Luka Chkhetiani
Anatomy of Industrial Scale Multilingual ASR
Apr 16, 2024
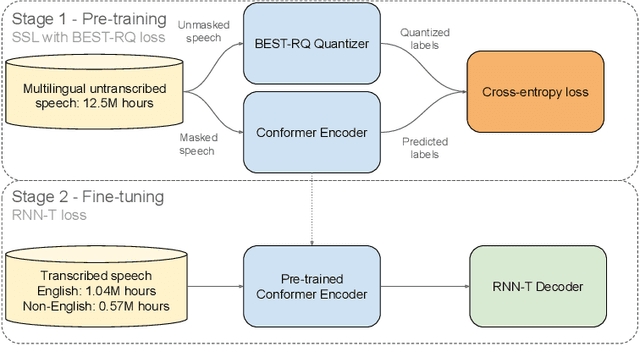


Abstract:This paper describes AssemblyAI's industrial-scale automatic speech recognition (ASR) system, designed to meet the requirements of large-scale, multilingual ASR serving various application needs. Our system leverages a diverse training dataset comprising unsupervised (12.5M hours), supervised (188k hours), and pseudo-labeled (1.6M hours) data across four languages. We provide a detailed description of our model architecture, consisting of a full-context 600M-parameter Conformer encoder pre-trained with BEST-RQ and an RNN-T decoder fine-tuned jointly with the encoder. Our extensive evaluation demonstrates competitive word error rates (WERs) against larger and more computationally expensive models, such as Whisper large and Canary-1B. Furthermore, our architectural choices yield several key advantages, including an improved code-switching capability, a 5x inference speedup compared to an optimized Whisper baseline, a 30% reduction in hallucination rate on speech data, and a 90% reduction in ambient noise compared to Whisper, along with significantly improved time-stamp accuracy. Throughout this work, we adopt a system-centric approach to analyzing various aspects of fully-fledged ASR models to gain practically relevant insights useful for real-world services operating at scale.
Conformer-1: Robust ASR via Large-Scale Semisupervised Bootstrapping
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents Conformer-1, an end-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) model trained on an extensive dataset of 570k hours of speech audio data, 91% of which was acquired from publicly available sources. To achieve this, we perform Noisy Student Training after generating pseudo-labels for the unlabeled public data using a strong Conformer RNN-T baseline model. The addition of these pseudo-labeled data results in remarkable improvements in relative Word Error Rate (WER) by 11.5% and 24.3% for our asynchronous and realtime models, respectively. Additionally, the model is more robust to background noise owing to the addition of these data. The results obtained in this study demonstrate that the incorporation of pseudo-labeled publicly available data is a highly effective strategy for improving ASR accuracy and noise robustness.
SE-MelGAN -- Speaker Agnostic Rapid Speech Enhancement
Jun 13, 2020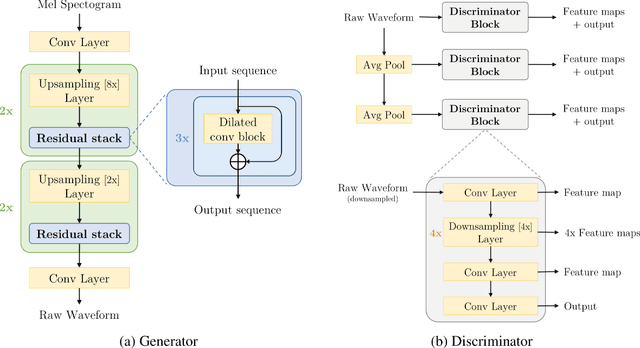
Abstract:Recent advancement in Generative Adversarial Networks in speech synthesis domain[3],[2] have shown, that it's possible to train GANs [8] in a reliable manner for high quality coherent waveform generation from mel-spectograms. We propose that it is possible to transfer the MelGAN's [3] robustness in learning speech features to speech enhancement and noise reduction domain without any model modification tasks. Our proposed method generalizes over multi-speaker speech dataset and is able to robustly handle unseen background noises during the inference. Also, we show that by increasing the batch size for this particular approach not only yields better speech results, but generalizes over multi-speaker dataset easily and leads to faster convergence. Additionally, it outperforms previous state of the art GAN approach for speech enhancement SEGAN [5] in two domains: 1. quality ; 2. speed. Proposed method runs at more than 100x faster than realtime on GPU and more than 2x faster than real time on CPU without any hardware optimization tasks, right at the speed of MelGAN [3].
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge