Luigi Troiano
Breaking the Conventional Forward-Backward Tie in Neural Networks: Activation Functions
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Gradient-based neural network training traditionally enforces symmetry between forward and backward propagation, requiring activation functions to be differentiable (or sub-differentiable) and strictly monotonic in certain regions to prevent flat gradient areas. This symmetry, linking forward activations closely to backward gradients, significantly restricts the selection of activation functions, particularly excluding those with substantial flat or non-differentiable regions. In this paper, we challenge this assumption through mathematical analysis, demonstrating that precise gradient magnitudes derived from activation functions are largely redundant, provided the gradient direction is preserved. Empirical experiments conducted on foundational architectures - such as Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and Binary Neural Networks (BNNs) - confirm that relaxing forward-backward symmetry and substituting traditional gradients with simpler or stochastic alternatives does not impair learning and may even enhance training stability and efficiency. We explicitly demonstrate that neural networks with flat or non-differentiable activation functions, such as the Heaviside step function, can be effectively trained, thereby expanding design flexibility and computational efficiency. Further empirical validation with more complex architectures remains a valuable direction for future research.
* 30 pages, 8 figures, 14 tables, in press, available online 11 August 2025
Adaptive binarization based on fuzzy integrals
Mar 04, 2020

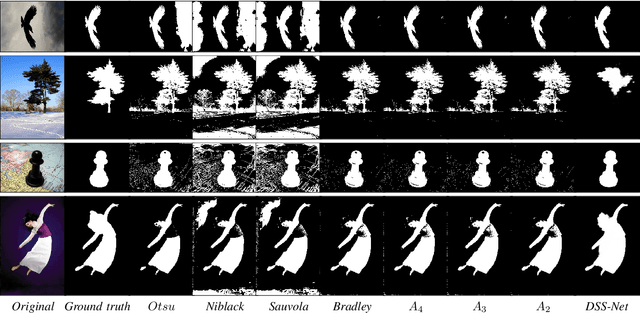
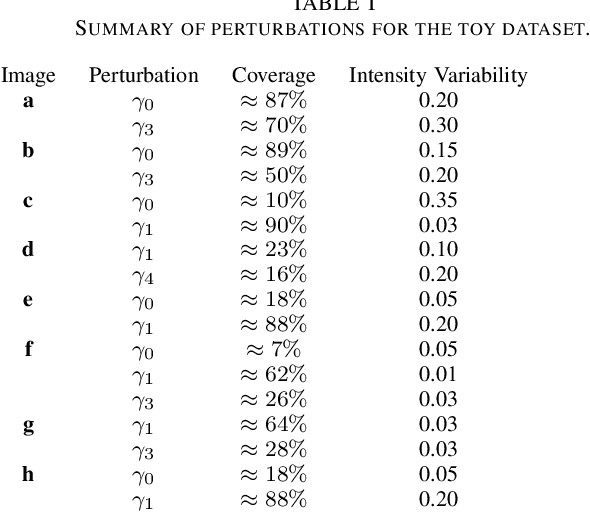
Abstract:Adaptive binarization methodologies threshold the intensity of the pixels with respect to adjacent pixels exploiting the integral images. In turn, the integral images are generally computed optimally using the summed-area-table algorithm (SAT). This document presents a new adaptive binarization technique based on fuzzy integral images through an efficient design of a modified SAT for fuzzy integrals. We define this new methodology as FLAT (Fuzzy Local Adaptive Thresholding). The experimental results show that the proposed methodology have produced an image quality thresholding often better than traditional algorithms and saliency neural networks. We propose a new generalization of the Sugeno and CF 1,2 integrals to improve existing results with an efficient integral image computation. Therefore, these new generalized fuzzy integrals can be used as a tool for grayscale processing in real-time and deep-learning applications. Index Terms: Image Thresholding, Image Processing, Fuzzy Integrals, Aggregation Functions
Deep Learning in Video Multi-Object Tracking: A Survey
Jul 31, 2019

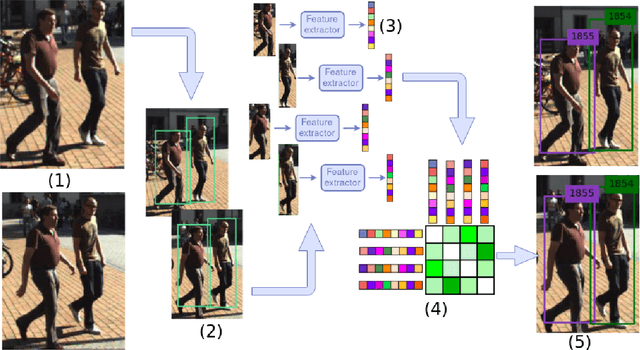

Abstract:The problem of Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) consists in following the trajectory of different objects in a sequence, usually a video. In recent years, with the rise of Deep Learning, the algorithms that provide a solution to this problem have benefited from the representational power of deep models. This paper provides a comprehensive survey on works that employ Deep Learning models to solve the task of MOT on single-camera videos. Four main steps in MOT algorithms are identified, and an in-depth review of how Deep Learning was employed in each one of these stages is presented. A complete experimental comparison of the presented works on the three MOTChallenge datasets is also provided, identifying a number of similarities among the top-performing methods and presenting some possible future research directions.
On Feature Reduction using Deep Learning for Trend Prediction in Finance
Apr 11, 2017



Abstract:One of the major advantages in using Deep Learning for Finance is to embed a large collection of information into investment decisions. A way to do that is by means of compression, that lead us to consider a smaller feature space. Several studies are proving that non-linear feature reduction performed by Deep Learning tools is effective in price trend prediction. The focus has been put mainly on Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBM) and on output obtained by them. Few attention has been payed to Auto-Encoders (AE) as an alternative means to perform a feature reduction. In this paper we investigate the application of both RBM and AE in more general terms, attempting to outline how architectural and input space characteristics can affect the quality of prediction.
Matching Media Contents with User Profiles by means of the Dempster-Shafer Theory
Apr 10, 2017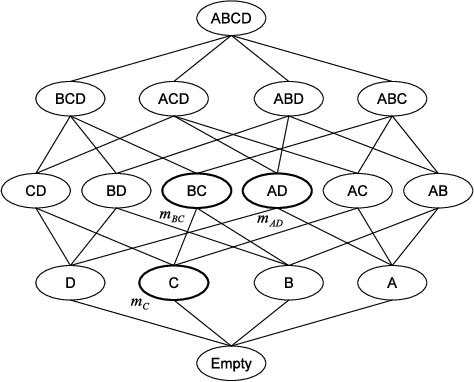
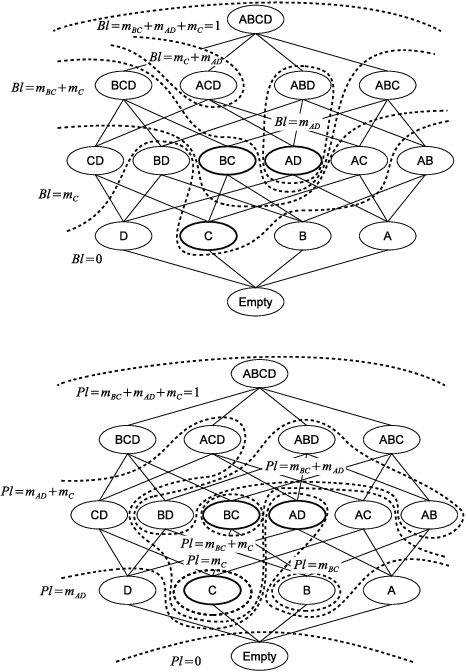
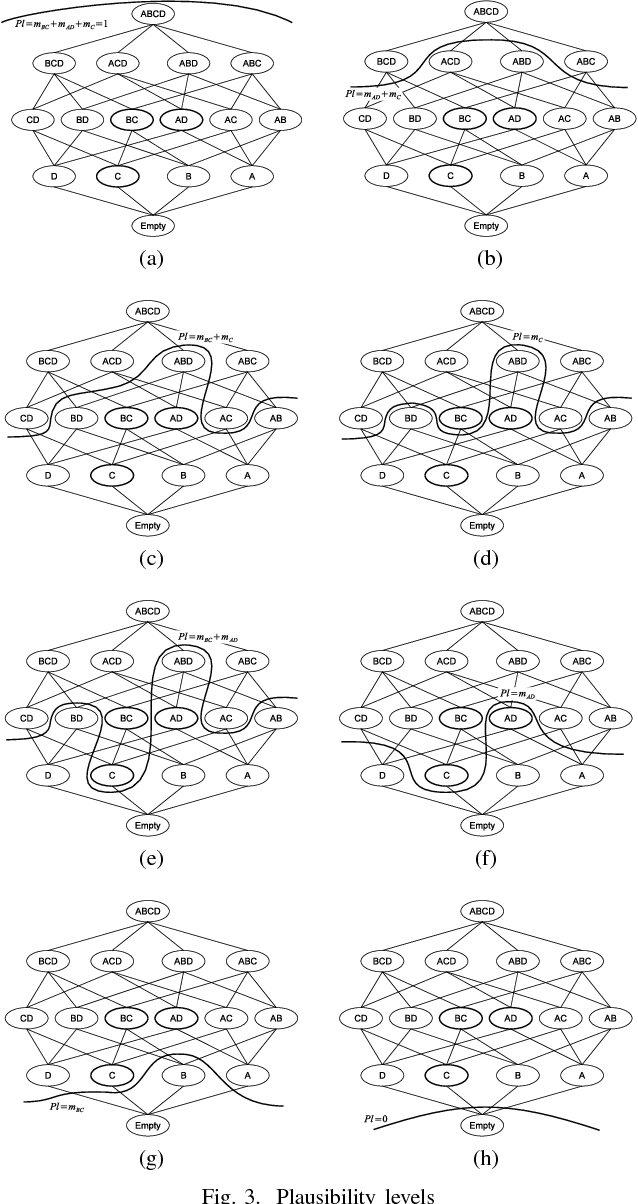
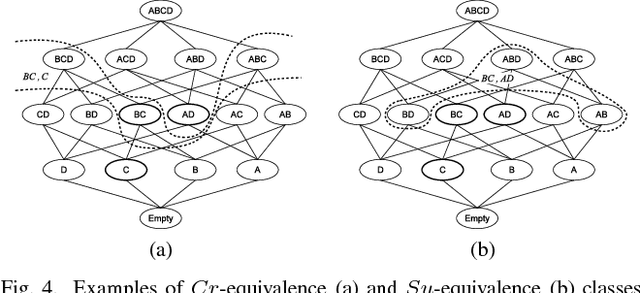
Abstract:The media industry is increasingly personalizing the offering of contents in attempt to better target the audience. This requires to analyze the relationships that goes established between users and content they enjoy, looking at one side to the content characteristics and on the other to the user profile, in order to find the best match between the two. In this paper we suggest to build that relationship using the Dempster-Shafer's Theory of Evidence, proposing a reference model and illustrating its properties by means of a toy example. Finally we suggest possible applications of the model for tasks that are common in the modern media industry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge