M. T. Islam
Development of a Voice Controlled Robotic Arm
Mar 16, 2023



Abstract:This paper describes a robotic arm with 5 degrees-of-freedom (DOF) which is controlled by human voice and has been developed in the Mechatronics Laboratory, CUET. This robotic arm is interfaced with a PC by serial communication (RS-232). Users' voice command is captured by a microphone, and this voice is processed by software which is made by Microsoft visual studio. Then the specific signal (obtained by signal processing) is sent to control unit. The main control unit that is used in the robotic arm is a microcontroller whose model no. is PIC18f452. Then Control unit drives the actuators, (Hitec HS-422, HS-81) according to the signal or signals to give required motion of the robotic arm. At present the robotic arm can perform a set action like pick & pull, gripping, holding & releasing, and some other extra function like dance-like movement, and can turn according to the voice commands.
Microsimulation of Space Time Trellis Code
Feb 25, 2021



Abstract:This letter explores the possibility of using microsimulation in space time trellis code. Performing a pairwise comparison between generator matrices is essential in the validation of optimality. This is often done with simulation, which can be a time consuming process altogether. Microsimulation considerably cuts down the computational cost of simulation by employing smaller data and iteration. The effort is feasible with the assistance of a machine learning model known as multilayer perceptron. When properly conducted, it can offer 93.86% accuracy and 98.25% reduction in temporal cost.
Coronavirus: Comparing COVID-19, SARS and MERS in the eyes of AI
Jun 08, 2020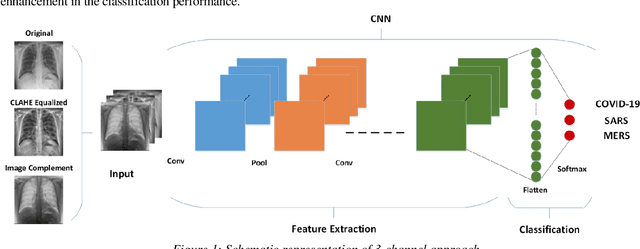
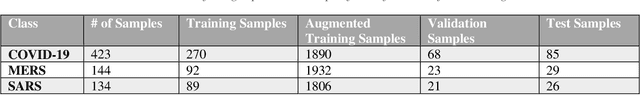
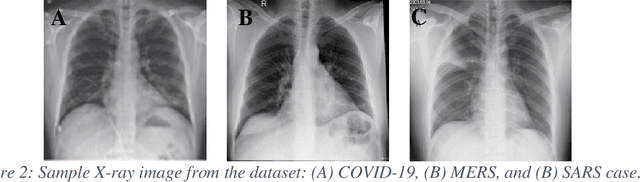
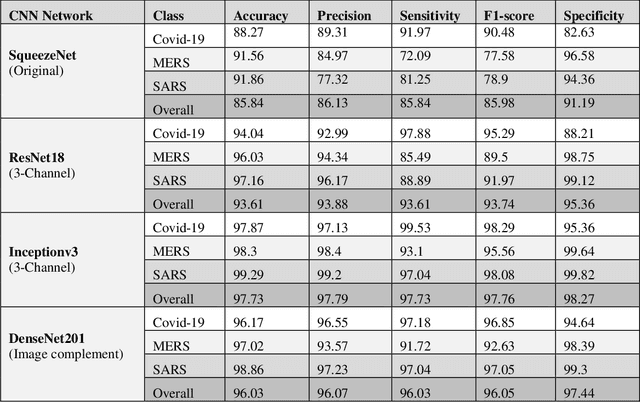
Abstract:Novel Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an extremely contagious and quickly spreading Coronavirus disease. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)-CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV outbreak in 2002 and 2011 and current COVID-19 pandemic all from the same family of Coronavirus. The fatality rate due to SARS and MERS were higher than COVID-19 however, the spread of those were limited to few countries while COVID-19 affected more than two-hundred countries of the world. In this work, authors used deep machine learning algorithms along with innovative image pre-processing techniques to distinguish COVID-19 images from SARS and MERS images. Several deep learning algorithms were trained, and tested and four outperforming algorithms were reported: SqueezeNet, ResNet18, Inceptionv3 and DenseNet201. Original, Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalized and complemented image were used individually and in concatenation as the inputs to the networks. It was observed that inceptionv3 outperforms all networks for 3-channel concatenation technique and provide an excellent sensitivity of 99.5%, 93.1% and 97% for classifying COVID-19, MERS and SARS images respectively. Investigating deep layer activation mapping of the correctly classified images and miss-classified images, it was observed that some overlapping features between COVID-19 and MERS images were identified by the deep layer network. Interestingly these features were present in MERS images and 10 out of 144 images were miss-classified as COVID while only one out of 423 COVID-19 images was miss-classified as MERS. None of the MERS images was miss-classified to SARS and only one COVID-19 image was miss-classified as SARS. Therefore, it can be summarized that SARS images are significantly different from MERS and COVID-19 in the eyes of AI while there are some overlapping feature available between MERS and COVID-19.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge