Margherita Zorzi
It could be worse, it could be raining: reliable automatic meteorological forecasting
Feb 08, 2019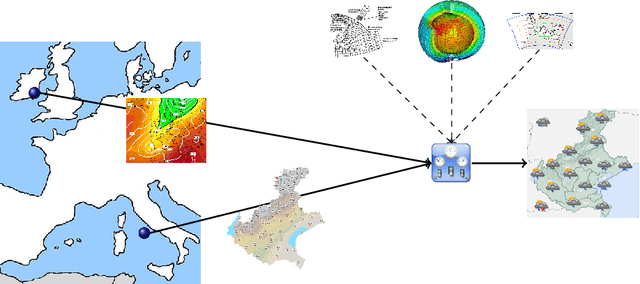
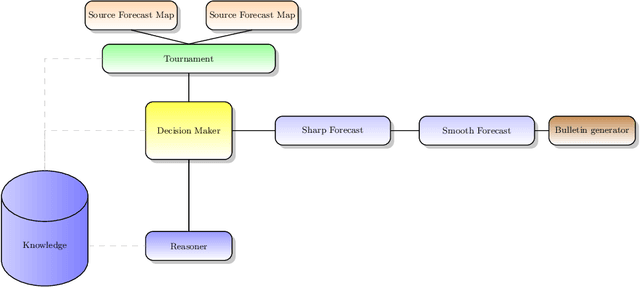

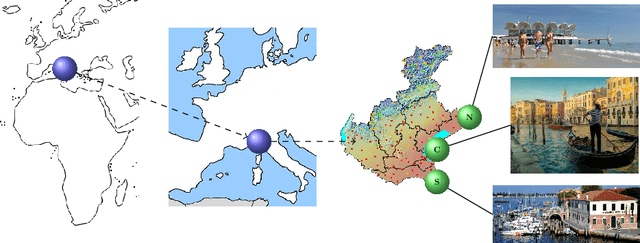
Abstract:Meteorological forecasting provides reliable prediction about the future weather within a given interval of time. Meteorological forecasting can be viewed as a form of hybrid diagnostic reasoning and can be mapped onto an integrated conceptual framework. The automation of the forecasting process would be helpful in a number of contexts, in particular: when the amount of data is too wide to be dealt with manually; to support forecasters education; when forecasting about underpopulated geographic areas is not interesting for everyday life (and then is out from human forecasters' tasks) but is central for tourism sponsorship. We present logic MeteoLOG, a framework that models the main steps of the reasoner the forecaster adopts to provide a bulletin. MeteoLOG rests on several traditions, mainly on fuzzy, temporal and probabilistic logics. On this basis, we also introduce the algorithm Tournament, that transforms a set of MeteoLOG rules into a defeasible theory, that can be implemented into an automatic reasoner. We finally propose an example that models a real world forecasting scenario.
Automagically encoding Adverse Drug Reactions in MedDRA
Jan 17, 2017
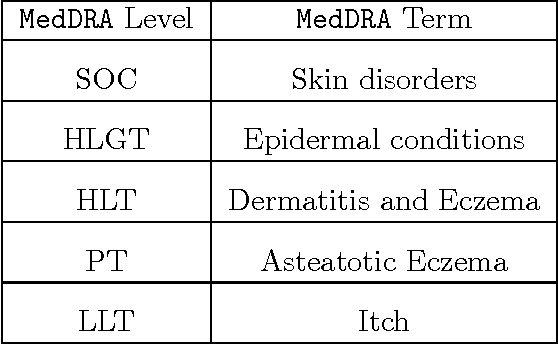


Abstract:Pharmacovigilance is the field of science devoted to the collection, analysis and prevention of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs). Efficient strategies for the extraction of information about ADRs from free text resources are essential to support the work of experts, employed in the crucial task of detecting and classifying unexpected pathologies possibly related to drug assumptions. Narrative ADR descriptions may be collected in several way, e.g. by monitoring social networks or through the so called spontaneous reporting, the main method pharmacovigilance adopts in order to identify ADRs. The encoding of free-text ADR descriptions according to MedDRA standard terminology is central for report analysis. It is a complex work, which has to be manually implemented by the pharmacovigilance experts. The manual encoding is expensive (in terms of time). Moreover, a problem about the accuracy of the encoding may occur, since the number of reports is growing up day by day. In this paper, we propose MagiCoder, an efficient Natural Language Processing algorithm able to automatically derive MedDRA terminologies from free-text ADR descriptions. MagiCoder is part of VigiWork, a web application for online ADR reporting and analysis. From a practical view-point, MagiCoder radically reduces the revision time of ADR reports: the pharmacologist has simply to revise and validate the automatic solution versus the hard task of choosing solutions in the 70k terms of MedDRA. This improvement of the expert work efficiency has a meaningful impact on the quality of data analysis. Moreover, our procedure is general purpose. We developed MagiCoder for the Italian pharmacovigilance language, but preliminarily analyses show that it is robust to language and dictionary changes.
From narrative descriptions to MedDRA: automagically encoding adverse drug reactions
Dec 12, 2016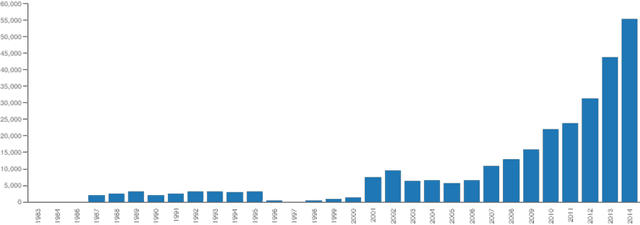
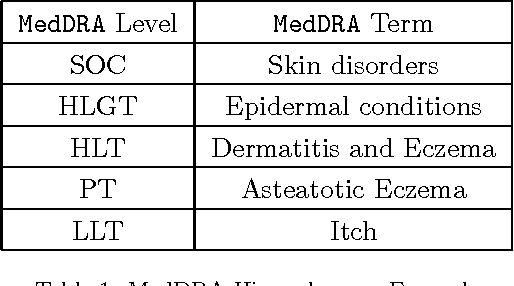
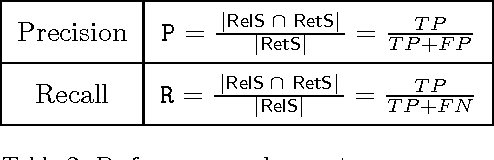
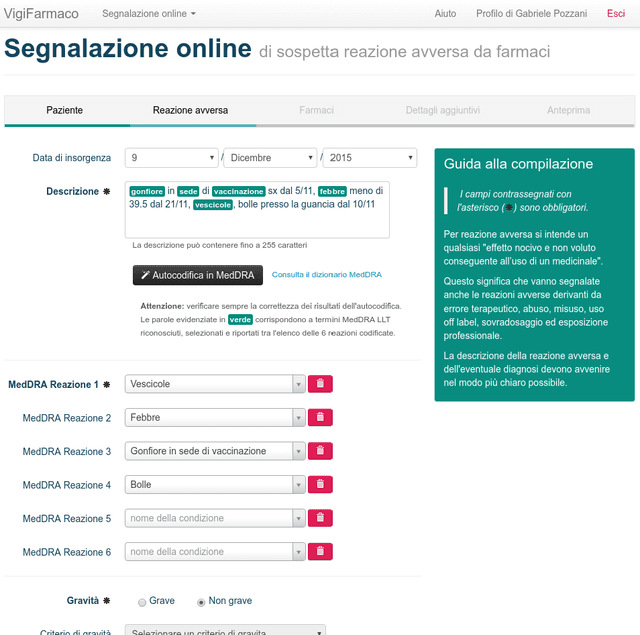
Abstract:The collection of narrative spontaneous reports is an irreplaceable source for the prompt detection of suspected adverse drug reactions (ADRs): qualified domain experts manually revise a huge amount of narrative descriptions and then encode texts according to MedDRA standard terminology. The manual annotation of narrative documents with medical terminology is a subtle and expensive task, since the number of reports is growing up day-by-day. MagiCoder, a Natural Language Processing algorithm, is proposed for the automatic encoding of free-text descriptions into MedDRA terms. MagiCoder procedure is efficient in terms of computational complexity (in particular, it is linear in the size of the narrative input and the terminology). We tested it on a large dataset of about 4500 manually revised reports, by performing an automated comparison between human and MagiCoder revisions. For the current base version of MagiCoder, we measured: on short descriptions, an average recall of $86\%$ and an average precision of $88\%$; on medium-long descriptions (up to 255 characters), an average recall of $64\%$ and an average precision of $63\%$. From a practical point of view, MagiCoder reduces the time required for encoding ADR reports. Pharmacologists have simply to review and validate the MagiCoder terms proposed by the application, instead of choosing the right terms among the 70K low level terms of MedDRA. Such improvement in the efficiency of pharmacologists' work has a relevant impact also on the quality of the subsequent data analysis. We developed MagiCoder for the Italian pharmacovigilance language. However, our proposal is based on a general approach, not depending on the considered language nor the term dictionary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge