MSVPJ Sathvik
Reliability Analysis of Psychological Concept Extraction and Classification in User-penned Text
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:The social NLP research community witness a recent surge in the computational advancements of mental health analysis to build responsible AI models for a complex interplay between language use and self-perception. Such responsible AI models aid in quantifying the psychological concepts from user-penned texts on social media. On thinking beyond the low-level (classification) task, we advance the existing binary classification dataset, towards a higher-level task of reliability analysis through the lens of explanations, posing it as one of the safety measures. We annotate the LoST dataset to capture nuanced textual cues that suggest the presence of low self-esteem in the posts of Reddit users. We further state that the NLP models developed for determining the presence of low self-esteem, focus more on three types of textual cues: (i) Trigger: words that triggers mental disturbance, (ii) LoST indicators: text indicators emphasizing low self-esteem, and (iii) Consequences: words describing the consequences of mental disturbance. We implement existing classifiers to examine the attention mechanism in pre-trained language models (PLMs) for a domain-specific psychology-grounded task. Our findings suggest the need of shifting the focus of PLMs from Trigger and Consequences to a more comprehensive explanation, emphasizing LoST indicators while determining low self-esteem in Reddit posts.
InterPrompt: Interpretable Prompting for Interrelated Interpersonal Risk Factors in Reddit Posts
Nov 21, 2023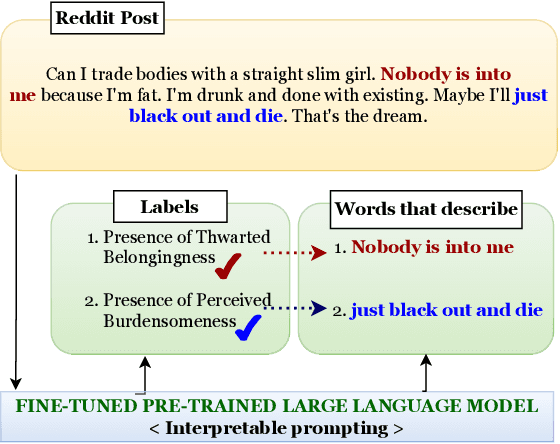

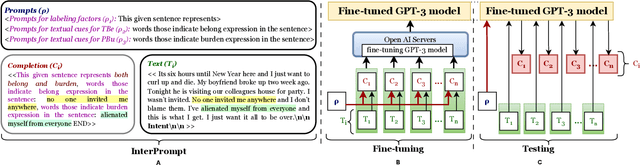

Abstract:Mental health professionals and clinicians have observed the upsurge of mental disorders due to Interpersonal Risk Factors (IRFs). To simulate the human-in-the-loop triaging scenario for early detection of mental health disorders, we recognized textual indications to ascertain these IRFs : Thwarted Belongingness (TBe) and Perceived Burdensomeness (PBu) within personal narratives. In light of this, we use N-shot learning with GPT-3 model on the IRF dataset, and underscored the importance of fine-tuning GPT-3 model to incorporate the context-specific sensitivity and the interconnectedness of textual cues that represent both IRFs. In this paper, we introduce an Interpretable Prompting (InterPrompt)} method to boost the attention mechanism by fine-tuning the GPT-3 model. This allows a more sophisticated level of language modification by adjusting the pre-trained weights. Our model learns to detect usual patterns and underlying connections across both the IRFs, which leads to better system-level explainability and trustworthiness. The results of our research demonstrate that all four variants of GPT-3 model, when fine-tuned with InterPrompt, perform considerably better as compared to the baseline methods, both in terms of classification and explanation generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge