Luís Paulo Reis
JEMA: A Joint Embedding Framework for Scalable Co-Learning with Multimodal Alignment
Oct 31, 2024Abstract:This work introduces JEMA (Joint Embedding with Multimodal Alignment), a novel co-learning framework tailored for laser metal deposition (LMD), a pivotal process in metal additive manufacturing. As Industry 5.0 gains traction in industrial applications, efficient process monitoring becomes increasingly crucial. However, limited data and the opaque nature of AI present challenges for its application in an industrial setting. JEMA addresses this challenges by leveraging multimodal data, including multi-view images and metadata such as process parameters, to learn transferable semantic representations. By applying a supervised contrastive loss function, JEMA enables robust learning and subsequent process monitoring using only the primary modality, simplifying hardware requirements and computational overhead. We investigate the effectiveness of JEMA in LMD process monitoring, focusing specifically on its generalization to downstream tasks such as melt pool geometry prediction, achieved without extensive fine-tuning. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates the high scalability and performance of JEMA, particularly when combined with Vision Transformer models. We report an 8% increase in performance in multimodal settings and a 1% improvement in unimodal settings compared to supervised contrastive learning. Additionally, the learned embedding representation enables the prediction of metadata, enhancing interpretability and making possible the assessment of the added metadata's contributions. Our framework lays the foundation for integrating multisensor data with metadata, enabling diverse downstream tasks within the LMD domain and beyond.
Computer Poker Research at LIACC
Jan 25, 2013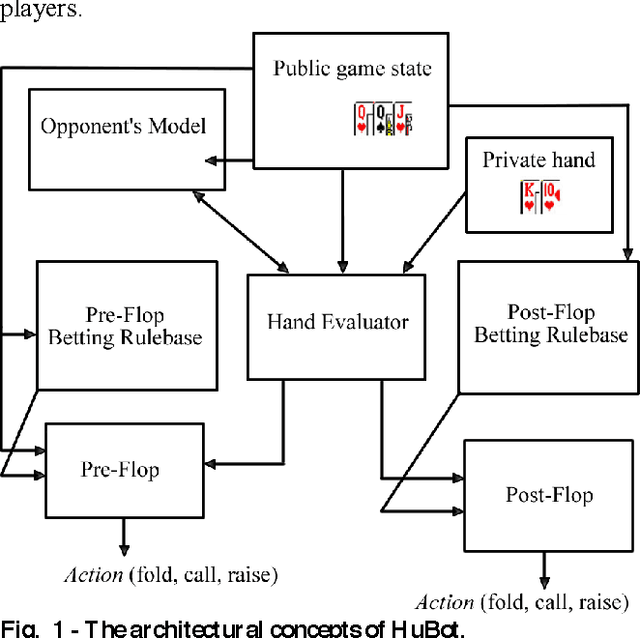
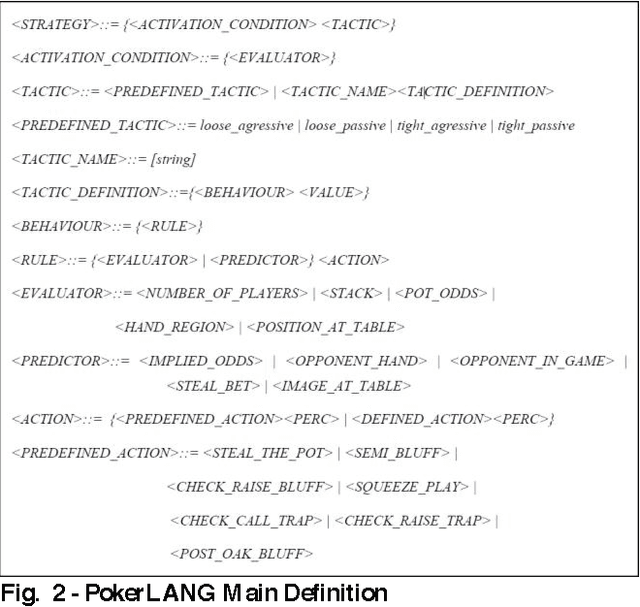
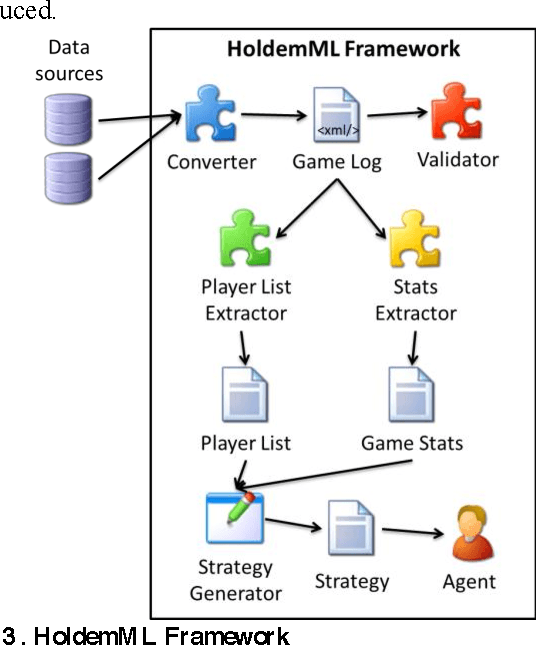
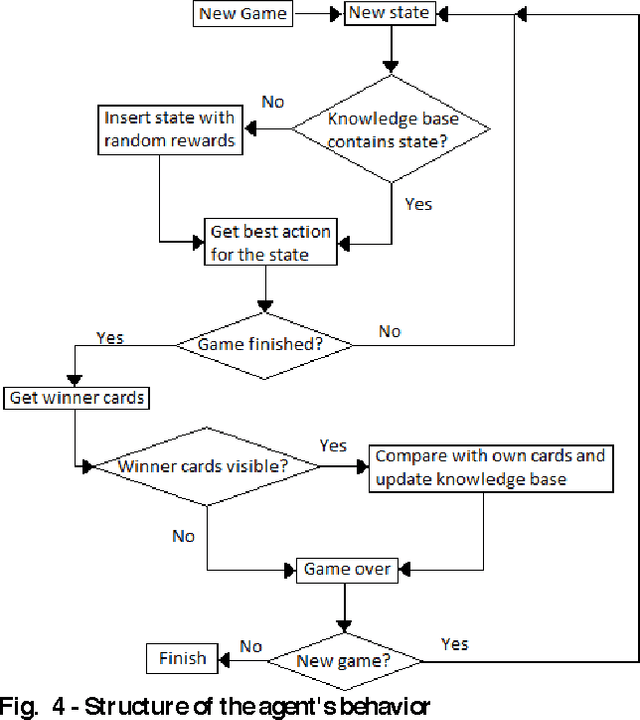
Abstract:Computer Poker's unique characteristics present a well-suited challenge for research in artificial intelligence. For that reason, and due to the Poker's market increase in popularity in Portugal since 2008, several members of LIACC have researched in this field. Several works were published as papers and master theses and more recently a member of LIACC engaged on a research in this area as a Ph.D. thesis in order to develop a more extensive and in-depth work. This paper describes the existing research in LIACC about Computer Poker, with special emphasis on the completed master's theses and plans for future work. This paper means to present a summary of the lab's work to the research community in order to encourage the exchange of ideas with other labs / individuals. LIACC hopes this will improve research in this area so as to reach the goal of creating an agent that surpasses the best human players.
Visualization Optimization : Application to the RoboCup Rescue Domain
Oct 13, 2008


Abstract:In this paper we demonstrate the use of intelligent optimization methodologies on the visualization optimization of virtual / simulated environments. The problem of automatic selection of an optimized set of views, which better describes an on-going simulation over a virtual environment is addressed in the context of the RoboCup Rescue Simulation domain. A generic architecture for optimization is proposed and described. We outline the possible extensions of this architecture and argue on how several problems within the fields of Interactive Rendering and Visualization can benefit from it.
* 1+4 pages, 3 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge