Liang Xin
NeuroLKH: Combining Deep Learning Model with Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun Heuristic for Solving the Traveling Salesman Problem
Oct 15, 2021



Abstract:We present NeuroLKH, a novel algorithm that combines deep learning with the strong traditional heuristic Lin-Kernighan-Helsgaun (LKH) for solving Traveling Salesman Problem. Specifically, we train a Sparse Graph Network (SGN) with supervised learning for edge scores and unsupervised learning for node penalties, both of which are critical for improving the performance of LKH. Based on the output of SGN, NeuroLKH creates the edge candidate set and transforms edge distances to guide the searching process of LKH. Extensive experiments firmly demonstrate that, by training one model on a wide range of problem sizes, NeuroLKH significantly outperforms LKH and generalizes well to much larger sizes. Also, we show that NeuroLKH can be applied to other routing problems such as Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP), Pickup and Delivery Problem (PDP), and CVRP with Time Windows (CVRPTW).
Heterogeneous Attentions for Solving Pickup and Delivery Problem via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Oct 06, 2021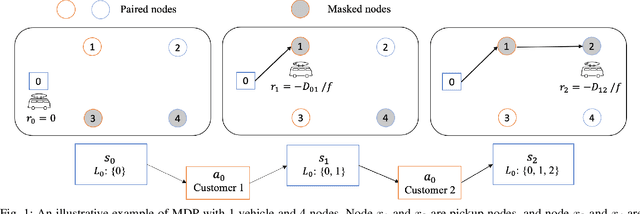
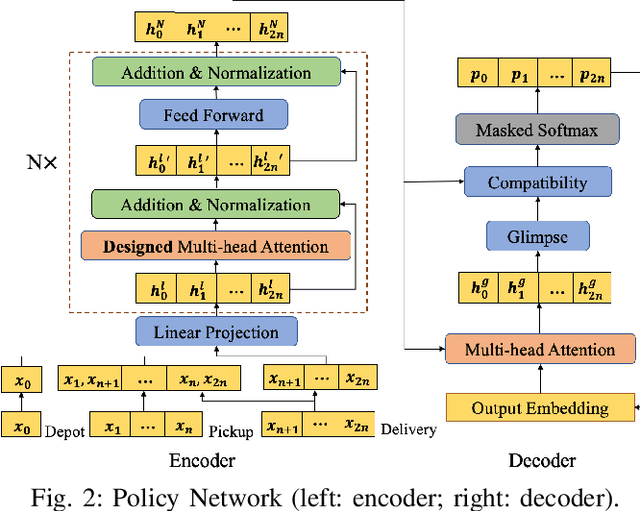
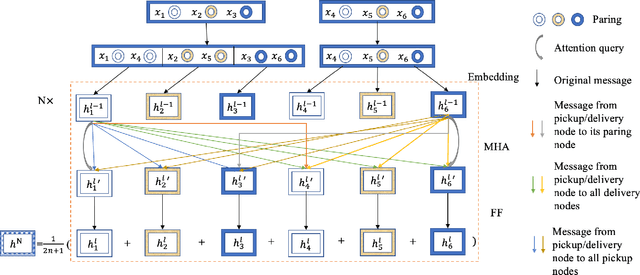
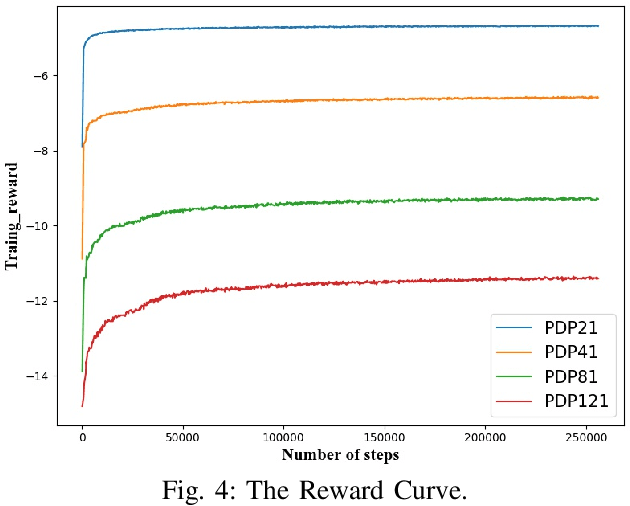
Abstract:Recently, there is an emerging trend to apply deep reinforcement learning to solve the vehicle routing problem (VRP), where a learnt policy governs the selection of next node for visiting. However, existing methods could not handle well the pairing and precedence relationships in the pickup and delivery problem (PDP), which is a representative variant of VRP. To address this challenging issue, we leverage a novel neural network integrated with a heterogeneous attention mechanism to empower the policy in deep reinforcement learning to automatically select the nodes. In particular, the heterogeneous attention mechanism specifically prescribes attentions for each role of the nodes while taking into account the precedence constraint, i.e., the pickup node must precede the pairing delivery node. Further integrated with a masking scheme, the learnt policy is expected to find higher-quality solutions for solving PDP. Extensive experimental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art heuristic and deep learning model, respectively, and generalizes well to different distributions and problem sizes.
Multi-Decoder Attention Model with Embedding Glimpse for Solving Vehicle Routing Problems
Dec 19, 2020



Abstract:We present a novel deep reinforcement learning method to learn construction heuristics for vehicle routing problems. In specific, we propose a Multi-Decoder Attention Model (MDAM) to train multiple diverse policies, which effectively increases the chance of finding good solutions compared with existing methods that train only one policy. A customized beam search strategy is designed to fully exploit the diversity of MDAM. In addition, we propose an Embedding Glimpse layer in MDAM based on the recursive nature of construction, which can improve the quality of each policy by providing more informative embeddings. Extensive experiments on six different routing problems show that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art deep learning based models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge