Linlan Huang
Continual Learning for VLMs: A Survey and Taxonomy Beyond Forgetting
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved impressive performance across diverse multimodal tasks by leveraging large-scale pre-training. However, enabling them to learn continually from non-stationary data remains a major challenge, as their cross-modal alignment and generalization capabilities are particularly vulnerable to catastrophic forgetting. Unlike traditional unimodal continual learning (CL), VLMs face unique challenges such as cross-modal feature drift, parameter interference due to shared architectures, and zero-shot capability erosion. This survey offers the first focused and systematic review of continual learning for VLMs (VLM-CL). We begin by identifying the three core failure modes that degrade performance in VLM-CL. Based on these, we propose a challenge-driven taxonomy that maps solutions to their target problems: (1) \textit{Multi-Modal Replay Strategies} address cross-modal drift through explicit or implicit memory mechanisms; (2) \textit{Cross-Modal Regularization} preserves modality alignment during updates; and (3) \textit{Parameter-Efficient Adaptation} mitigates parameter interference with modular or low-rank updates. We further analyze current evaluation protocols, datasets, and metrics, highlighting the need for better benchmarks that capture VLM-specific forgetting and compositional generalization. Finally, we outline open problems and future directions, including continual pre-training and compositional zero-shot learning. This survey aims to serve as a comprehensive and diagnostic reference for researchers developing lifelong vision-language systems. All resources are available at: https://github.com/YuyangSunshine/Awesome-Continual-learning-of-Vision-Language-Models.
Restoring Forgotten Knowledge in Non-Exemplar Class Incremental Learning through Test-Time Semantic Evolution
Mar 21, 2025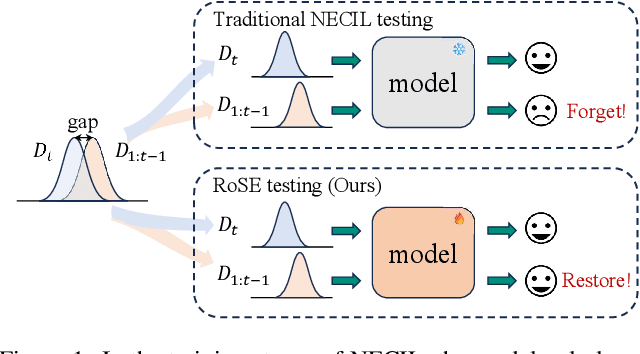
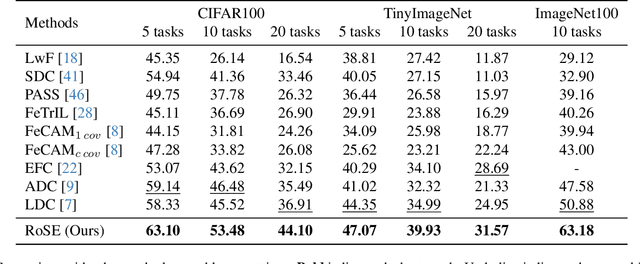
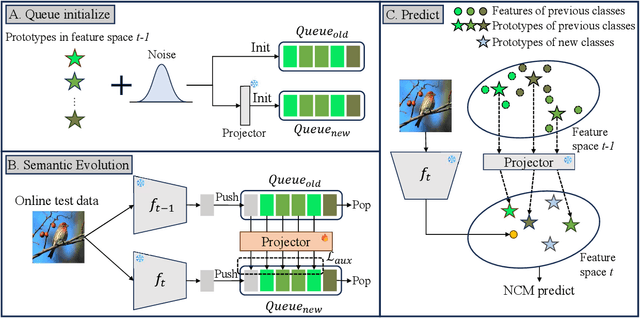
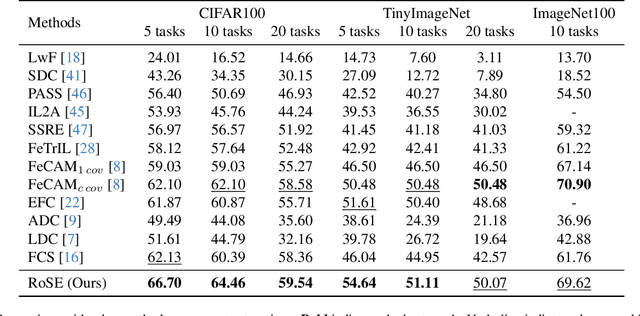
Abstract:Continual learning aims to accumulate knowledge over a data stream while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. In Non-exemplar Class Incremental Learning (NECIL), forgetting arises during incremental optimization because old classes are inaccessible, hindering the retention of prior knowledge. To solve this, previous methods struggle in achieving the stability-plasticity balance in the training stages. However, we note that the testing stage is rarely considered among them, but is promising to be a solution to forgetting. Therefore, we propose RoSE, which is a simple yet effective method that \textbf{R}est\textbf{o}res forgotten knowledge through test-time \textbf{S}emantic \textbf{E}volution. Specifically designed for minimizing forgetting, RoSE is a test-time semantic drift compensation framework that enables more accurate drift estimation in a self-supervised manner. Moreover, to avoid incomplete optimization during online testing, we derive an analytical solution as an alternative to gradient descent. We evaluate RoSE on CIFAR-100, TinyImageNet, and ImageNet100 datasets, under both cold-start and warm-start settings. Our method consistently outperforms most state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods across various scenarios, validating the potential and feasibility of test-time evolution in NECIL.
Class-Incremental Learning with CLIP: Adaptive Representation Adjustment and Parameter Fusion
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Class-incremental learning is a challenging problem, where the goal is to train a model that can classify data from an increasing number of classes over time. With the advancement of vision-language pre-trained models such as CLIP, they demonstrate good generalization ability that allows them to excel in class-incremental learning with completely frozen parameters. However, further adaptation to downstream tasks by simply fine-tuning the model leads to severe forgetting. Most existing works with pre-trained models assume that the forgetting of old classes is uniform when the model acquires new knowledge. In this paper, we propose a method named Adaptive Representation Adjustment and Parameter Fusion (RAPF). During training for new data, we measure the influence of new classes on old ones and adjust the representations, using textual features. After training, we employ a decomposed parameter fusion to further mitigate forgetting during adapter module fine-tuning. Experiments on several conventional benchmarks show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/linlany/RAPF}.
Generative Multi-modal Models are Good Class-Incremental Learners
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:In class-incremental learning (CIL) scenarios, the phenomenon of catastrophic forgetting caused by the classifier's bias towards the current task has long posed a significant challenge. It is mainly caused by the characteristic of discriminative models. With the growing popularity of the generative multi-modal models, we would explore replacing discriminative models with generative ones for CIL. However, transitioning from discriminative to generative models requires addressing two key challenges. The primary challenge lies in transferring the generated textual information into the classification of distinct categories. Additionally, it requires formulating the task of CIL within a generative framework. To this end, we propose a novel generative multi-modal model (GMM) framework for class-incremental learning. Our approach directly generates labels for images using an adapted generative model. After obtaining the detailed text, we use a text encoder to extract text features and employ feature matching to determine the most similar label as the classification prediction. In the conventional CIL settings, we achieve significantly better results in long-sequence task scenarios. Under the Few-shot CIL setting, we have improved by at least 14\% accuracy over all the current state-of-the-art methods with significantly less forgetting. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/DoubleClass/GMM}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge