Loes van Bemmel
Optimising MFCC parameters for the automatic detection of respiratory diseases
Aug 14, 2024Abstract:Voice signals originating from the respiratory tract are utilized as valuable acoustic biomarkers for the diagnosis and assessment of respiratory diseases. Among the employed acoustic features, Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) is widely used for automatic analysis, with MFCC extraction commonly relying on default parameters. However, no comprehensive study has systematically investigated the impact of MFCC extraction parameters on respiratory disease diagnosis. In this study, we address this gap by examining the effects of key parameters, namely the number of coefficients, frame length, and hop length between frames, on respiratory condition examination. Our investigation uses four datasets: the Cambridge COVID-19 Sound database, the Coswara dataset, the Saarbrucken Voice Disorders (SVD) database, and a TACTICAS dataset. The Support Vector Machine (SVM) is employed as the classifier, given its widespread adoption and efficacy. Our findings indicate that the accuracy of MFCC decreases as hop length increases, and the optimal number of coefficients is observed to be approximately 30. The performance of MFCC varies with frame length across the datasets: for the COVID-19 datasets (Cambridge COVID-19 Sound database and Coswara dataset), performance declines with longer frame lengths, while for the SVD dataset, performance improves with increasing frame length (from 50 ms to 500 ms). Furthermore, we investigate the optimized combination of these parameters and observe substantial enhancements in accuracy. Compared to the worst combination, the SVM model achieves an accuracy of 81.1%, 80.6%, and 71.7%, with improvements of 19.6%, 16.10%, and 14.90% for the Cambridge COVID-19 Sound database, the Coswara dataset, and the SVD dataset respectively.
Beyond Neural-on-Neural Approaches to Speaker Gender Protection
Jun 30, 2023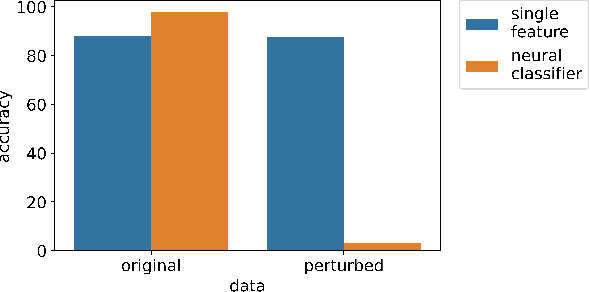
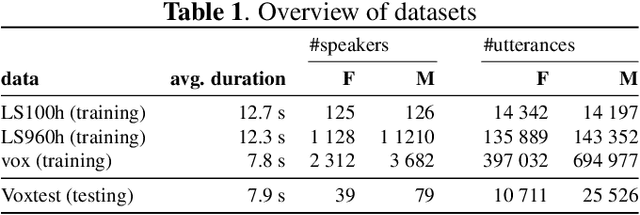
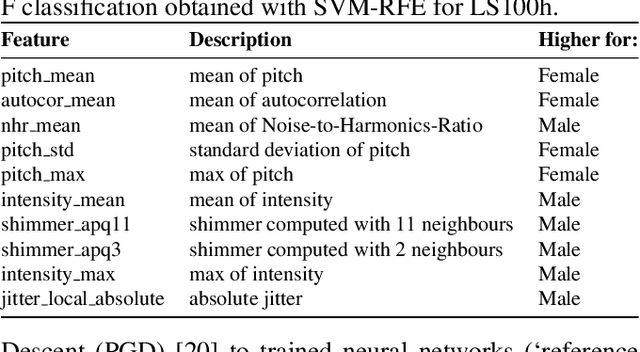
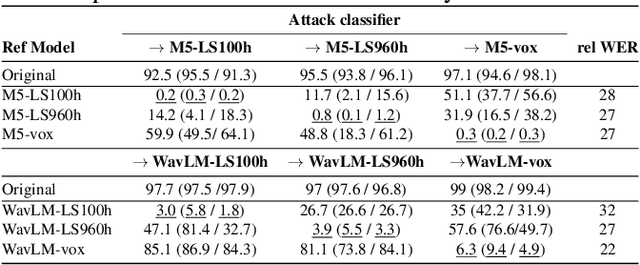
Abstract:Recent research has proposed approaches that modify speech to defend against gender inference attacks. The goal of these protection algorithms is to control the availability of information about a speaker's gender, a privacy-sensitive attribute. Currently, the common practice for developing and testing gender protection algorithms is "neural-on-neural", i.e., perturbations are generated and tested with a neural network. In this paper, we propose to go beyond this practice to strengthen the study of gender protection. First, we demonstrate the importance of testing gender inference attacks that are based on speech features historically developed by speech scientists, alongside the conventionally used neural classifiers. Next, we argue that researchers should use speech features to gain insight into how protective modifications change the speech signal. Finally, we point out that gender-protection algorithms should be compared with novel "vocal adversaries", human-executed voice adaptations, in order to improve interpretability and enable before-the-mic protection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge