Lisa Meeden
AI Toolkit: Libraries and Essays for Exploring the Technology and Ethics of AI
Jan 17, 2025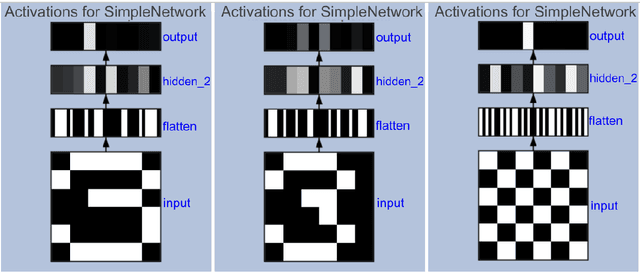
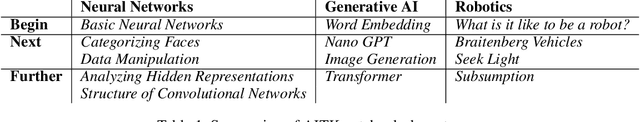
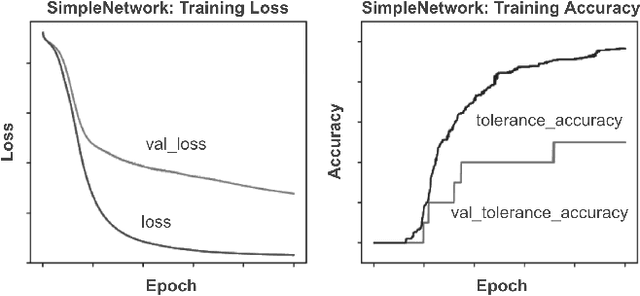
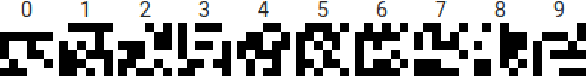
Abstract:In this paper we describe the development and evaluation of AITK, the Artificial Intelligence Toolkit. This open-source project contains both Python libraries and computational essays (Jupyter notebooks) that together are designed to allow a diverse audience with little or no background in AI to interact with a variety of AI tools, exploring in more depth how they function, visualizing their outcomes, and gaining a better understanding of their ethical implications. These notebooks have been piloted at multiple institutions in a variety of humanities courses centered on the theme of responsible AI. In addition, we conducted usability testing of AITK. Our pilot studies and usability testing results indicate that AITK is easy to navigate and effective at helping users gain a better understanding of AI. Our goal, in this time of rapid innovations in AI, is for AITK to provide an accessible resource for faculty from any discipline looking to incorporate AI topics into their courses and for anyone eager to learn more about AI on their own.
Experimental Evidence that Empowerment May Drive Exploration in Sparse-Reward Environments
Jul 14, 2021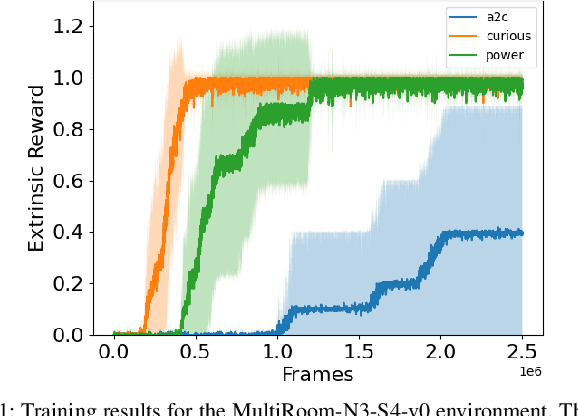
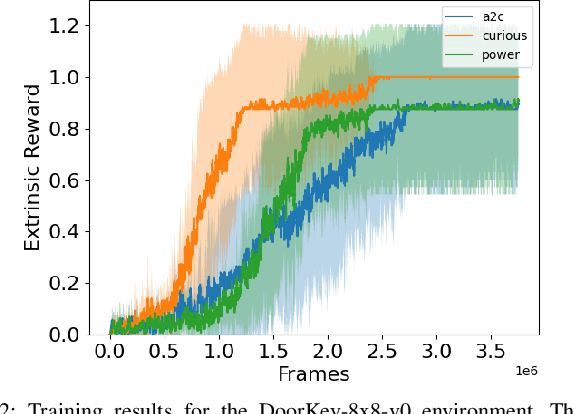
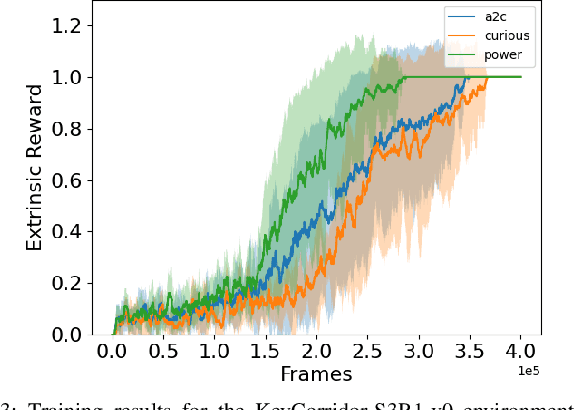

Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) is known to be often unsuccessful in environments with sparse extrinsic rewards. A possible countermeasure is to endow RL agents with an intrinsic reward function, or 'intrinsic motivation', which rewards the agent based on certain features of the current sensor state. An intrinsic reward function based on the principle of empowerment assigns rewards proportional to the amount of control the agent has over its own sensors. We implemented a variation on a recently proposed intrinsically motivated agent, which we refer to as the 'curious' agent, and an empowerment-inspired agent. The former leverages sensor state encoding with a variational autoencoder, while the latter predicts the next sensor state via a variational information bottleneck. We compared the performance of both agents to that of an advantage actor-critic baseline in four sparse reward grid worlds. Both the empowerment agent and its curious competitor seem to benefit to similar extents from their intrinsic rewards. This provides some experimental support to the conjecture that empowerment can be used to drive exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge