Luca Viganò
A Logic for Policy Based Resource Exchanges in Multiagent Systems
Aug 18, 2024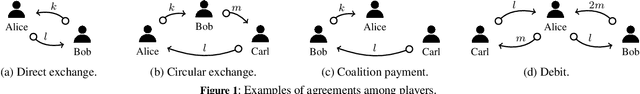
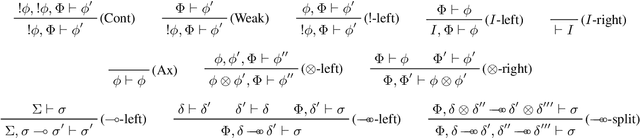
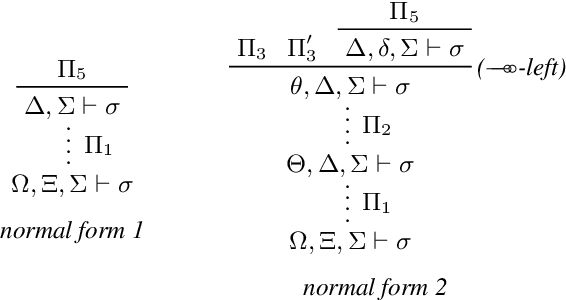
Abstract:In multiagent systems autonomous agents interact with each other to achieve individual and collective goals. Typical interactions concern negotiation and agreement on resource exchanges. Modeling and formalizing these agreements pose significant challenges, particularly in capturing the dynamic behaviour of agents, while ensuring that resources are correctly handled. Here, we propose exchange environments as a formal setting where agents specify and obey exchange policies, which are declarative statements about what resources they offer and what they require in return. Furthermore, we introduce a decidable extension of the computational fragment of linear logic as a fundamental tool for representing exchange environments and studying their dynamics in terms of provability.
It could be worse, it could be raining: reliable automatic meteorological forecasting
Feb 08, 2019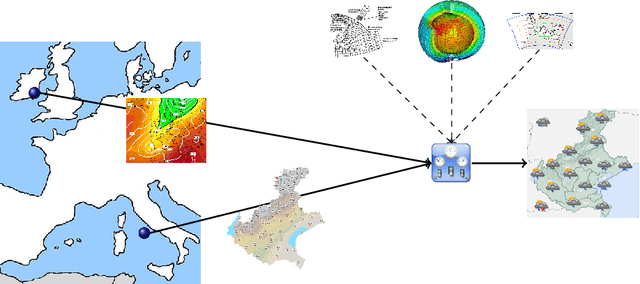
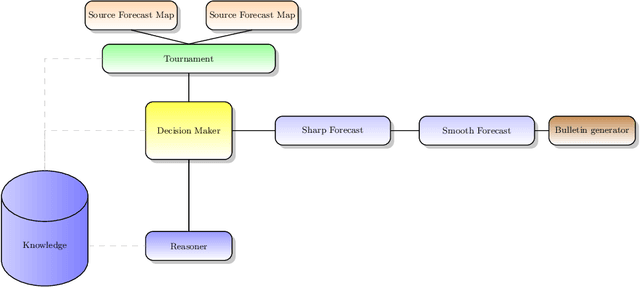

Abstract:Meteorological forecasting provides reliable prediction about the future weather within a given interval of time. Meteorological forecasting can be viewed as a form of hybrid diagnostic reasoning and can be mapped onto an integrated conceptual framework. The automation of the forecasting process would be helpful in a number of contexts, in particular: when the amount of data is too wide to be dealt with manually; to support forecasters education; when forecasting about underpopulated geographic areas is not interesting for everyday life (and then is out from human forecasters' tasks) but is central for tourism sponsorship. We present logic MeteoLOG, a framework that models the main steps of the reasoner the forecaster adopts to provide a bulletin. MeteoLOG rests on several traditions, mainly on fuzzy, temporal and probabilistic logics. On this basis, we also introduce the algorithm Tournament, that transforms a set of MeteoLOG rules into a defeasible theory, that can be implemented into an automatic reasoner. We finally propose an example that models a real world forecasting scenario.
Explainable Security
Jul 11, 2018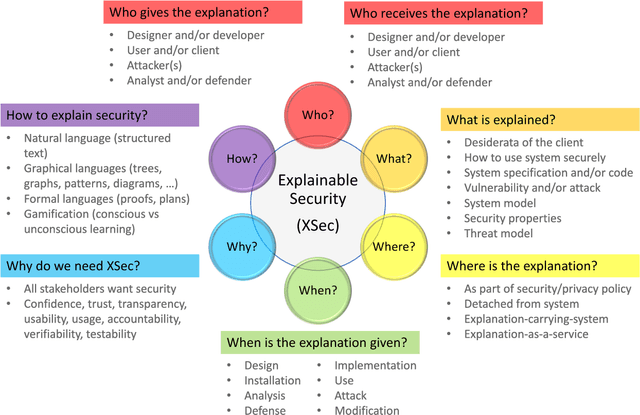
Abstract:The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) recently launched the Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) program that aims to create a suite of new AI techniques that enable end users to understand, appropriately trust, and effectively manage the emerging generation of AI systems. In this paper, inspired by DARPA's XAI program, we propose a new paradigm in security research: Explainable Security (XSec). We discuss the ``Six Ws'' of XSec (Who? What? Where? When? Why? and How?) and argue that XSec has unique and complex characteristics: XSec involves several different stakeholders (i.e., the system's developers, analysts, users and attackers) and is multi-faceted by nature (as it requires reasoning about system model, threat model and properties of security, privacy and trust as well as about concrete attacks, vulnerabilities and countermeasures). We define a roadmap for XSec that identifies several possible research directions.
Meaning Negotiation as Inference
Jan 23, 2011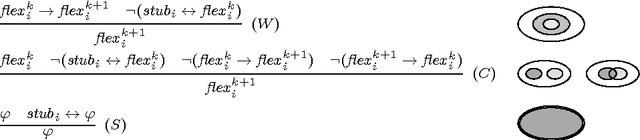
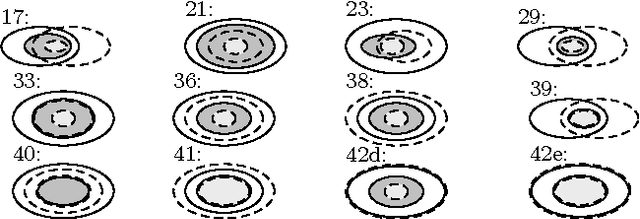
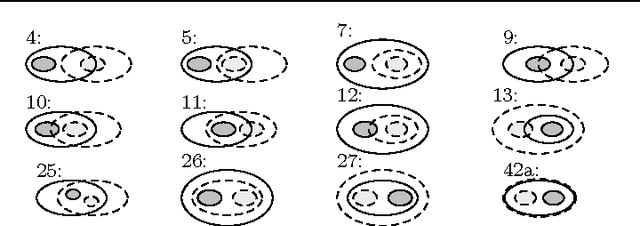

Abstract:Meaning negotiation (MN) is the general process with which agents reach an agreement about the meaning of a set of terms. Artificial Intelligence scholars have dealt with the problem of MN by means of argumentations schemes, beliefs merging and information fusion operators, and ontology alignment but the proposed approaches depend upon the number of participants. In this paper, we give a general model of MN for an arbitrary number of agents, in which each participant discusses with the others her viewpoint by exhibiting it in an actual set of constraints on the meaning of the negotiated terms. We call this presentation of individual viewpoints an angle. The agents do not aim at forming a common viewpoint but, instead, at agreeing about an acceptable common angle. We analyze separately the process of MN by two agents (\emph{bilateral} or \emph{pairwise} MN) and by more than two agents (\emph{multiparty} MN), and we use game theoretic models to understand how the process develops in both cases: the models are Bargaining Game for bilateral MN and English Auction for multiparty MN. We formalize the process of reaching such an agreement by giving a deduction system that comprises of rules that are consistent and adequate for representing MN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge