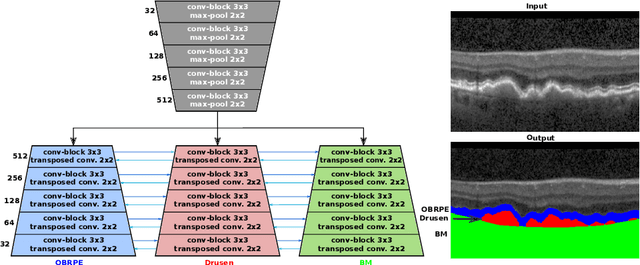
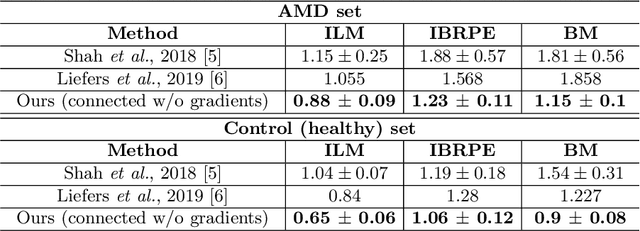
Abstract:Automated drusen segmentation in retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans is relevant for understanding age-related macular degeneration (AMD) risk and progression. This task is usually performed by segmenting the top/bottom anatomical interfaces that define drusen, the outer boundary of the retinal pigment epithelium (OBRPE) and the Bruch's membrane (BM), respectively. In this paper we propose a novel multi-decoder architecture that tackles drusen segmentation as a multitask problem. Instead of training a multiclass model for OBRPE/BM segmentation, we use one decoder per target class and an extra one aiming for the area between the layers. We also introduce connections between each class-specific branch and the additional decoder to increase the regularization effect of this surrogate task. We validated our approach on private/public data sets with 166 early/intermediate AMD Spectralis, and 200 AMD and control Bioptigen OCT volumes, respectively. Our method consistently outperformed several baselines in both layer and drusen segmentation evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge