Letterio Galletta
A Logic for Policy Based Resource Exchanges in Multiagent Systems
Aug 18, 2024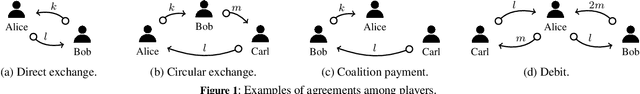
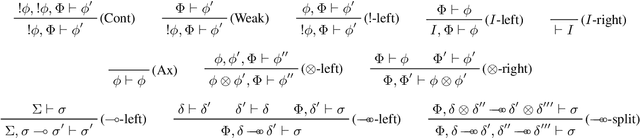
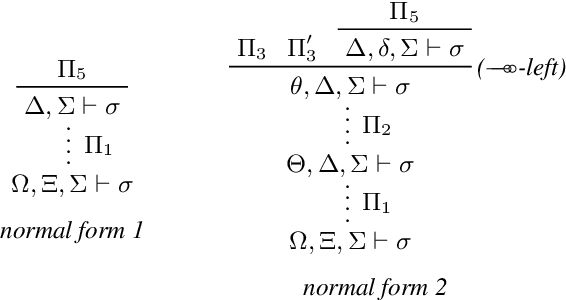
Abstract:In multiagent systems autonomous agents interact with each other to achieve individual and collective goals. Typical interactions concern negotiation and agreement on resource exchanges. Modeling and formalizing these agreements pose significant challenges, particularly in capturing the dynamic behaviour of agents, while ensuring that resources are correctly handled. Here, we propose exchange environments as a formal setting where agents specify and obey exchange policies, which are declarative statements about what resources they offer and what they require in return. Furthermore, we introduce a decidable extension of the computational fragment of linear logic as a fundamental tool for representing exchange environments and studying their dynamics in terms of provability.
Sharpening Ponzi Schemes Detection on Ethereum with Machine Learning
Jan 12, 2023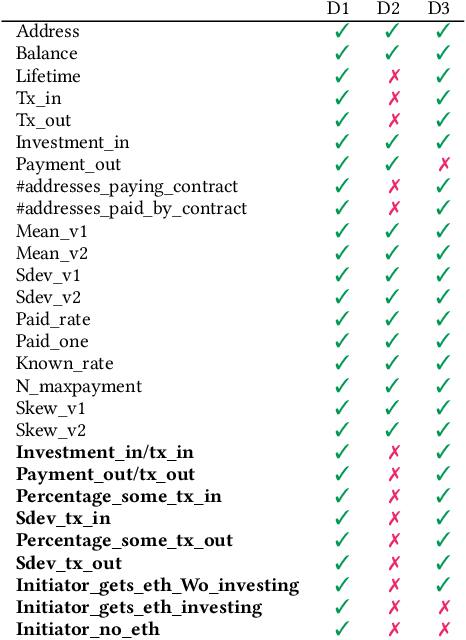
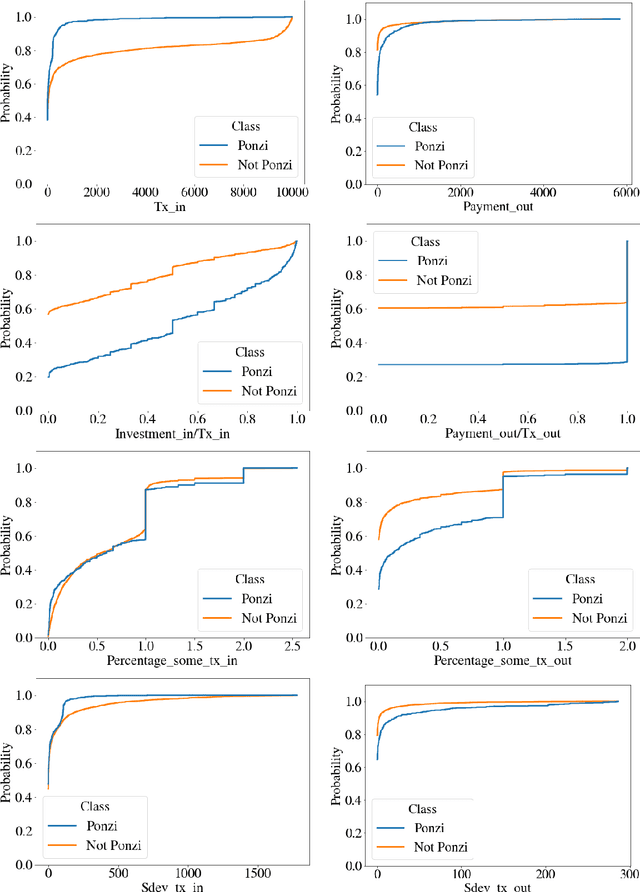
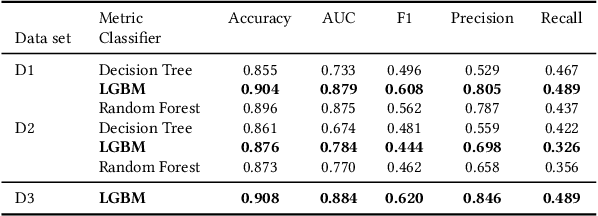
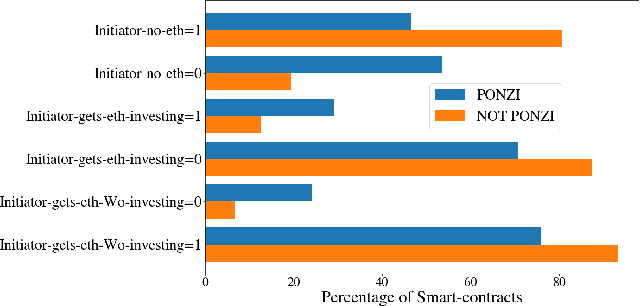
Abstract:Blockchain technology has been successfully exploited for deploying new economic applications. However, it has started arousing the interest of malicious users who deliver scams to deceive honest users and to gain economic advantages. Among the various scams, Ponzi schemes are one of the most common. Here, we present an automatic technique for detecting smart Ponzi contracts on Ethereum. We release a reusable data set with 4422 unique real-world smart contracts. Then, we introduce a new set of features that allow us to improve the classification. Finally, we identify a small and effective set of features that ensures a good classification quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge